中国研究人员用纯金微球解决了关键的电子挑战
诸平
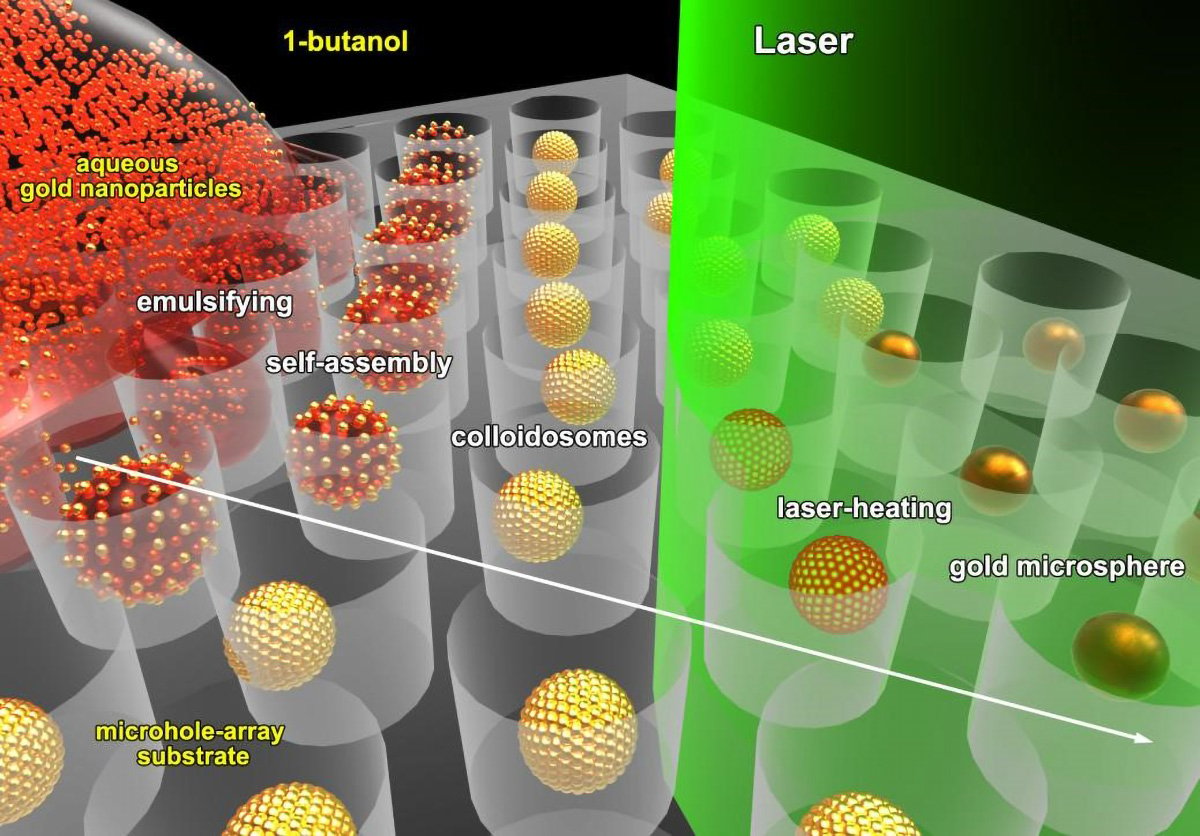
Fig. 1 Credit: An Cao
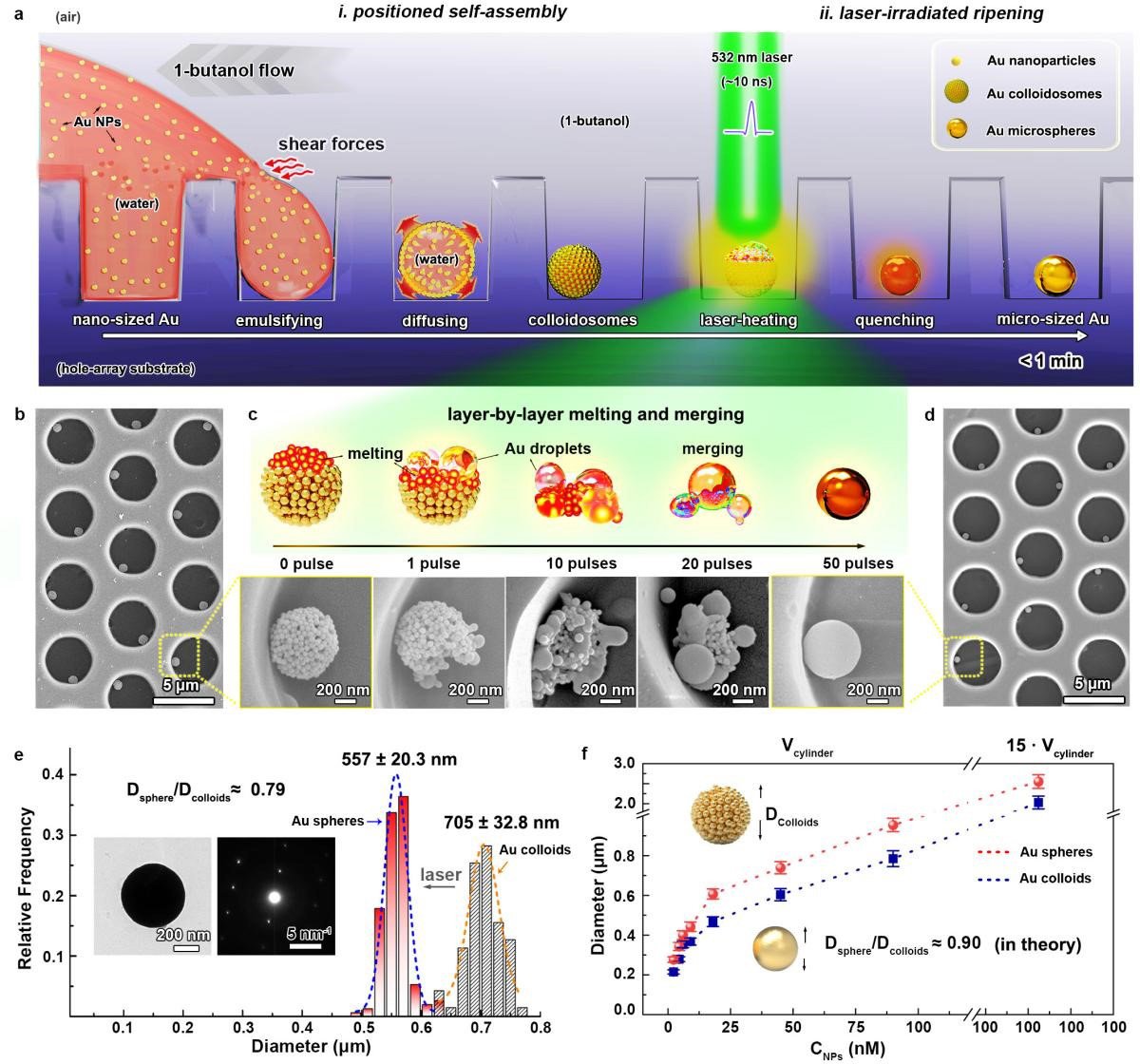
Fig. 2 Rapid approach to pure gold microsphere array fabrication. Credit: An Cao
据《科技日报》(SciTechDaily)网站刊发来自中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院(Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences)2024年11月30日提供的消息,中国研究人员用纯金微球解决了关键的电子挑战(Chinese Researchers Solve Key Electronics Challenge With Pure Gold Microspheres)。
研究人员开发了一种制造纯金微球阵列的方法,用于先进的电子产品,提高了连接可靠性和微显示性能,在高分辨率显示器中有很好的应用前景。(Researchers developed a method to fabricate pure gold microsphere arrays for advanced electronics, improving connection reliability and micro-display performance, with promising applications in high-resolution displays.)
由中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院固体物理研究所(Institute of Solid State Physics at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, part of the Chinese Academy of Sciences)的专家领导的一个研究小组,成功地开发了一种高效的方法,用于构建金微球阵列基各向异性导电胶膜(anisotropic conductive adhesive films简称ACF),用于先进的包装应用。相关研究结果于2024年10月24日已经在《自然通讯》(Nature Communications)杂志网站发表——An Cao, Yi Gong, Dilong Liu, Fan Yang, Yulong Fan, Yinghui Guo, Xingyou Tian, Yue Li. Rapid fabrication of gold microsphere arrays with stable deep-pressing anisotropic conductivity for advanced packaging. Nature Communications, 2024, 15, Article number: 9182. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-53407-x. Published: 24 October 2024. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-53407-x
参与此项研究的有来自中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院固体物理研究所(Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei, PR China)、中国合肥中欧电子材料国际创新中心(China-Europe Electronic Materials International Innovation Center, Hefei, PR China)、天津工业大学(Tiangong University, Tianjin, PR China)、中国科学院(成都)光场操纵科学与技术国家重点实验室(National Key Laboratory of Optical Field Manipulation Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu, PR China)、中国科学院(成都)光电研究所光学技术纳米加工与微工程国家重点实验室(State Key Laboratory of Optical Technologies on Nano-Fabrication and Micro-Engineering, Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu, PR China)以及中国深圳广东粤港澳大湾区量子科学中心{Quantum Science Center of Guangdong-HongKong-Macao Greater Bay Area (Guangdong), Shenzhen, PR China}的研究人员。
随着电子设备变得越来越小,实现可靠和安全的高质量连接变得越来越困难。2014年,一家日本公司开发了阵列- ACF,使用金属涂层聚合物微球阵列来实现这些连接,但金属和聚合物之间的连接在压力下可能会破裂,从而影响性能。
在这项研究中,研究人员开发了一种新的方法,通过定位自组装和激光辐照成熟策略,在1分钟内制造纯金微球阵列。该技术依赖于快速的逐层激光诱导熔化和融合过程,有效地避免了各向异性生长原理(anisotropic growth principle)。
该策略的根本优势在于初始模板微孔决定了金微球的形成尺寸,并精确定位在其中。该功能不仅便于精确控制,而且还确保了与行业中光刻技术的兼容性。
通用性和材料优势(Versatility and Material Advantages)
这项技术也很灵活,可以用来制造不同种类的微球,包括由金和其他金属制成的合金微球。当这些微球用激光处理时,它们会平滑地融合在一起,形成稳定耐用的材料。
与商业镀金微球相比,纯金微球更灵活,抗压力下的电气故障。这些金微球阵列可以帮助改善微显示器的结合,就像μLED芯片中使用的那样,这是制造高分辨率显示器的关键。这一突破可能会对电子和显示技术的未来产生重大影响。
本研究得到了中国国家自然科学基金{ National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 92263209;Grant Nos. 52171232)}、中国国家杰出青年科学基金{ National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (Grant No. 51825103)}、中国科学院青年创新促进会{Youth Innovation Promotion Association of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant Nos. 2022449;Grant Nos. 2020446)}、合肥物质科学研究院院长专项基金{ Special Foundation of President of Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (Nos. BJPY2022B01)}、CPSF博士后奖学金计划{Postdoctoral Fellowship Program of CPSF (Grant No. GZC20241743)}、安徽省重大科技项目{Anhui Major Provincial Science & Technology Project (Grant No. 202203a05020003)}、中国国家重点研发计划{National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFA1401003)}的资助。
上述介绍,仅供参考。欲了解更多信息,敬请注意浏览原文或者相关报道。
Smooth metal microspheres with uniform sizes are ideal for constructing particle-arrayed anisotropic conductive films (ACF), but synthesis is hindered by challenges in controlling anisotropic metal growth. Here, we present a positioned transient-emulsion self-assembly and laser-irradiation strategy to fabricate pure gold microsphere arrays with smooth surfaces and uniform sizes. The fabrication involves assembling gold nanoparticles into uniform colloidosomes within a pre-designed microhole array, followed by rapid transformation into well-defined microspheres through laser heating. The gold nanoparticles melt and merge in a layer-by-layer manner due to the finite skin depth of the laser, leading to a localized photothermal effect. This strategy circumvents anisotropic growth, enables tunable control of microsphere size and positioning, and is compatible with conventional lithography. Importantly, these pure gold microspheres exhibit stable conductivity under deep compression, offering promising applications in soldering micro-sized chips onto integrated circuits.
转载本文请联系原作者获取授权,同时请注明本文来自诸平科学网博客。
链接地址:https://wap.sciencenet.cn/blog-212210-1462508.html?mobile=1
收藏