《中医药循证医学与技术评估(英文)》
(eCMTA)第1卷第1期

eCMTA文章概览
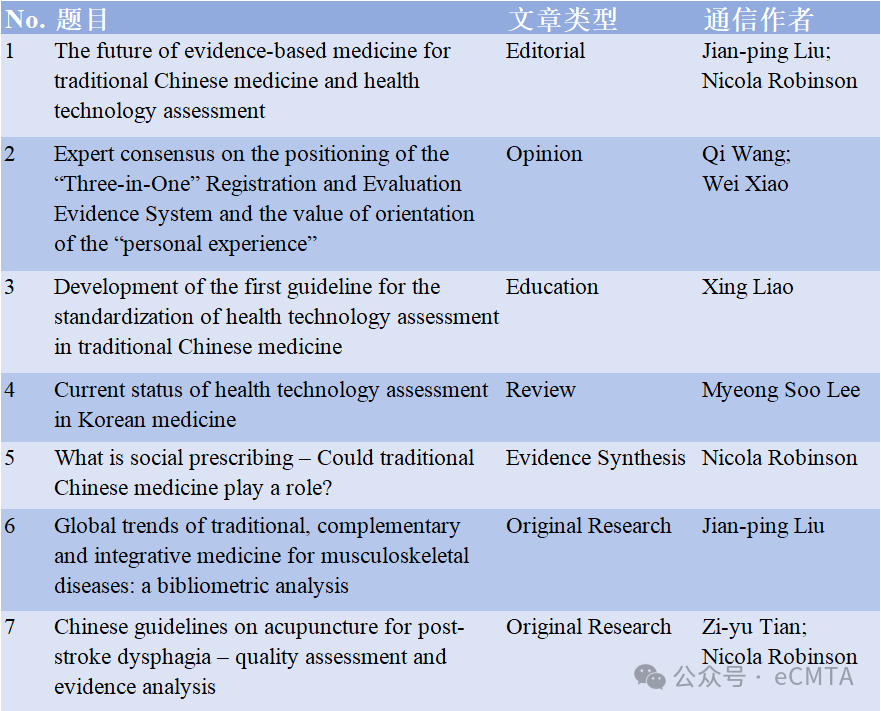
Editorial
1 The future of evidence-based medicine for traditional Chinese medicine and health technology assessment
中医药循证医学与卫生技术评估的未来发展方向
作者
Jian-ping Liu and Nicola Robinson
摘要
Evidence-Based Chinese Medicine and Technology Assessment (eCMTA) addresses gaps in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) research by promoting rigorous evidence synthesis, clinical trials, and health technology assessment. It aims to standardize TCM methodologies, enhance global credibility, and expedite high-quality research dissemination to support integrative healthcare policies and practices worldwide.
《中医药循证医学与技术评估(英文)》(简称“eCMTA”)旨在通过推动严谨的证据整合、临床试验和卫生技术评估,弥补传统中医药(TCM)研究中的不足。旨在规范中医药研究方法,提升其全球可信度,并加速高质量研究成果传播,从而为全球整合医疗政策与实践提供支持。
引用
Liu JP, Robinson N. The future of evidence-based medicine for traditional Chinese medicine and health technology assessment. Evidence-Based Chinese Medicine and Technology Assessment, 2025, 1: 9570004

Opinion Paper
1 Expert consensus on the positioning of the “Three-in-One” Registration and Evaluation Evidence System and the value of orientation of the “personal experience”
“三结合”注册审评证据体系的定位及“人用经验”价值取向的专家共识
作者
Qi Wang, Yong-yan Wang, Wei Xiao, Jin-zhou Tian, Shi-lin Chen, Li-guo Zhu, Guang-rong Sun, Da-ning Zhang, Dai-han Zhou, Guo-qiang Mei, Bao-fan Shen, Qing-guo Wang, Xi-xing Wang, Zheng Nan, Ming-xiang Han, Yue Gao, Xiao-he Xiao, Xiao-bo Sun, Kai-wen Hu, Li-qun Jia, Li Feng, Cheng-yu Wu, and Xia Ding
摘要
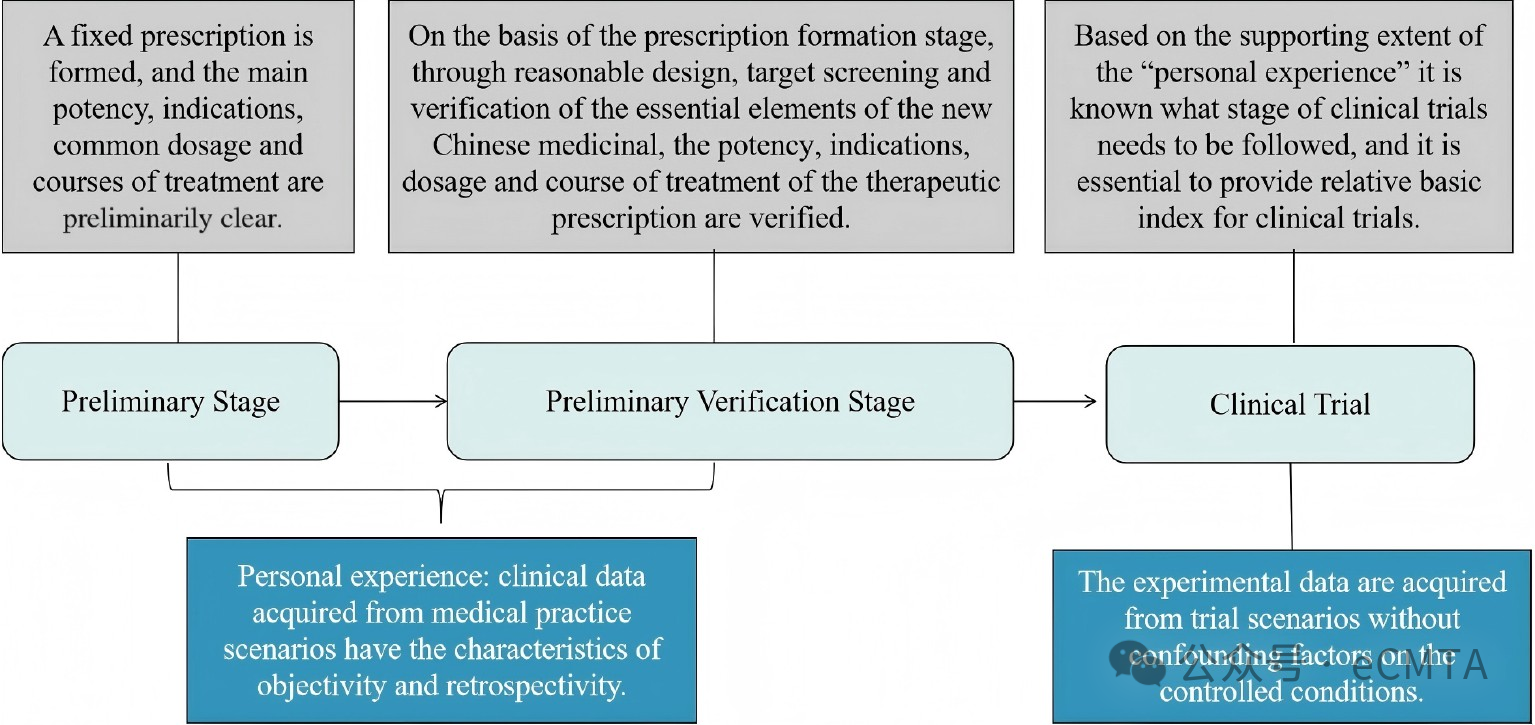
China’s “Three-in-One” traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) evaluation system integrates theory, human experience (core element), and clinical trials to advance TCM innovation. Expert consensus emphasizes real-world clinical data as the foundation. Multidisciplinary collaboration is required to refine this evidence-based framework and promote high-quality TCM development.
中医药“三位一体”评价体系融合了理论、人用经验(核心要素)和临床试验,以推动中医药创新。专家共识强调真实世界临床数据应作为该体系的基础。需要开展多学科交叉融合研究,以完善这一循证框架并促进中医药高质量发展。
引用
Wang Q, Wang YY, Xiao W, et al. Expert consensus on the positioning of the “Three-in-One” Registration and Evaluation Evidence System and the value of orientation of the “personal experience”. Evidence-Based Chinese Medicine and Technology Assessment, 2025, 1: 9570006.

Education Article
1 Development of the first guideline for the standardization of health technology assessment in traditional Chinese medicine
中医药卫生技术评估的首部标准化指南制定
作者
Xue Wu, Jian-ping Liu, and Xing Liao
摘要
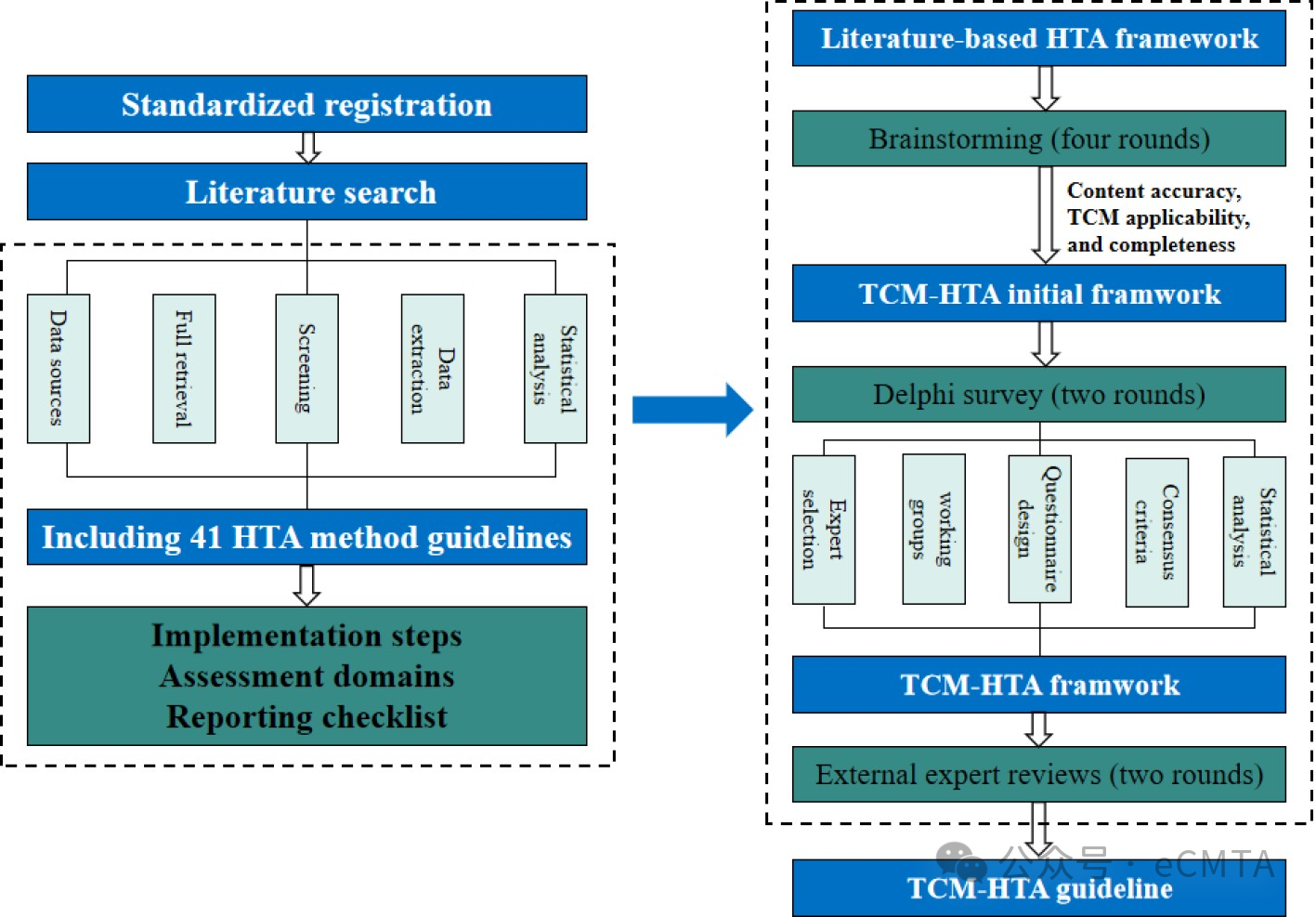
To advance traditional Chinese medicine-health technology assessment (TCM-HTA), key steps include defining assessment targets (e.g., therapies, diagnostics), developing technical standards, prioritizing patient needs in evaluation, adapting methods to TCM’s holistic approach, and fostering multi-stakeholder collaboration. This structured framework will optimize resource allocation, enhance evidence-based decision making, and integrate TCM effectively into modern healthcare systems.
推进中医药卫生技术评估(TCM-HTA)需采取以下关键步骤:明确评估对象(如疗法、诊断技术),制定统一技术标准,在评估过程中优先考虑患者需求,制定符合中医整体观特色的研究方法,并积极推动多方协作。该结构化框架优化资源配置、强化循证决策机制,最终实现中医药与现代医疗体系的深度融入。
引用
Wu X, Liu JP, Liao X. Development of the first guideline for the standardization of health technology assessment in traditional Chinese medicine. Evidence Based Chinese Medicine and Technology Assessment, 2025, 1: 9570005.

Review
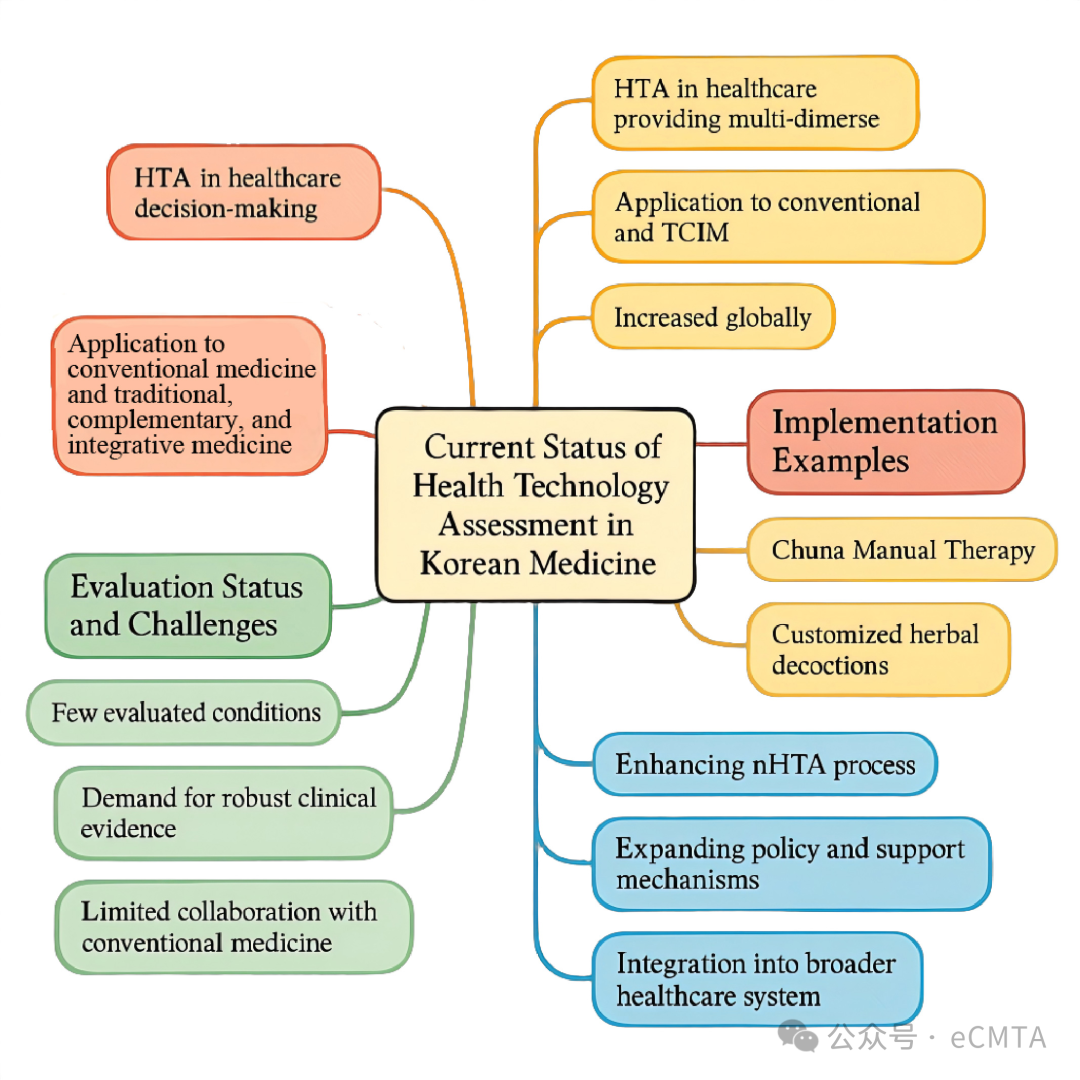
1 Current status of health technology assessment in Korean medicine
韩医卫生技术评估发展现状
作者
Myeong Soo Lee and Hye Won Lee
摘要
This review discusses Korean medicine's application in Republic of Korea's New Health Technology Assessment (nHTA) system, highlighting safety and efficacy assessments. Successful cases like Chuna Manual Therapy and herbal decoctions, now covered by insurance, are examined. Challenges and strategies for broader adoption are explored to enhance Korean medicine's integration into the HTA framework.
本文论述了韩医学在韩国新卫生技术评估体系(nHTA)中的应用,重点聚焦安全性与有效性评估,并介绍了纳入医保体系的典型案例,如推拿整脊疗法、汤药等。再者,文章探讨了韩医学在HTA框架中更广泛应用所面临的现实挑战与策略,旨在推动其深度融入国家卫生技术评估体系。
引用
Lee MS, Lee HW. Current status of health technology assessment in Korean medicine. Evidence-Based Chinese Medicine and Technology Assessment, 2025, 1: 9570003.

Evidence Synthesis
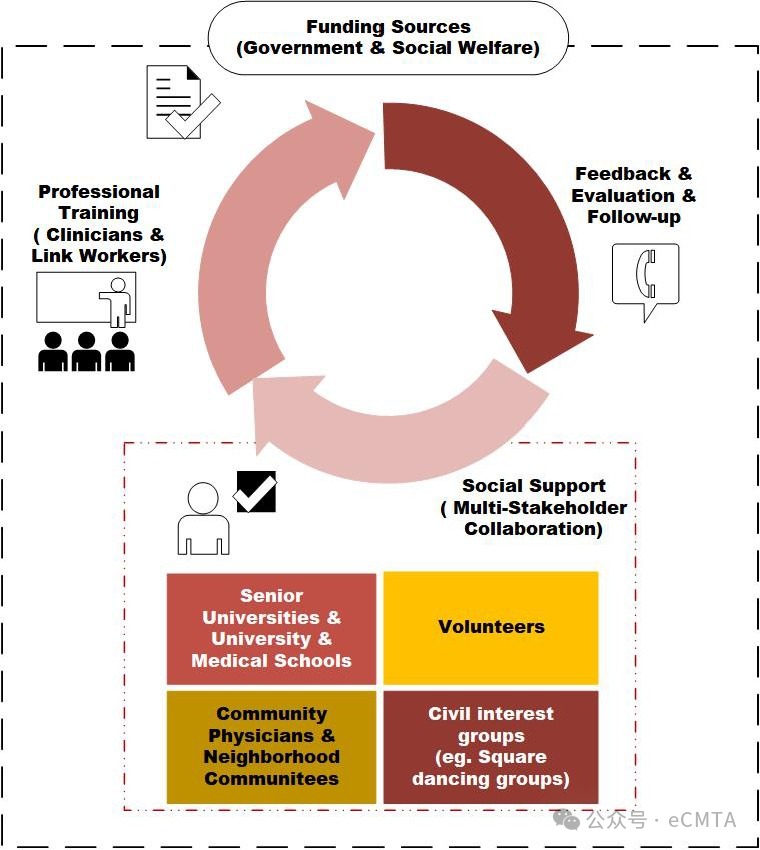
1 What is social prescribing – Could traditional Chinese medicine play a role?
社会处方是什么——中医药能否发挥作用?
作者
Chen-lu Wang, Yi-ying Wang, Xue-feng Wang, and Nicola Robinson
摘要
This article explores social prescribing, a United Kingdom-originated holistic health approach linking individuals to non-clinical community services via link workers. Introduced in China in 2018, it remains underutilized. The paper suggests integrating traditional Chinese medicine into this model to enhance its adoption and effectiveness in China's healthcare system.
本文探讨了起源于英国的社会处方机制——这种整体健康干预模式通过联络专员将个体与社区非医疗资源服务相连接。该机制自2018年引入中国后普及程度不高。研究建议将中医特色融入该模式,以提升其在中国医疗体系中的适用性与有效性。
引用
Wang CL, Wang YY, Wang XF, Robinson N. What is social prescribing: could traditional Chinese medicine play a role? Evidence-Based Chinese Medicine and Technology Assessment, 2025, 1: 9570007.

Original Research Articles
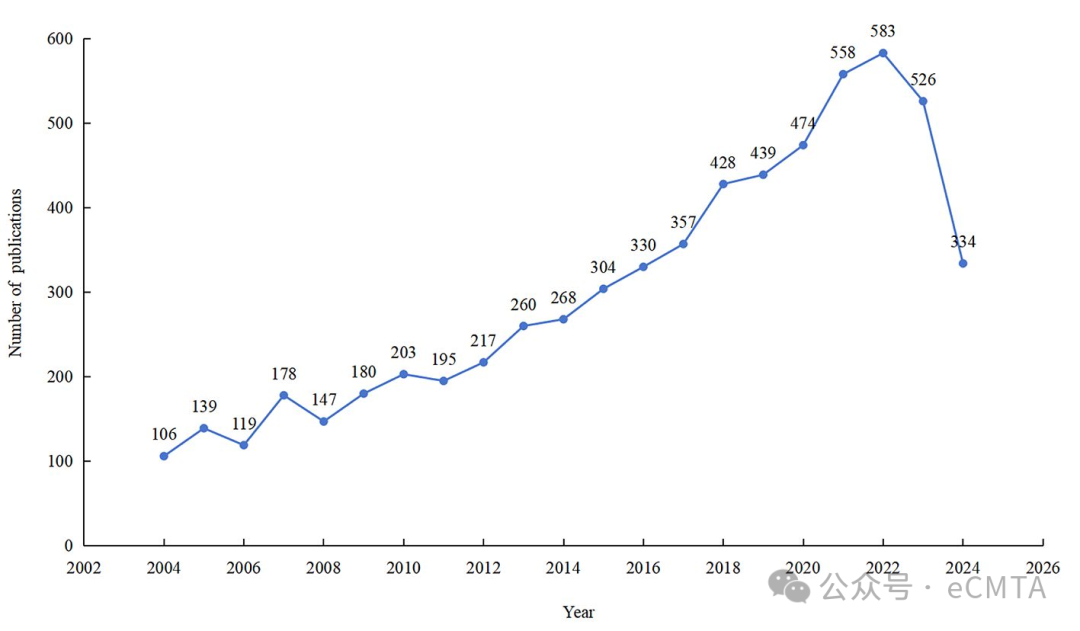
1 Global trends of traditional, complementary and integrative medicine for musculoskeletal diseases: a bibliometric analysis
传统补充整合医学治疗骨骼肌肉系统疾病的全球趋势:一项文献计量学研究
作者
Xue-feng Wang, Zhi-qiang Li, Heng Yin, Trine Stub, and Jian-ping Liu
摘要
This bibliometric analysis examines 6345 publications (2004–2024) on Traditional, Complementary, and Integrative Medicine (TCIM) for musculoskeletal diseases (MSDs). Key findings include rising research output, focus on vitamin D and osteoporosis, and shifting trends from epidemiology to risk factors and management. International collaboration and TCIM’s role in preventive healthcare are emphasized.
本研究通过文献计量分析考察了2004‒2024年间6345篇关于传统与补充整合医学(TCIM)治疗肌肉骨骼疾病(MSDs)的文章。主要结果包括:论文产出持续增长,聚焦维生素D与骨质疏松症领域,研究重心从流行病学转向风险因素与疾病管理。国际科研合作及TCIM在预防保健中的作用得到了重点探讨。
Wang XF, Li ZQ, Yin H, Stub T, Liu JP. Global trends of traditional, complementary and integrative medicine for musculoskeletal diseases: a bibliometric analysis. Evidence-Based Chinese Medicine and Technology Assessment, 2025, 1: 9570001.

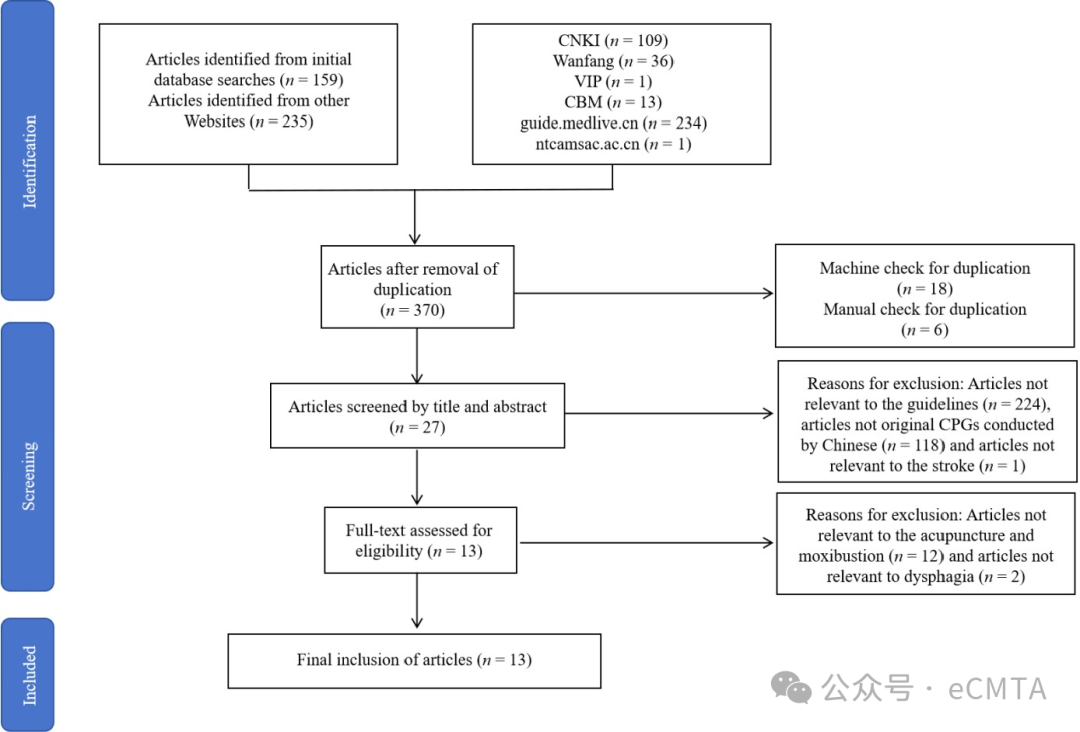
2 Chinese guidelines on acupuncture for post-stroke dysphagia – quality assessment and evidence analysis
针灸治疗脑卒中后吞咽障碍国内相关临床实践指南的质量评价与证据分析
作者
Lan Yuan, Zi-yu Tian, Bin Liu, Yu-ying Hong, and Nicola Robinson
摘要
This study evaluated 13 Chinese clinical practice guidelines (CPGs) on acupuncture for post-stroke dysphagia (2011–2024). The Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation II assessment revealed varying quality (5 high, 2 moderate, 6 low), with weak and outdated evidence. Most CPGs lacked multidisciplinary input, highlighting the need for methodologically rigorous, evidence-based guideline development.
本研究评估了2011‒2024年间中国发布的13份针灸治疗中风后吞咽障碍临床实践指南(CPGs)。采用AGREE II工具评估显示指南质量参差不齐(高质量5份、中等质量2份、低质量6份),证据基础薄弱且时效性不足。多数指南缺乏多学科参与,亟需建立方法学严谨、循证支持的指南制定体系。
引用
Yuan L, Tian ZY, Liu B, Hong YY, Robinson N. Chinese guidelines on acupuncture for post-stroke dysphagia: quality assessment and evidence analysis. Evidence-Based Chinese Medicine and Technology Assessment, 2025, 1: 9570002.

关于期刊
《中医药循证医学与技术评估(英文)》(Evidence-Based Chinese Medicine and Technology Assessment ,简称“eCMTA”)是由北京中医药大学和清华大学出版社共同主办的同行评议英文期刊。本刊使用ScholarOne投稿平台,依托清华大学出版社SciOpen平台出版和发行。北京中医药大学刘建平教授和英国Nicola Robinson教授共同担任主编。
目的
本刊旨在促进循证的中医药学和整合医学的发展,提高医疗决策的科学性,同时为以中医药学和整合医学为重点的医疗保健服务提供高质量的循证医学证据,增强医疗保健的标准化和规范化。
收录范围
1. 技术方法:中医药学和整合医学的方法学研究(疗效评估、证据分级与评价)、指南研制、临床评价量表研制、疾病发病风险及疗效预测模型、人工智能及其应用;
2. 证据综合:系统评价/meta分析、网络分析、文献计量、范围性综述和可视化分析;
3. 标准规范:临床实践指南、临床路径、专家共识和报告规范;
4. 技术评估:技术评估(优势病种研究、适宜技术评估、技术筛选及应用)、药物经济学研究;
5. 循证决策:循证临床实践、循证公共卫生、循证政策制定、临床稽查和实施科学;
6. 循证研究:临床研究、真实世界研究、混合方法研究、卫生服务研究和卫生经济分析。
期刊官网
https://www.sciopen.com/journal/3078-7963
编辑部邮箱
ecmta@bucm.edu.cn
投稿网址
https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/ecmta

转载本文请联系原作者获取授权,同时请注明本文来自SciOpen TUP科学网博客。
链接地址:https://wap.sciencenet.cn/blog-3563286-1494596.html?mobile=1
收藏

