博文
[转载]hLife 2025年第十期正式出版
||

封面解读
Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae (hvKp) is a formidable community-acquired pathogen that causes life-threatening infections such as liver abscess, endophthalmitis, and meningitis. At the heart of its virulence lies the plasmid-encoded regulator RmpA. By combining CRISPR interference (CRISPRi)-based knockdown with transcriptomic and genomic binding analyses, we reveal RmpA as a central “metabolic hub regulator.” RmpA drives capsule biosynthesis by activating the capsule polysaccharide locus and redirecting glucose metabolism and the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle toward precursor supply, while simultaneously repressing type III fimbriae through direct binding to the mrkABCDF promoter. This dual role enables hvKp to toggle between hypermucoviscosity and biofilm formation. This cover page underscores RmpA as a master switch that orchestrates these opposing phenotypes, illuminating its pivotal role in bacterial physiology and highlighting its promise as a novel target for therapeutic intervention.
Jie Feng
导读
✦
All Papers
✦
通讯作者:Jiahe Li, Allen P. Liu

In this commentary, we want to highlight the recent work by Yichuan Xiao, Chenli Liu, and coworkers on engineered bacteria for cancer immunotherapy and share our perspectives on the future of bacterial immunotherapy.
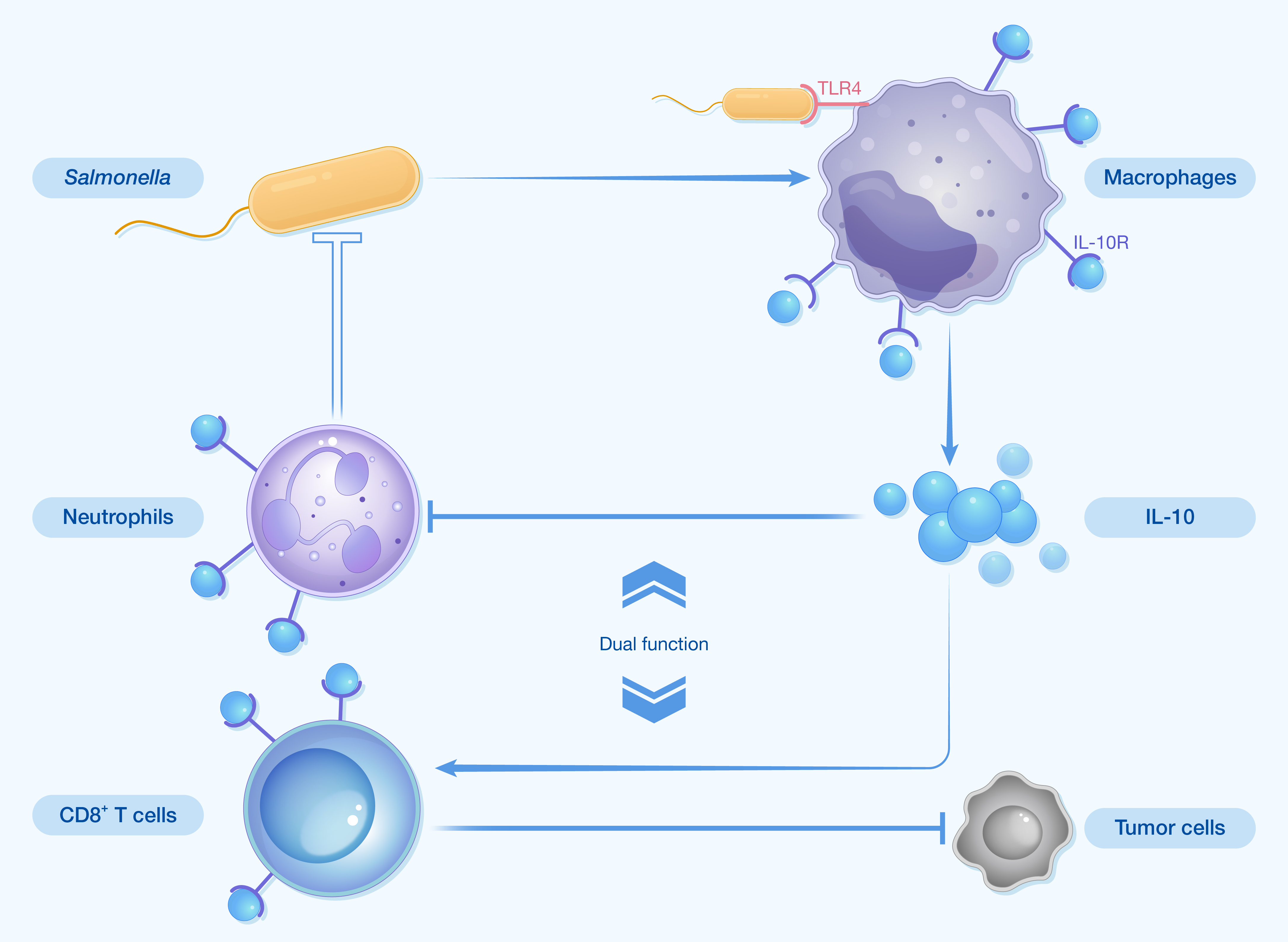
引用:
Li J, Liu AP. The promise of synthetic bacteria in cancer immunotherapy: Revitalizing tumor immunity via IL-10R modulation. hLife 2025; 3: 459–461.
hLife | 肿瘤微环境中的微生物与固有免疫互作:肿瘤免疫治疗新视角
通讯作者:徐冉、韩新巍

本文总结了健康和肿瘤状态下微生物与宿主固有免疫系统之间错综复杂的相互作用,阐述了肿瘤发生发展过程中的免疫识别和极化调节,介绍了利用微生物进行肿瘤免疫治疗的最新进展和挑战,为基于微生物的创新肿瘤免疫疗法的开发提供了新视角。
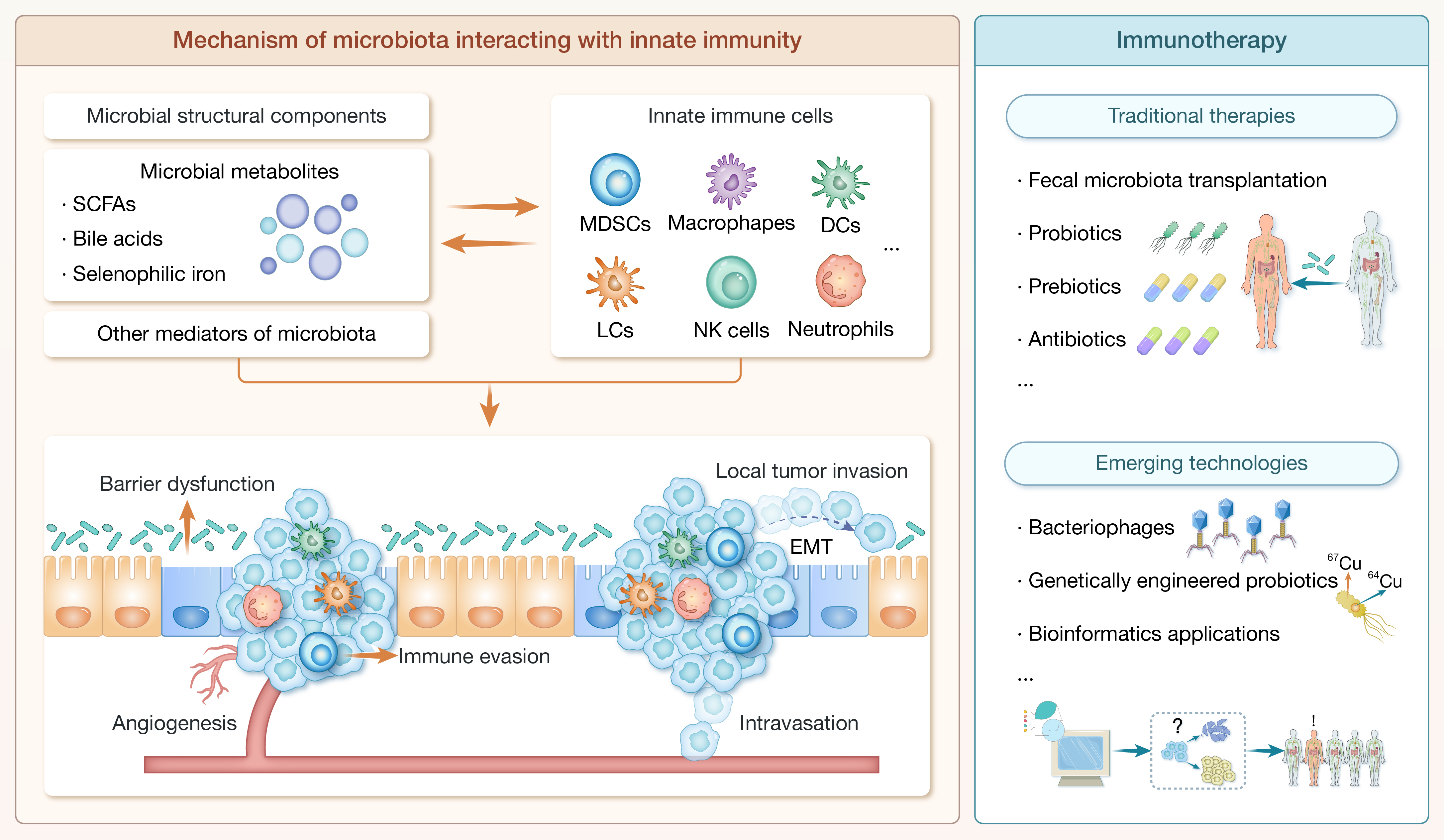
引用:
Zhou Z, Lv Y, Zuo A, et al. Interactions between microbiota and innate immunity in tumor microenvironment: Novel insights into cancer progression and immunotherapy. hLife 2025; 3: 462–493.
通讯作者:Vadim Molodtsov、王程远
本文系统总结了细菌和古菌在转录-翻译偶联及因子依赖型转录终止复合体结构方面的最新研究成果,重点比较了二者在这些关键调控机制上的异同点。基于结构生物学证据,作者探讨了古菌中潜在的TTC机制及其结构模型,为理解古菌基因表达调控提供了新思路。
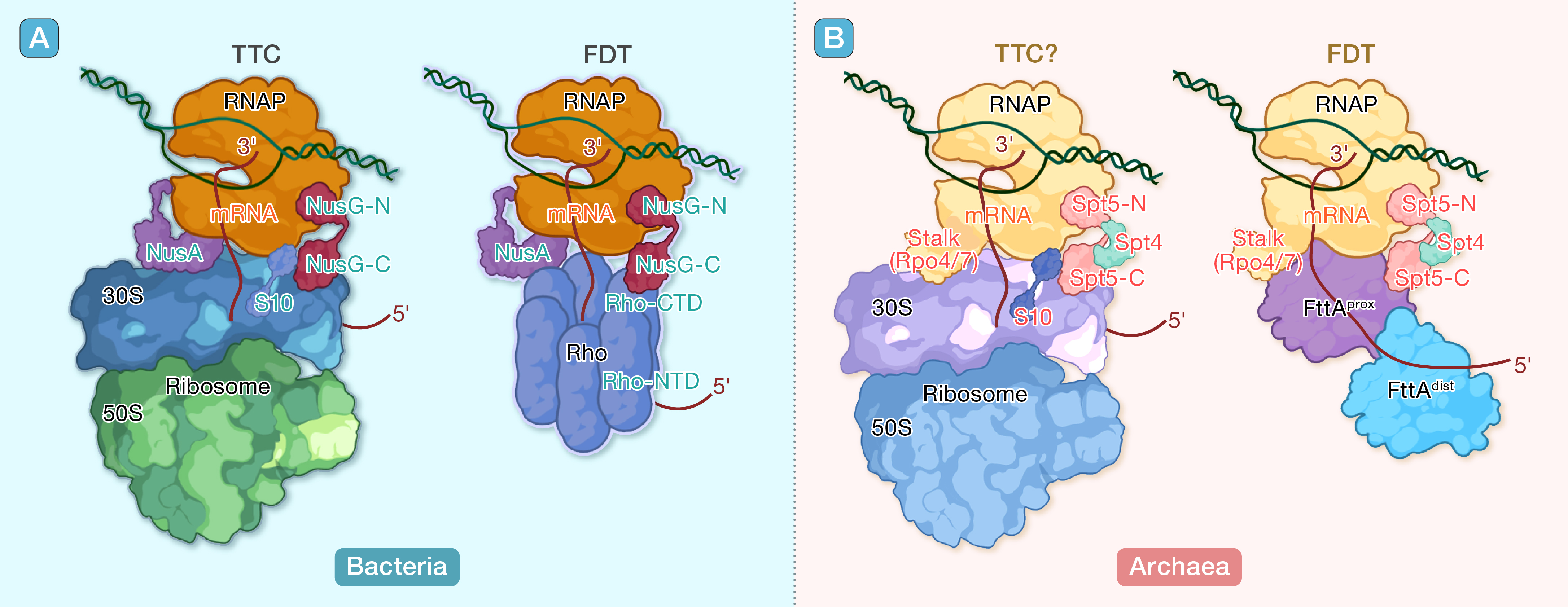
引用:
Li R, Molodtsov V, Wang C. Structural insights from the bacterial world: Coordination of transcription–translation coupling and transcription termination in archaea. hLife 2025; 3: 494–497.
4. Unveiling the multifaceted roles of ISG15 and ISGylation in copper metabolism and cuproptosis
hLife | 西南大学谢建平研究团队阐述ISG15和ISGylation在铜代谢和铜死亡中的作用
通讯作者:谢建平

本文深入探讨了ISG15、ISGylation、铜代谢与铜蛋白凋亡之间的复杂关系。旨在强调这些生物过程的参与者在疾病背景下的创新性和重要性,尤其关注结核病。
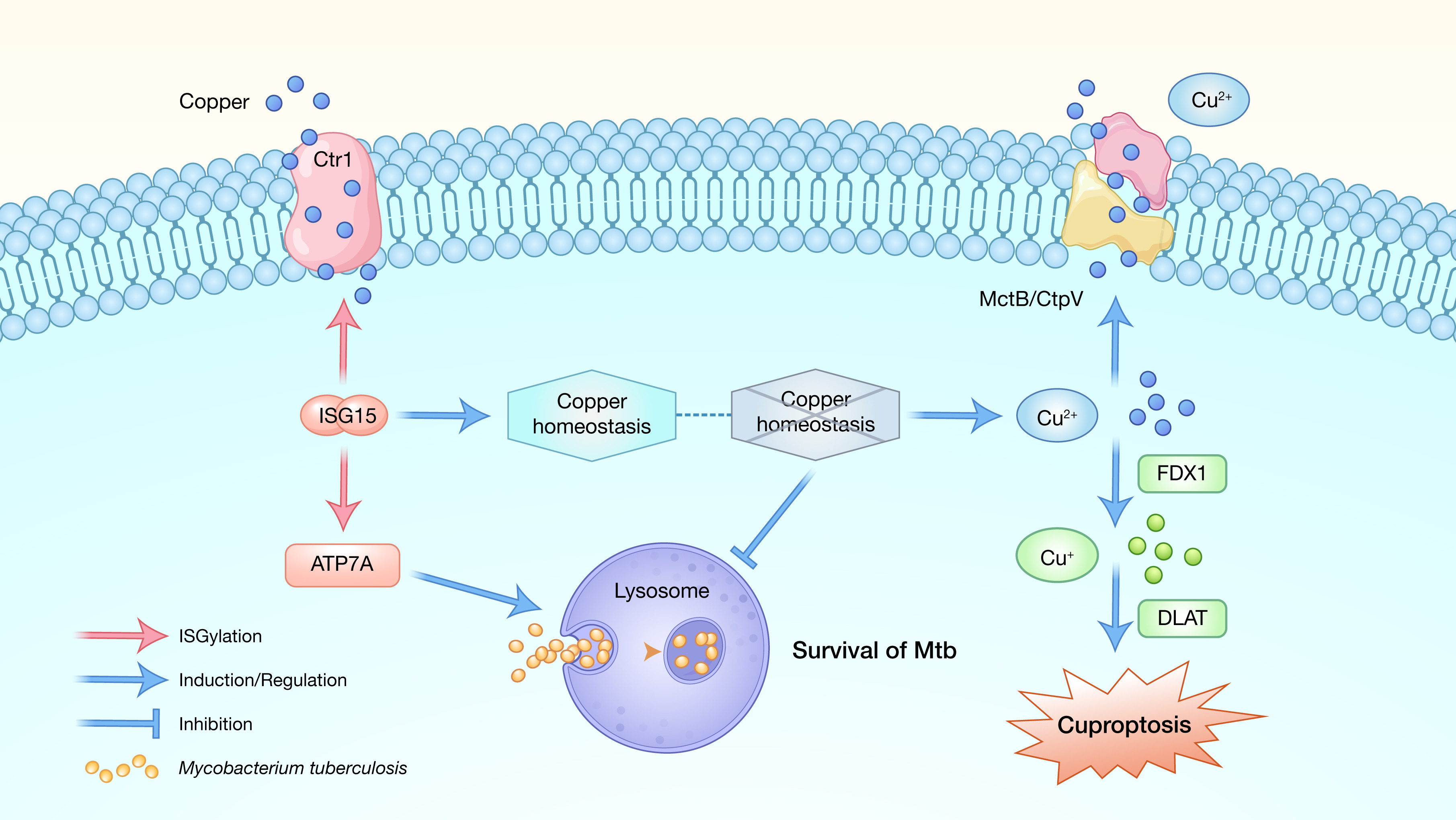
引用:
Xu J, Zhang Q, Suleiman IM, et al. Unveiling the multifaceted roles of ISG15 and ISGylation in copper metabolism and cuproptosis. hLife 2025; 3: 498–500
通讯作者:王明贵

高耐高毒肺炎克雷伯菌的出现和广泛传播是潜在的公共卫生危机,这类菌株正悄然改变临床感染格局。未来研究和防控策略可聚焦于:基于CRISPR-Cas或毒素-抗毒素系统的去定植研究、针对毒力因子的靶向治疗研究、结合新型分子检测与监测网络的早期预警系统的建立等。只有通过加强基础研究、研发诊断手段、推动多学科协作,才能有效遏制其蔓延,守护临床安全与公共卫生防线。
引用:
Jiang J, Zhang J, Sun Z, et al. Convergence of carbapenem resistance and hypervirulence in Klebsiella pneumoniae: An emerging public health threat. hLife 2025; 3: 501–503.
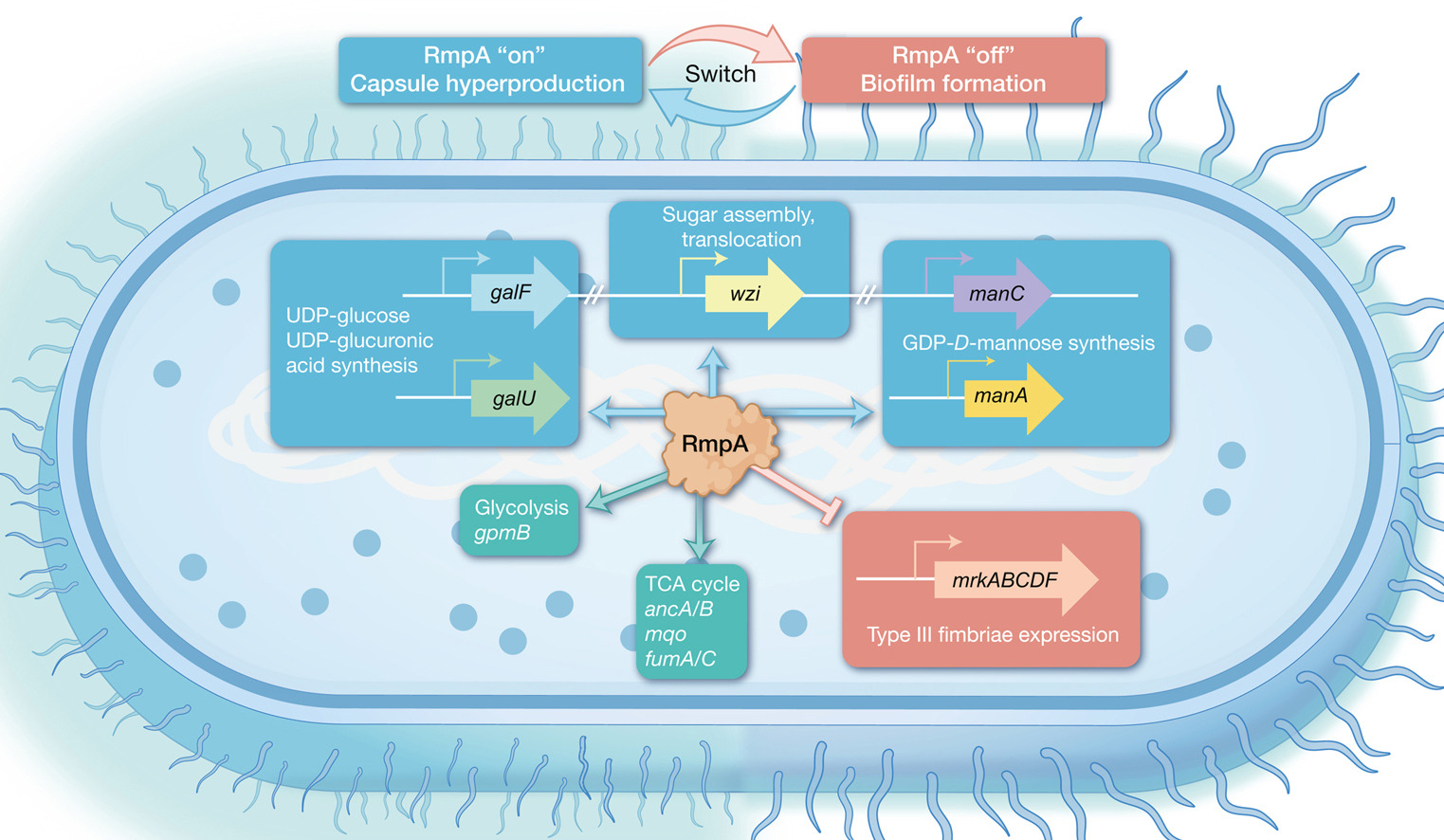
hLife | 冯婕研究团队揭示RmpA是操控高毒力肺炎克雷伯菌在高粘液性与生物膜间切换的代谢开关
通讯作者:冯婕
本文通过在高毒力肺炎克雷伯菌中构建针对rmpA基因的dCas9敲低菌株,结合RNA-seq和ChIP-seq技术,揭示了RmpA作为“代谢中枢调控器”的双重功能。
引用:
Yao S, Huang J, Geng J, et al. RmpA drives metabolic reprogramming to modulate the phenotypic switch between hypermucoviscosity and biofilm formation in hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. hLife 2025; 3: 504–516.
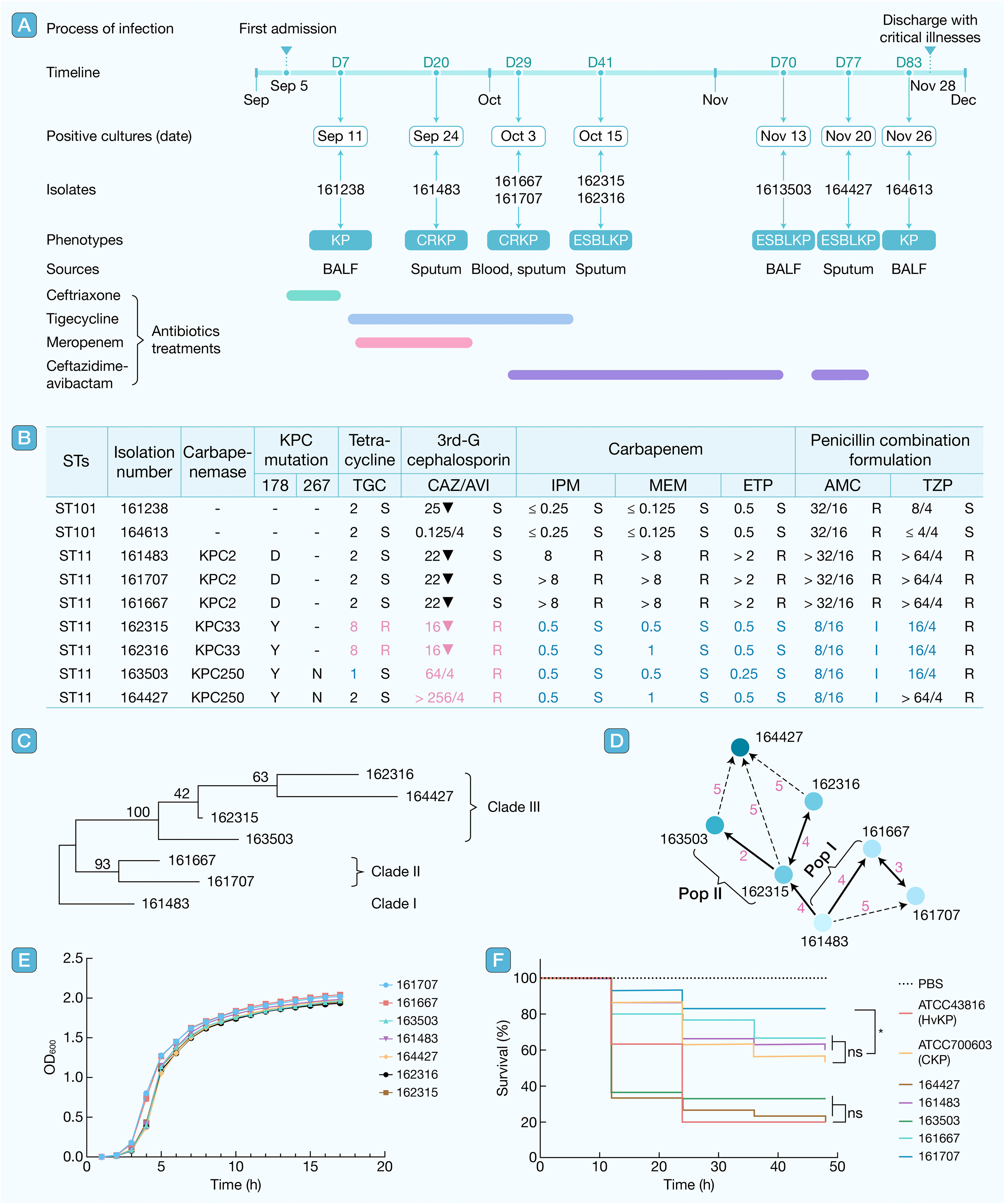
hLife | 深圳三院曲久鑫研究团队揭示高毒高耐肺炎克雷伯菌ST11持续感染过程中的宿主内进化
通讯作者:曲久鑫

本文通过全基因组测序(WGS)分析了从一名持续感染患者体内时序性分离的一系列肺炎克雷伯菌菌株,揭示并表征了肺炎克雷伯菌基因组、耐药表型和毒力在宿主内分化和适应过程,并呼吁借鉴病毒学,从准种理论的角度认识病原细菌持续性感染。
引用:
Li L, Jiang Z, Wang X, et al. Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11 index from a single strain enhances rapid parallel evolution during persistent infection. hLife 2025; 3: 517–520.
期刊简介
hLife 由高福院士、董晨院士和Jules A. Hoffmann教授(2011诺奖获得者)领衔,是中国科学院微生物研究所主办,中国生物工程学会,浙江大学陈廷骅大健康学院,西湖大学医学院,上海市免疫治疗创新研究院和广州霍夫曼免疫研究所联合支持,与国际出版商爱思唯尔合作的健康科学领域综合性英文期刊。
hLife 聚焦健康科学领域的前沿进展,旨在促进基础研究与临床应用的融合发展。期刊发表与医学相关各研究领域最新成果,学科领域包括(但不限于)病原生物学、流行病学、生理学、免疫学、结构生物学、疾病监测、肿瘤、药物、疫苗和健康政策等。
hLife是一本金色开放获取期刊,月刊出版;2022年成功入选“中国科技期刊卓越行动计划高起点新刊”;2023年11月正式创刊;2024年5月被DOAJ收录;2024年8月被Scopus收录;2024年10月入选“首都科技期刊卓越行动计划——重点英文科技期刊支持项目”;2025年6月入选北京市科委“2025年度支持高水平国际科技期刊建设-强刊提升”项目;2025年8月入选中国科学引文数据库(CSCD)核心库。
hLife实行高标准与高效率并重的同行评审机制:
投稿至给出“是否送审”决定⏰1天
投稿至给出“首轮审稿”决定⏰28天
投稿至给出“是否录用”决定⏰61天
2026年前hLife接收的稿件免收文章处理费(APC)。
https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/hlife
https://wap.sciencenet.cn/blog-3552961-1508126.html
上一篇:[转载]hLife | 温州医科大学陆家海研究团队评述广东基孔肯雅热疫情:“同一健康”的启示与新策略
下一篇:[转载]第16期hLife Café在巴西里约热内卢举办