博文
LPS 与炎症∶ 小小脂多糖 (LPS) 如何能轻松 "拿捏" 炎症造模_MedChemExpress(MCE 中国)
|
LPS,它与炎症反应有着千丝万缕的联系......
 LPS 何方神圣?在体内如何诱发炎症反应?
LPS 何方神圣?在体内如何诱发炎症反应? 如何选择 LPS 构建"合拍"的炎症疾病模型?
如何选择 LPS 构建"合拍"的炎症疾病模型? 来来来,一起了解下!Section.01LPS 与炎症发生
来来来,一起了解下!Section.01LPS 与炎症发生 嘘,可不要小瞧了它!脂多糖 (Lipopolysaccharide;LPS) ,是由脂质和多糖组成的大分子,广泛存在于革兰氏阴性菌细胞壁中,又被称为内毒素,它可是具有强烈的促炎性质[1]。
嘘,可不要小瞧了它!脂多糖 (Lipopolysaccharide;LPS) ,是由脂质和多糖组成的大分子,广泛存在于革兰氏阴性菌细胞壁中,又被称为内毒素,它可是具有强烈的促炎性质[1]。
LPS 结构LPS 是由脂质 A、核心多糖和 O-特异性抗原组成。包含这三个组分的为光滑型 S-LPS,缺乏 O 抗原的则被称为粗糙型 R-LPS,或脂寡糖 (LOS)[2]。
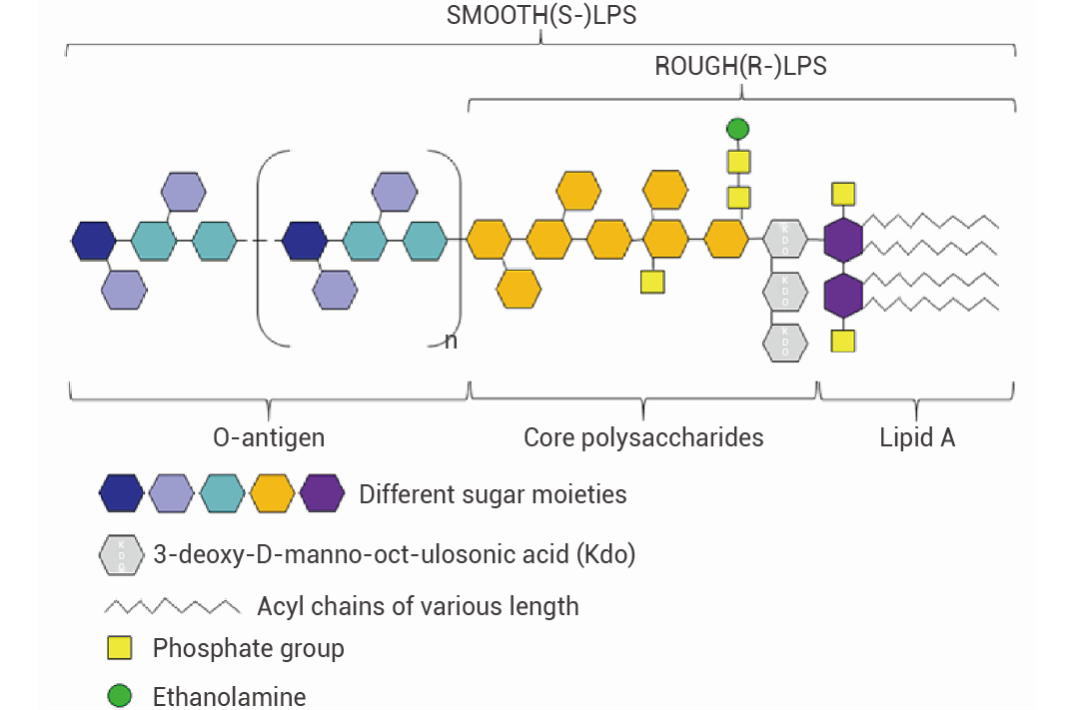 图 1. LPS 的经典结构[2]。
图 1. LPS 的经典结构[2]。• 脂质 A:LPS 的脂质部分,嵌在细菌外膜的磷脂层中,是内毒素的主要毒性成分。不同革兰氏阴性菌的脂质 A 结构具有一定差异,但在同一菌株中结构基本相同。脂质 A 的任何结构变化都可能改变 LPS 的免疫效力并决定其毒性。此外,脂质 A 对于宿主受体的特异性识别非常重要,能够刺激宿主的免疫反应[2]。
• 特异性抗原:由多个寡糖重复单位组成,位于 LPS 的最外层,是 LPS 中变化最大的部分。O-特异性抗原的糖残基种类、长度、排列顺序和连接方式具有菌株特异性,决定了细菌的抗原特异性[2]。根据 O 抗原的差异可将大肠杆菌分为不同的血清群,如 O55、O111 等。• 核心多糖:连接了 O-特异性抗原和脂质 A。由庚糖、半乳糖等组成,结构相对保守[2]。
LPS 诱导炎症反应
LPS 与 TLR4
TLR4:Toll 样受体 4,可在单核细胞、巨噬细胞和树突细胞等髓样细胞中表达,是重要的细胞表面模式识别受体,负责启动和维持宿主的炎症反应[2]。LPS 主要通过其经典受体 Toll 样受体 4 (TLR4) 诱导强烈的炎症反应。LPS 进入宿主体内,会与 LPS 结合蛋白 (LBP) 结合,然后进一步与细胞膜上的 CD14 (CD14 是很多免疫细胞的 GPI 锚定膜蛋白) 结合,形成 CD14-LPS 复合物。这一结合过程促使 LPS 与 TLR4-MD2 复合物相互作用,进而激活细胞内的信号通路[2][3]。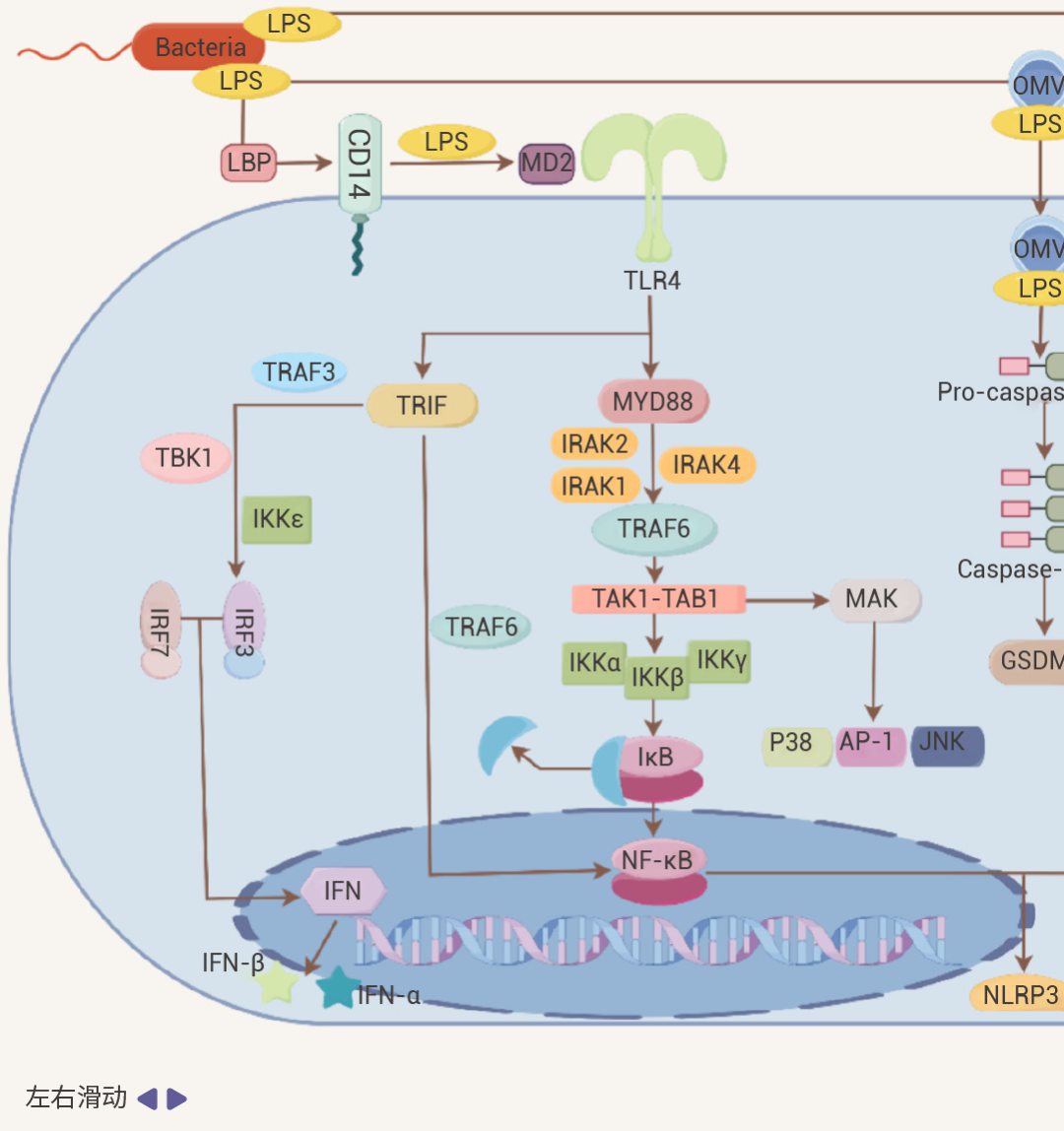
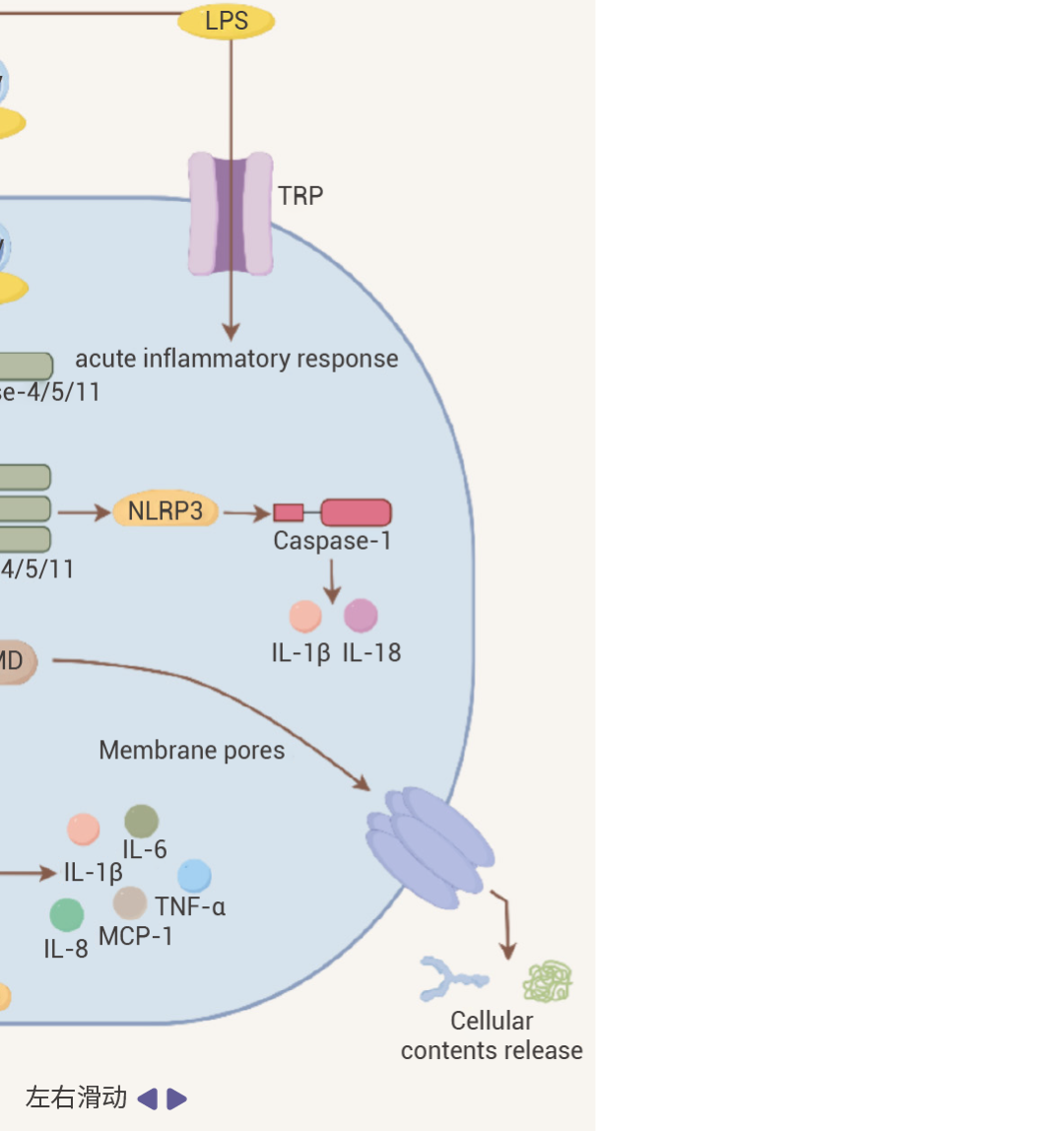
图 2. LPS 作用机制[2]。
细胞内 LPS/TLR4 下游信号传导主要分为两类,MyD88 依赖性通路和 TRIF 依赖性通路。它们分别介导促炎细胞因子和 I 型干扰素基因的激活[2][4]。• 在 MyD88 依赖性通路中:活化的 MyD88 可募集并激活 IRAK4、IRAK1 和 IRAK2,接着与 TRAF6 发生相互作用。进一步激活 TAK1-TAB1 复合物,刺激 IKKα/IKKβ 复合物,然后诱导 NF-κB 等转录因子核转位,启动炎症细胞因子基因的转录,促使细胞释放如 IL-1β、IL - 6、TNF-α 等多种炎症细胞因子。• 在 TRIF 介导 MyD88 非依赖性通路中:TRIF 通过招募 TRAF3 可激活 IRF3,然后,IRF3 与 IRF7 形成同源或异源二聚体,进而转录 IFN 和 IFN 诱导型基因,诱导 IFN-α 和 IFN-β 释放。同时,TRIF 也可以通过招募 TRAF6 激活 NF-κB。此外,除了经典的 LBP-CD14-TLR4 途径外,LPS 还可以通过 Caspase 途径和 TRP 通道等激活免疫细胞。
总之,上述因素都可以促进炎症信号并引起免疫反应。
Section.02LPS: 炎症造模好帮手通过前面的介绍,我们了解了 LPS 的定义以及它如何通过复杂的信号通路激活细胞内的炎症反应。鉴于 LPS 具备强大的促炎特性,这使其成为我们构建诱导炎症模型的得力助手!首先,解答大家在选购 LPS 时的一个小疑惑!MCE 网站为啥子有十几种 LPS?它们名字后长长长长长长的后缀是什么?前面我们提到,LPS 是细菌细胞壁的成分。So,MCE 网站上不同的 LPS 代表它们来自于不同的细菌。小贴士:举个例子,我们在诱导炎症模型中常用的 LPS, from E. coli O55: B5,它是来自于大肠杆菌 O55: B5 血清型的内毒素。其中,大肠杆菌血清型是大肠杆菌的一种分类方式,O55 代表了特异性 O 链中 O 抗原的一种特定类型,B5 表示鞭毛抗原的一种类型。血清型不同,激活的炎症途径和炎症因子可能会有差异,从而转化为不同的表型反应和临床症状。下面,我们就一起了解一下 LPS 可以诱导哪些模型以及一些注意事项~一、体外细胞炎症模型[5][6][7][8]
1. 推荐的 LPS 类型 (排名有先后顺序哦~):
1) Lipopolysaccharides, from E. coli O55: B5 (广泛使用!);2) Lipopolysaccharides, from E. coli O111: B4 (广泛使用!);3) Lipopolysaccharides, from P. gingivalis (牙周炎相关研究)。
2. 常用细胞类型:
1) 巨噬细胞,如 RAW 264.7、BMDMs;2) 小胶质细胞,如 N9、原代细胞;3) 肿瘤细胞,如 Caco-2、A549 和 PC3。3. 参考浓度范围和处理时间:0.1-10 μg/mL;1-24 h。
4. 推荐检测指标:1) 上清或细胞中炎症因子:IL-1β、IL-6 及 TNF-α 等 (ELISA/qPCR/WB);2) NO 释放/NO 代谢物含量 (Kits 检测);3) 炎症基因:iNOS、NF-kB 及 NLRP3 等 (qPCR/WB);4) 细胞活力:CCK-8 或 MTT。
5. 注意事项:1) 在正式实验前,应根据细胞系和 LPS 来源等查找相关参考文献,进行浓度和时间梯度的筛选以确定最优的实验方案。2) LPS 刺激细胞不一定会引起细胞死亡,因此不宜仅仅通过检测细胞活力来确定 LPS 造模浓度和时间,建议检测炎症因子的表达和分泌。3) 在 LPS 刺激细胞的过程中,应定期观察细胞的形态变化,过高浓度可能引发细胞毒性,过低浓度则可能无法有效损伤细胞。4) 一定浓度的 DMSO 可显著抑制 LPS 诱导的炎症反应,建议用 PBS 或 ddH2O 溶解。5) 在体外炎症模型构建研究中,Lipopolysaccharides, from E. coli O55: B5 和 Lipopolysaccharides, from E. coli O111: B4 是应用最为广泛的 LPS,推荐使用!若开展牙周炎相关研究时,也可选用 Lipopolysaccharides, from P. gingivalis。二、体内动物模型
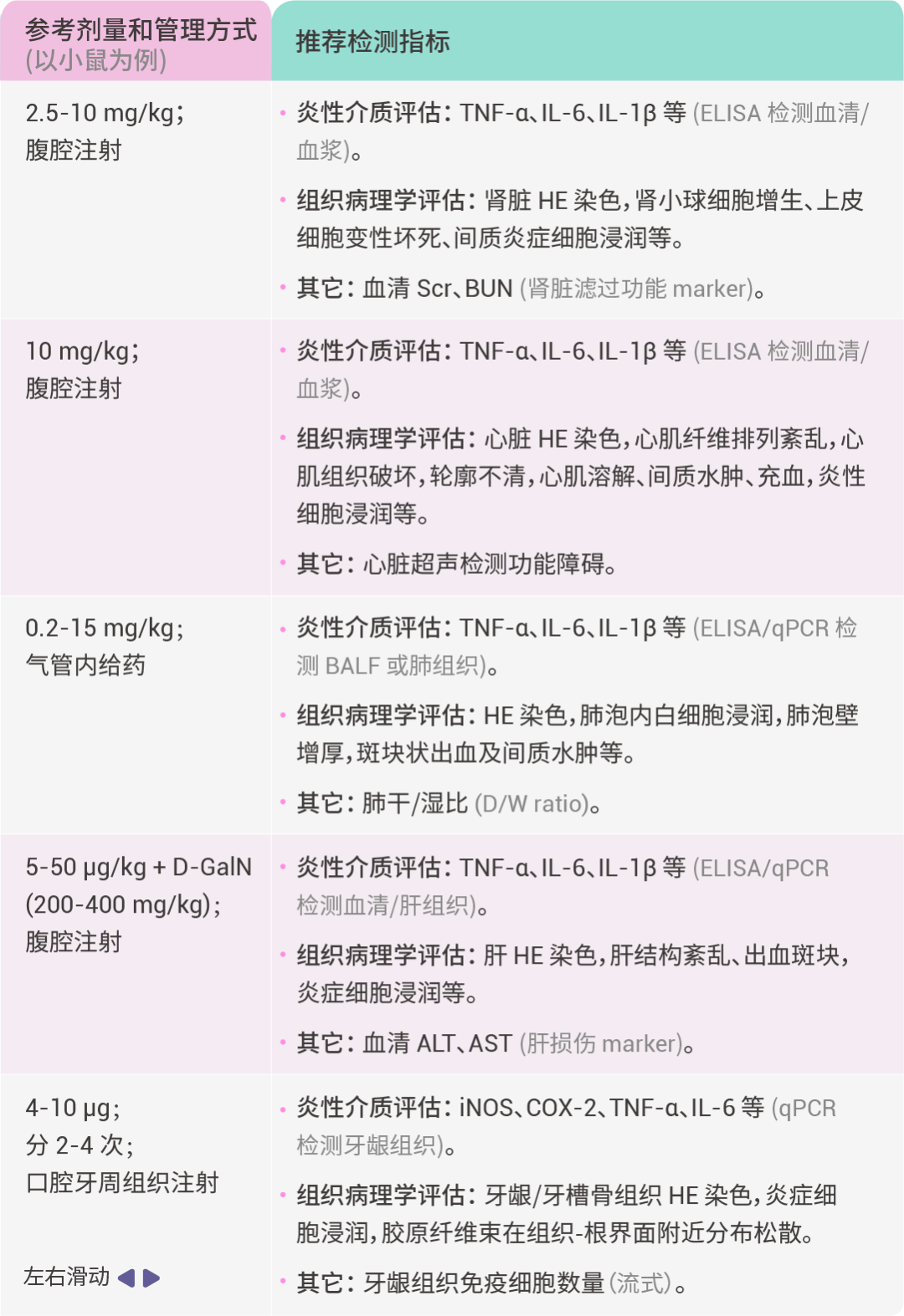


注意事项:
1) 在 LPS 诱导动物模型前,应根据实验目的、动物类型等,查找相关参考文献,进行预实验,以确定最优的实验方案。
2) 在 LPS 给药后,不同的炎症因子,其含量峰值出现的时间点可能不一致,建议根据参考文献确定实验方案,以及预实验时应多选几个时间点检测。3) LPS 溶解后可在 -20℃ 稳定保存约一个月,-80℃ 约 6 个月。LPS 需避光保存,并避免反复冻融。由于内毒素具有较强的吸附性,建议储存于硅烷化容器内。如果使用玻璃容器,使用前请确保充分混合,以保证 LPS 完全重新溶解 (若 LPS 浓度超过 1 mg/mL,则对小瓶侧面的吸附可忽略不计)。Section.03小结宝子们,今天小 M 带着大家梳理了 LPS 的相关知识。面对五花八门的 LPS,大家再也不用犯愁啦。希望这些知识能帮助大家轻松拿捏实验,在炎症研究领域发光发热!如果觉得这篇 LPS 干货秘籍有帮助,别忘了点赞、分享哦~| 产品推荐 |
| Lipopolysaccharides, from E. coli O55:B5Lipopolysaccharides, from E. coli O55:B5 (HY-D1056),多用于体外细胞诱导炎症模型。 |
| Lipopolysaccharides, from E. coli O111:B4Lipopolysaccharides, from E. coli O111:B4 (HY-D1056A1),多用于体内动物诱导炎症模型。 |
| Lipopolysaccharides, from P. gingivalisLipopolysaccharides, from P. gingivalis (HY-D1056D),多用于牙周炎相关研究。 |
| Cell Counting Kit-8Cell Counting Kit-8 (HY-K0301),快速、高灵敏度细胞活性检测试剂盒。 |
| Nitric Oxide Detection KitNitric Oxide Detection Kit (HY-K0318),NO 检测试剂盒 (Griess 法)。 |
 [1] Bertani B, et al. Function and Biogenesis of Lipopolysaccharides. EcoSal Plus. 2018 Aug;8(1):10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0001-2018. [2] Zhang X, et al. Application of lipopolysaccharide in establishing inflammatory models. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Nov;279(Pt 4):135371.[3] Cohen J. The immunopathogenesis of sepsis. Nature. 2002 Dec 19-26;420(6917):885-91.[4] Lu YC, et al, Ohashi PS. LPS/TLR4 signal transduction pathway. Cytokine. 2008 May;42(2):145-151.[5] Huang S, et al. Disruption of the Na+/K+-ATPase-purinergic P2X7 receptor complex in microglia promotes stress-induced anxiety. Immunity. 2024 Mar 12;57(3):495-512.e11.[6] Guo D, et al. Synergistic rheumatoid arthritis therapy by interrupting the detrimental feedback loop to orchestrate hypoxia M1 macrophage polarization using an enzyme-catalyzed nanoplatform. Bioact Mater. 2024 Jul 23;41:221-238.[7] Tezcan G, et al. Azithromycin and Ceftriaxone Differentially Activate NLRP3 in LPS Primed Cancer Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 22;23(16):9484.[8] Park J, et al. Fucoidan inhibits LPS-induced inflammation in vitro and during the acute response in vivo. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017 Feb;43:91-98. [9] Li CC, et al. Suppression of Dendritic Cell-Derived IL-12 by Endogenous Glucocorticoids Is Protective in LPS-Induced Sepsis. PLoS Biol. 2015 Oct 6;13(10):e1002269.[10] Rialdi A, et al. Topoisomerase 1 inhibition suppresses inflammatory genes and protects from death by inflammation. Science. 2016 May 27;352(6289):aad7993.[11] Hagiwara S, et al. Antagonist of the type-1 ANG II receptor prevents against LPS-induced septic shock in rats. Intensive Care Med. 2009 Aug;35(8):1471-8.[12] Makrecka-Kuka M, et al. Inhibition of CPT2 exacerbates cardiac dysfunction and inflammation in experimental endotoxaemia. J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Oct;24(20):11903-11911.[13] Chen XS, et al. Angiotensin-(1-7) ameliorates sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy by alleviating inflammatory response and mitochondrial damage through the NF-κB and MAPK pathways. J Transl Med. 2023 Jan 2;21(1):2.[14] Yang J, et al. MicroRNA-106a Provides Negative Feedback Regulation in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation by targeting TLR4. Int J Biol Sci. 2019 Aug 22;15(11):2308-2319.[15] Zhang Y, et al. Melatonin alleviates acute lung injury through inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome. J Pineal Res. 2016 May;60(4):405-14.[16] Kwon WY, et al. Niacin attenuates lung inflammation and improves survival during sepsis by downregulating the nuclear factor-κB pathway. Crit Care Med. 2011 Feb;39(2):328-34.[17] Ma J, et al. Geraniol ameliorates acute liver failure induced by lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine via regulating macrophage polarization and NLRP3 inflammasome activation by PPAR-γ methylation Geraniol alleviates acute liver failure. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Apr;210:115467.[18] Firth JD, et al. Lipopolysaccharide induces a stromal-epithelial signalling axis in a rat model of chronic periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol. 2013 Jan;40(1):8-17.[19] Park J, et al. Fucoidan inhibits LPS-induced inflammation in vitro and during the acute response in vivo. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017 Feb;43:91-98.[20] Li L, et al. Ablation of Siglec-E augments brain inflammation and ischemic injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2022 Jul 20;19(1):191.[21] Yamawaki Y, et al. Imipramine prevents Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide-induced microglial neurotoxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022 Dec 17;634:92-99.[22] Arioz BI, et al. Melatonin Attenuates LPS-Induced Acute Depressive-Like Behaviors and Microglial NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation Through the SIRT1/Nrf2 Pathway. Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 2;10:1511.[23] Liu Q, et al. BGP-15 alleviates LPS-induced depression-like behavior by promoting mitophagy. Brain Behav Immun. 2024 Jul;119:648-664.[24] Huang B, et al. Polydatin Prevents Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Parkinson's Disease via Regulation of the AKT/GSK3β-Nrf2/NF-κB Signaling Axis. Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 5;9:2527.[25] Zhao Y, et al. Connexin43 inhibition attenuated dopaminergic neuronal loss in the lipopolysaccharide-induced mice model of Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Lett. 2022 Feb 6;771:136471.
[1] Bertani B, et al. Function and Biogenesis of Lipopolysaccharides. EcoSal Plus. 2018 Aug;8(1):10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0001-2018. [2] Zhang X, et al. Application of lipopolysaccharide in establishing inflammatory models. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Nov;279(Pt 4):135371.[3] Cohen J. The immunopathogenesis of sepsis. Nature. 2002 Dec 19-26;420(6917):885-91.[4] Lu YC, et al, Ohashi PS. LPS/TLR4 signal transduction pathway. Cytokine. 2008 May;42(2):145-151.[5] Huang S, et al. Disruption of the Na+/K+-ATPase-purinergic P2X7 receptor complex in microglia promotes stress-induced anxiety. Immunity. 2024 Mar 12;57(3):495-512.e11.[6] Guo D, et al. Synergistic rheumatoid arthritis therapy by interrupting the detrimental feedback loop to orchestrate hypoxia M1 macrophage polarization using an enzyme-catalyzed nanoplatform. Bioact Mater. 2024 Jul 23;41:221-238.[7] Tezcan G, et al. Azithromycin and Ceftriaxone Differentially Activate NLRP3 in LPS Primed Cancer Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 22;23(16):9484.[8] Park J, et al. Fucoidan inhibits LPS-induced inflammation in vitro and during the acute response in vivo. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017 Feb;43:91-98. [9] Li CC, et al. Suppression of Dendritic Cell-Derived IL-12 by Endogenous Glucocorticoids Is Protective in LPS-Induced Sepsis. PLoS Biol. 2015 Oct 6;13(10):e1002269.[10] Rialdi A, et al. Topoisomerase 1 inhibition suppresses inflammatory genes and protects from death by inflammation. Science. 2016 May 27;352(6289):aad7993.[11] Hagiwara S, et al. Antagonist of the type-1 ANG II receptor prevents against LPS-induced septic shock in rats. Intensive Care Med. 2009 Aug;35(8):1471-8.[12] Makrecka-Kuka M, et al. Inhibition of CPT2 exacerbates cardiac dysfunction and inflammation in experimental endotoxaemia. J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Oct;24(20):11903-11911.[13] Chen XS, et al. Angiotensin-(1-7) ameliorates sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy by alleviating inflammatory response and mitochondrial damage through the NF-κB and MAPK pathways. J Transl Med. 2023 Jan 2;21(1):2.[14] Yang J, et al. MicroRNA-106a Provides Negative Feedback Regulation in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation by targeting TLR4. Int J Biol Sci. 2019 Aug 22;15(11):2308-2319.[15] Zhang Y, et al. Melatonin alleviates acute lung injury through inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome. J Pineal Res. 2016 May;60(4):405-14.[16] Kwon WY, et al. Niacin attenuates lung inflammation and improves survival during sepsis by downregulating the nuclear factor-κB pathway. Crit Care Med. 2011 Feb;39(2):328-34.[17] Ma J, et al. Geraniol ameliorates acute liver failure induced by lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine via regulating macrophage polarization and NLRP3 inflammasome activation by PPAR-γ methylation Geraniol alleviates acute liver failure. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Apr;210:115467.[18] Firth JD, et al. Lipopolysaccharide induces a stromal-epithelial signalling axis in a rat model of chronic periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol. 2013 Jan;40(1):8-17.[19] Park J, et al. Fucoidan inhibits LPS-induced inflammation in vitro and during the acute response in vivo. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017 Feb;43:91-98.[20] Li L, et al. Ablation of Siglec-E augments brain inflammation and ischemic injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2022 Jul 20;19(1):191.[21] Yamawaki Y, et al. Imipramine prevents Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide-induced microglial neurotoxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022 Dec 17;634:92-99.[22] Arioz BI, et al. Melatonin Attenuates LPS-Induced Acute Depressive-Like Behaviors and Microglial NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation Through the SIRT1/Nrf2 Pathway. Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 2;10:1511.[23] Liu Q, et al. BGP-15 alleviates LPS-induced depression-like behavior by promoting mitophagy. Brain Behav Immun. 2024 Jul;119:648-664.[24] Huang B, et al. Polydatin Prevents Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Parkinson's Disease via Regulation of the AKT/GSK3β-Nrf2/NF-κB Signaling Axis. Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 5;9:2527.[25] Zhao Y, et al. Connexin43 inhibition attenuated dopaminergic neuronal loss in the lipopolysaccharide-induced mice model of Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Lett. 2022 Feb 6;771:136471. https://wap.sciencenet.cn/blog-3536222-1489095.html
上一篇:药物筛选在PROTAC中的应用_MedChemExpress(MCE 中国)
下一篇:多肽与多肽的固相合成技术_MedChemExpress(MCE 中国)
扫一扫,分享此博文