博文
科学家发现生姜中的化合物可以自然对抗IBD  精选
精选
||
科学家发现生姜中的化合物可以自然对抗IBD
诸平
据加拿大多伦多大学(University of Toronto简称U of T)2025年2月24日提供的消息,科学家发现生姜中的化合物可以自然对抗IBD(Scientists Discover Compound in Ginger That Fights IBD Naturally)。
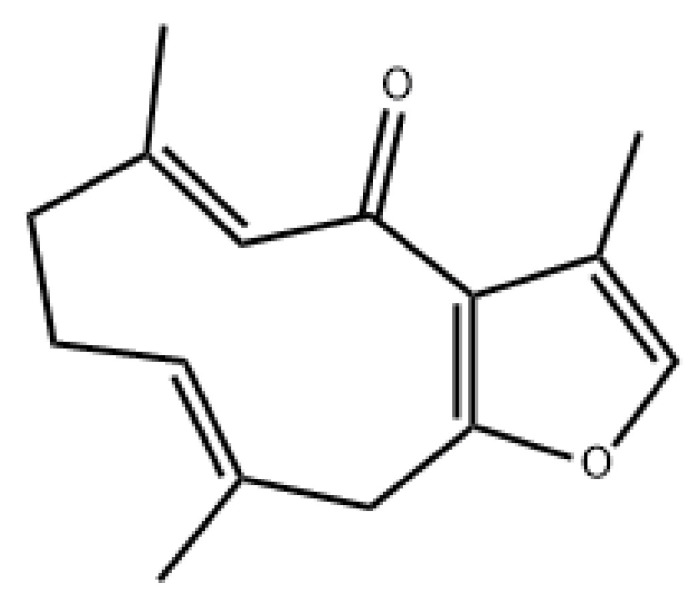
Fig. 2 Chemical structure of Furanodienone{IUPAC NAME: (5E,9E)-3,6,10-trimethyl-8,11-dihydro-7H-cyclodeca[b]furan-4-one}
生姜化合物呋喃二烯酮(furanodienone简称FDN)被发现可以通过靶向妊娠X受体(pregnane X receptor)来减少炎症和修复IBD患者的肠道损伤,为目前的治疗提供了一种更安全、更有效的替代方案。(A ginger compound, furanodienone (FDN), has been found to reduce inflammation and repair gut damage in IBD patients by targeting the pregnane X receptor, offering a safer and more effective alternative to current treatments.)
呋喃二烯酮(furanodienone)并非新发现的,据PubMed数据库记载,早在20世纪80年代初,德国联邦共和国维尔茨堡大学制药与化学研究所(Institut für Pharmazie und Lebensmittelchemie der Universität Würzburg, Federal Republik of Germany)的研究人员在研究“没药精油的成分(Constituents of the essential oil of myrrh)”一文中已经提及到呋喃二烯酮。详见:C H Brieskorn, P Noble. Constituents of the essential oil of myrrh (Article in German). Planta Med, 1982 Feb; 44(2): 87-90. DOI: 10.1055/s-2007-971408. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17402085/.但是,在1982-2025年之间,通过PubMed数据库检索到与呋喃二烯酮相关的文献仅有47条,具体的年度分布见图3所示。
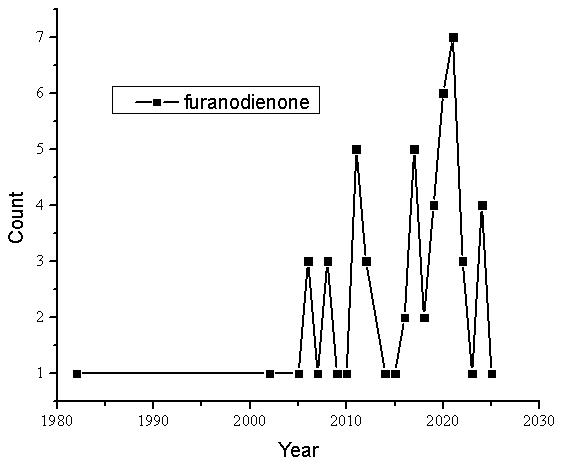
Fig. 3 Search query: Furanodienone, 1982-2025 (PubMed).
由图3可知,关于呋喃二烯酮的文献数量变化,20世纪80年代到21世纪初的20年间几乎没有变化,仅仅是有一两篇文献而已。进入21世纪之后,相关文献数量才有所增加,2020年有6篇,2021年有7篇,是目前的峰值。
由加拿大多伦多大学的科学家领导的一个国际研究小组已经在生姜中发现了一种化合物,即呋喃二烯酮(FDN),它可以选择性地结合并调节与炎症性肠病(inflammatory bowel disease 简称IBD)有关的核受体。
通过筛选生姜与IBD相关受体相互作用的化学成分,研究人员发现FDN与妊娠X受体(pregnane X receptor简称PXR)强烈结合。这种相互作用通过增强PXR抑制促炎细胞因子(pro-inflammatory cytokines)产生的能力,有助于减少结肠炎症。虽然FDN已经被发现了几十年,但其生物学功能和分子靶点至今仍不清楚。
多伦多大学唐纳利细胞和生物分子研究中心(U of T’s Donnelly Centre for Cellular and Biomolecular Research)的助理研究员刘家宝(Jiabao Liu音译)说:“我们发现,通过口服注射FDN,我们可以减少小鼠结肠的炎症。我们发现FDN的靶核受体突出了补充和结合医学治疗IBD的潜力。我们相信天然产物可能比合成化合物更精确地调节核受体,这可能会导致成本效益高且可广泛获得的替代疗法。”相关研究结果于2025年2月3日已经在《自然通讯》(Nature Communications)杂志发表——Xiaojuan Wang, Guohui Zhang, Zhiwei Bian, Vimanda Chow, Marina Grimaldi, Coralie Carivenc, Savannah Sirounian, Hao Li, Lucia Sladekova, Stefano Mott, Yulia Luperi, Yufeng Gong, Cait Costello, Linhao Li, Matthew Jachimowicz, Miao Guo, Shian Hu, Derek Wilson, Patrick Balaguer, William Bourguet, Sridhar Mani, Laura Bonati, Hui Peng, John March, Hongbing Wang, Shengpeng Wang, Henry M. Krause, Jiabao Liu. An abundant ginger compound furanodienone alleviates gut inflammation via the xenobiotic nuclear receptor PXR in mice. Nature Communications, 2025, 16: 1280. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-56624-0. Published: 03 February 2025.
参与此项研究的有来自中国兰州大学(School of Pharmacy, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, Gansu, People’s Republic of China)、中国澳门大学(State Key Laboratory of Quality Research in Chinese Medicine, Institute of Chinese Medical Sciences, University of Macau, Macau, People’s Republic of China)、加拿大多伦多的约克大学(Department of Chemistry, York University, Toronto, ON, Canada)、法国蒙彼利埃大学{Institut de Recherche en Cancérologie de Montpellier (IRCM), Université Montpellier, Institut régional du Cancer de Montpellier (ICM), Montpellier, France; Centre de Biologie Structurale, INSERM, CNRS, Université de Montpellier, Montpellier, France}、美国布朗克斯的艾伯特·爱因斯坦医学院(Department of Molecular Pharmacology; Department of Genetics; Department of Medicine, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY, USA)、捷克奥洛穆茨的帕拉基大学(Department of Cell Biology and Genetics, Faculty of Science, Palacky University, Olomouc, Czech Republic)、意大利米兰比科卡大学(Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, University of Milano-Bicocca, Milan, Italy)、加拿大多伦多大学(Department of Chemistry, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada; Donnelly Centre for Cellular and Biomolecular Research, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada; Department of Molecular Genetics, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada; School of the Environment, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada)、美国伊萨卡的康奈尔大学(Department of Biological and Environmental Engineering, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA)以及美国马里兰大学药学院(Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy, Baltimore, MD, USA)的研究人员。
IBD的影响和需要新的治疗方法(IBD’s Impact and the Need for New Treatments)
IBD患者通常在生命早期就开始出现症状;大约25%的患者在20岁之前被诊断出来。目前还没有治愈IBD的方法,因此患者必须坚持终身治疗来控制他们的症状,包括腹痛和腹泻,承受重大的心理和经济后果。
Fig. 4 Research Associate Jiabao Liu and Professor Henry Krause. Credit: University of Toronto
虽然炎症性肠病患者通过改变饮食和草药补充剂发现了一些缓解,但尚不清楚食物和补充剂中的哪些化学化合物负责减轻肠道炎症。随着FDN现在被确定为一种具有治疗IBD潜力的化合物,可以提取生姜的这种特定成分以开发更有效的治疗方法。
FDN的额外好处(Additional Benefits of FDN)
FDN的另一个好处是它可以增加紧密连接蛋白(tight junction proteins )的产生,这种蛋白可以修复由炎症引起的肠壁损伤。研究表明,FDN的作用仅限于结肠,防止对身体其他部位产生有害副作用。
核受体(Nuclear receptors)在体内充当各种分子的传感器,包括那些参与代谢和炎症的分子。
PXR特别在外来物质的代谢中起作用,如饮食毒素(dietary toxins)和药物。FDN和PXR之间的结合需要仔细调节,因为过度激活受体会导致体内其他药物和信号代谢物的代谢和效力增加。
FDN是一种相对较小的分子,仅填充PXR结合口袋(PXR binding pocket)的一部分。研究表明,这允许另一种化合物同时结合,从而以可控的方式增加结合的整体强度及其抗炎作用。
多伦多大学特默蒂医学院(U of T’s Temerty Faculty of Medicine)的首席研究员和分子遗传学(molecular genetics)教授亨利·克劳斯(Henry Krause)说:“在发达国家和发展中国家,被诊断为IBD的人数正在上升,因为人们转向了更多加工、高脂肪和高糖的饮食。从生姜中提取的天然产品是治疗IBD比目前治疗方法更好的选择,因为它不会抑制免疫系统或影响肝功能,这可能导致主要的副作用。FDN可以形成一种更有效的治疗的基础,同时也是更安全、更便宜的。”
这项研究得到了加拿大卫生研究院{Canadian Institutes of Health Research (PJT-186117) }、国家协同研究机构{Agence Nationale de la Recherche SYNERGY grant (ANR-23-CE34-0006)}、中国广东省重点区域研究开发计划{Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province, China grant (2020B1111110003)}、美国国立卫生研究院{National Institutes of Health grants (R01CA222469)}、中国国家自然科学基金{National Natural Science Foundation of China grant (82204227)}、加拿大自然科学与工程研究委员会{Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) Discovery grants (RGPIN480432, and CRDPJ597036); NSERC Research Tools and Instrument grants}、加拿大新前沿研究基金{New Frontiers in Research Fund grant (NRFRE-2019-00901)}、加拿大查尔斯H.贝斯特博士后奖学金(Charles H. Best Postdoctoral Fellowship)、加拿大精准医学倡议(PRiME)奖学金{Precision Medicine Initiative (PRiME) Fellowship}、捷克科学基金会{Czech Science Foundation (22-00355S)}、加拿大创新基金会(Canada Foundation for Innovation)、加拿大安大略省研究基金(Ontario Research Fund)以及法国国家研究机构{French National Research Agency (ANR-10-INBS-04-01 and ANR-10-INBS-05)}的支持或资助。
上述介绍仅供参考,欲了解更多信息敬请注意浏览原文和相关报道。
Anika Hazra. U of T researchers lead discovery of ginger compound with potential to treat inflammatory bowel disease. Feb 19, 2025.
The literature documenting the value of drug-like molecules found in natural products is vast. Although many dietary and herbal remedies have been found to be effective for treating intestinal inflammation, the identification of their active components has lagged behind. In this study, we find that a major ginger component, furanodienone (FDN), is a selective pregnane X receptor (PXR) ligand with agonistic transcriptional outcomes. We show that FDN binds within a sub-pocket of the PXR ligand binding domain (LBD), with subsequent alterations in LBD structure. Using male mice, we show that orally provided FDN has potent PXR-dependant anti-inflammatory outcomes that are colon-specific. Increased affinity and target gene activation in the presence of synergistically acting agonists indicates further opportunities for augmenting FDN activity, efficacy and safety. Collectively, these results support the translational potential of FDN as a therapeutic agent for the treatment and prevention of colonic diseases.
https://wap.sciencenet.cn/blog-212210-1474800.html
上一篇:CRISPR剪掉多余的染色体,为治疗唐氏综合症带来新希望
下一篇:不孕症研究:当姐妹细胞一起同归时

