 精选
精选
多胺(polyanines)简介
诸平
多胺(Polyamines简称PAs),如腐胺(putrescine简称PUT)、精胺(spermine简称SPE)和亚精胺(spermidine简称SPD),是有机多阳离子烷基胺(organic polycationic alkylamines),由L -鸟氨酸(L-ornithine)或氨基酸脱羧合成[1,2,3]。它们存在于所有活细胞中,哺乳动物细胞中含有一毫摩尔浓度的PAs [4]。1678年,安东尼·范·列文虎克(Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, born October 24, 1632, Delft, Netherlands—died August 26, 1723, Delft)首次在干精液中发现了SPE晶体,但在新鲜精液中没有发现。
安东尼·范·列文虎克是荷兰显微镜学家,他1632年10月24日在荷兰代尔夫特出生,1723年8月26日卒于荷兰代尔夫特,享年91岁。是第一位观察细菌和原生动物的荷兰显微镜学家。他对低等动物的研究驳斥了自然发生学说(doctrine of spontaneous generation),他的观察为细菌学(bacteriology)和原生动物学(protozoology)奠定了基础。
1791年,法国化学家尼古拉斯-路易斯·沃克兰(Nicolas-Louis Vauquelin, born May 16, 1763, Saint-André-d’Hébertot, France—died Nov. 14, 1829, Saint-André-d’Hébertot)鉴定出安东尼·范·列文虎克在干精液中发现的这些晶体是一种未知的磷酸盐衍生化合物[5]。此外,P. 施赖纳(von Ph. Schreiner)于1878年将SPE报道为一种碱性化合物,A. Ladenburg和 J. Abel于1888年将其命名为精胺[6,7]。十年后(1898年),Poehl建议使用SPE治疗几种疾病[8],最终在1924年,Rosenheim合成了SPE、SPD和PUT,从而奠定了现代PAs科学的基础[9]。此外,PUT在19世纪初在微生物中被发现,SPD在20世纪初被发现[10]。
1 不同多胺的结构(Structures of different polyamines)

Figure 1. Structures of different polyamines.
2 多胺的功能(Functions of PAs)
PAs的功能包括细胞分化(cell differentiation)、细胞增殖(cell proliferation)、基因调控(gene regulation)、细胞信号传导(cell signaling)和细胞凋亡(apoptosis)[4,18,39,40]。PAs还在翻译因子eIF5A的帮助下刺激翻译后修饰[41]。PAs与细胞分子广泛相互作用,并在体内发挥各种关键功能(Figure 2)。PAs的重要已知功能如下所述。

Figure 2 Biological functions related to polyamines
2.1 细胞增殖与分化(Cell Proliferation and Differentiation)
2.2 基因表达与调控(Gene Expression and Regulation)
2.3 转录、翻译和翻译后修饰(Hypusine和eIF5A){Transcription, Translation, and Post-Translation (Hypusine and eIF5A)}
2.4 离子通道的调控功能(Regulating the Function of Ion Channels)
2.4.1 向内整流钾通道Inward Rectifier Potassium (Kir) Channels
2.4.2 瞬时受体电位规范(TRPC)通道和连接蛋白{Transient Receptor Potential Canonical (TRPC) Channels and Connexins}
2.4.3 配体门控离子通道(Ligand-Gated Ion Channels)
2.5 免疫应答(Immune Response)
2.6 谷氨酰胺转胺酶的调节(Regulation of Transglutaminase)
3 人体多胺的代谢和转运途径(Metabolic and Transport Pathway of Polyamines in Humans)
哺乳动物体内PAs的稳态可以通过合成、分解代谢和转运三个步骤来理解。PAs在细胞质中产生。在体内,多胺的产生始于通过食物摄入氨基酸{精氨酸(Arg)、赖氨酸(Lys)和蛋氨酸(Met)},这些氨基酸通过微生物/酶的作用作为多胺合成的底物[2] (Figure 3).。
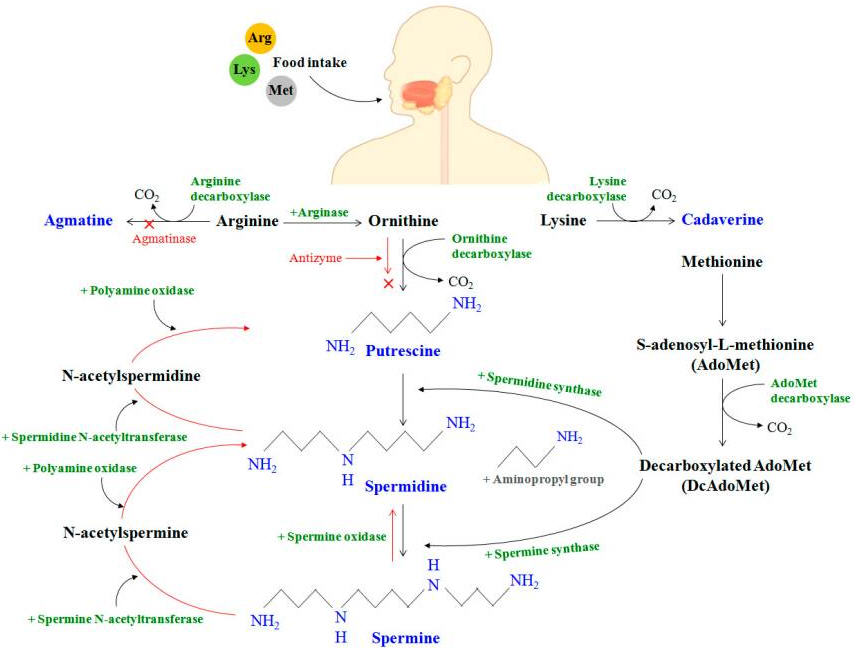
Figure 3 Polyamine synthesis (black/blue) and regulatory (red) pathways in the human gut after ingestion of amino acids: arginine (Arg), lysine (Lys), and methionine (Met).
4. 多胺在维持健康和预防疾病中的营养作用(Nutritional Roles of Polyamines in Health Maintenance and Disease Prevention)
4.1. Aging and Longevity
4.2. Stress
4.3. Memory
4.4. Cardioprotective Role
4.5. Cancer Prevention
4.6. Huntington’s Disease (HD)
4.7. Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease
5. 结论、当前问题和未来展望(Conclusions, Current Problems, and Future Perspectives)
PAs是由氨基酸脱羧合成的分子,在生物体的多种生理生化过程中起着重要作用。它们控制和调节各种重要的细胞和遗传功能,如细胞增殖、转录、翻译和翻译后修饰。据了解,PAs的功能取决于每种PA(即PUT、SPD和SPE)的细胞浓度。然而,需要进一步的研究来了解PAs在活细胞中的稳态,它促进了生物合成、分解代谢、偶联和相互转化的调节。此外,了解应激条件下生物活性PAs的细胞水平也很重要。膳食中PAs的摄入量表明,PAs的最佳摄入量对维持健康和控制各种疾病具有积极作用。此外,PAs减缓了衰老过程,延长了寿命。各种健康疾病也可以通过靶向代谢过程中的PAs来治愈。
另一方面,较高的PA水平会影响一些健康疾病,如压力、癌症和心血管疾病。一些研究显示,由于它们的集体使用,PA对不同疾病的影响是复杂的,这为未来的研究揭示每种PA (PUT、SPE和SPD)在衰老、癌症、记忆丧失和帕金森病中的作用和作用提供了空白。
此外,膳食摄入PAs显示了治疗各种健康疾病的另一种途径。因此,优化的饮食方法可以与临床应用一起用于预防致命疾病,以保持身体健康。如果对目标疾病进行严格监管,PAs可以成为解决各种健康问题的有力工具。作为一种未来的治疗工具,PAs及其类似物可能与纳米颗粒结合,形成靶向营养保健纳米药物。

Figure 4 Polyamine biosynthesis, degradation, and transmembrane transport.

Figure 5 Biological activities of polyamine and polyphenols.
References for A circled:[17,18,19,20,21,22,23,25,26,28,29,30,31];
References for B circled:[49,121,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134,135,136,137,138,139,140,141,142,143,144,145,146,147,148,149,150,151,152,153,154,155,156,157,158,159];
References for “?”:[22,25,26,27,28,30,31].
黑色文字表示物质名称,而亚精胺和精胺分别以绿色和蓝色显示。红色字母表示酶的名称。黑色实线箭头表示代谢途径,黑色虚线箭头表示上游物质的部分转移。粗灰色箭头表示靶上的活性,粗灰色t形条表示靶上的抑制活性。

Black text indicates the substance name, while spermidine and spermine are shown in green and blue, respectively. Red letters indicate enzyme names. The solid black arrows indicate the metabolic pathway, and the dashed black arrows indicate the transfer of some material from the upstream material. The thick gray arrow indicates activity on the target, and thick gray T-bar indicates the inhibitory activity on target.
ODC: Ornithine decarboxylase; SAM: S-adenosylmethionine; AdoMetDC: Adenosylmethionine decarboxylase; dcSAM: Decarboxylated S-adenosylmethionine; DNMT: DNA methyltransferase.
多胺摄入增加可提高血液精胺水平并抑制ODC活性。精胺浓度的增加强烈抑制AdoMetDC活性,导致SAM数量增加,dcSAM数量减少。由于SAM是DNA甲基化的甲基供体,而dcSAM抑制DNMT的活性,因此DNMT被激活。结果,整个基因组的异常甲基化增强和ITGAL的去甲基化增加被逆转和调节。

Increased polyamine intake elevates blood spermine levels and inhibits ODC activity. Increased spermine concentration strongly suppresses AdoMetDC activity, resulting in an increased amount of SAM and reduced amount of dcSAM. Since SAM is a methyl group donor for DNA methylation and dcSAM inhibits the activity of DNMTs, DNMTs are activated. As a result, enhanced aberrant methylation of entire genome and increased demethylation of ITGAL are reversed and regulated.
Black text indicates the substance name, while spermidine and spermine are shown in green and blue, respectively. Red letters indicate enzyme names. The solid black arrows indicate the metabolic pathway, and the dashed black arrows indicate the transfer of the methyl group from SAM. The brown arrows indicate the conditions of enzymatic activities (upward and downward arrows). Upward arrows indicate activation of the enzyme, and downward arrows indicate the inhibition of enzyme activity. Green arrows indicate the change in material quantity and enzymatic activity. The thick gray arrows indicate the stimulus given to the target by the upstream enzyme activity, and the thick gray T-bars indicate the inhibitory activities on the target.
The right figures show the condition and changes in DNA methylation status. The length of the line of black circles with bars indicates the progression of demethylation and hyper-methylation. The upward line indicates the progression of demethylation, and the downward lines indicate the progression of hyper-methylation.
ODC: ornithine decarboxylase; SSAT: Spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase; APAO: N1-acetylpolyamine oxidase; SAM: S-adenosylmethionine; AdoMetDC: Adenosylmethionine decarboxylase; dcSAM: Decarboxylated S-adenosylmethionine; DNMT: DNA methyltransferase; ITGAL: gene promoter area that is responsible for the LFA-1 expression.
多胺在癌症进展中的作用是众所周知的。多胺加速肿瘤生长,促进转移扩散[69]。然而,在不存在致癌因素的正常细胞(导致致癌的遗传异常、暴露于先前致癌物和致癌刺激物等)中,多胺是否作为致癌的引发剂存在争议。有几份报告表明,在健康个体中,多胺摄入量的增加不会增加致癌,而是对致癌有抑制作用[53,265,266]。在之前的评论中已经讨论过这些问题[267]。
[267] Kuniyasu Soda. Polyamine Metabolism and Gene Methylation in Conjunction with One-Carbon Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018; 19: 3106. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103106. [PMC free article]

Figure 8 Bioactivities and mechanism of polyamines contributing to healthy long life.
The mechanism by which increased polyamine intake inhibits onset or progression of aging-associated diseases and senescence. Increased polyamine intake elevates blood spermine levels in humans, in spite the fact that many foods contain spermidine much more than spermine. Polyamine binds to the cell membrane, proteins, and genes by electric charge. Polyamine (spermine and spermidine) protects cells and genes from harmful stimuli indicated in red. Spermine inhibits aberrant DNA methylation and regulates DNA methylation status. These biological activities contribute to a healthy longevity.
增加多胺摄入,有益于健康长寿(Fig. 8)!
上述介绍,仅供参考,欲了解更多信息请注意浏览原文。
转载本文请联系原作者获取授权,同时请注明本文来自诸平科学网博客。
链接地址:https://wap.sciencenet.cn/blog-212210-1469387.html?mobile=1
收藏

