博文
Phenomics | 《表型组学(英文)》2025 年第三期文章合集
|
本文介绍了Phenomics期刊2025年第三期收录文章合集,文章概览如下,请查收!

(Phenomics期刊2025年第三期封面图)
1
MVPCR: Multiplex Visual Detection Strategy Based on Ultrafast PCR for Point-of-Care Pathogens Detection Within 10 Min

扫描二维码 | 下载PDF原文
论文DOI链接:
https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-024-00216-3
论文引用格式:
Zhang, Z., Wu, C., Bai, L. et al. MVPCR: Multiplex Visual Detection Strategy Based on Ultrafast PCR for Point-of-Care Pathogens Detection Within 10 Min. Phenomics 5, 239–251 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-024-00216-3
Abstract
Pathogens pose significant threats to biosecurity and environmental health due to their potential for widespread outbreaks. Effective pathogen detection requires methods that are rapid, sensitive, specific, and informative. Here, we proposed a multiplex visual detection system that integrated ultrafast polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and molecular beacons, allowing the simultaneous detection of three pathogens in a one-pot reaction. The ultrafast PCR protocol employed cycles of just 7 s each, allowing the entire process-from sampling to result-to be completed within only 10 min. Molecular beacons hybridized with target sequences during ultrafast PCR, generating fluorescence signals that are visually detectable without specialized equipment. Additionally, we developed a compact, portable cartridge integrated with online software for fluorescence visualization and direct result output, eliminating the need for bulky instruments and specialized personnel, thereby facilitating point-of-care testing (POCT). The method demonstrated high specificity and sensitivity, with a limit of detection (LOD) as low as 23 copies per reaction. It achieved a 100% positive detection rate in practical applications, performing comparably to standard PCR. Furthermore, the method effectively identified low concentrations of pathogens in animal infection samples. This ultrafast, highly sensitive, specific, and informative method shows significant potential for POCT applications, including food safety monitoring and clinical diagnostics.
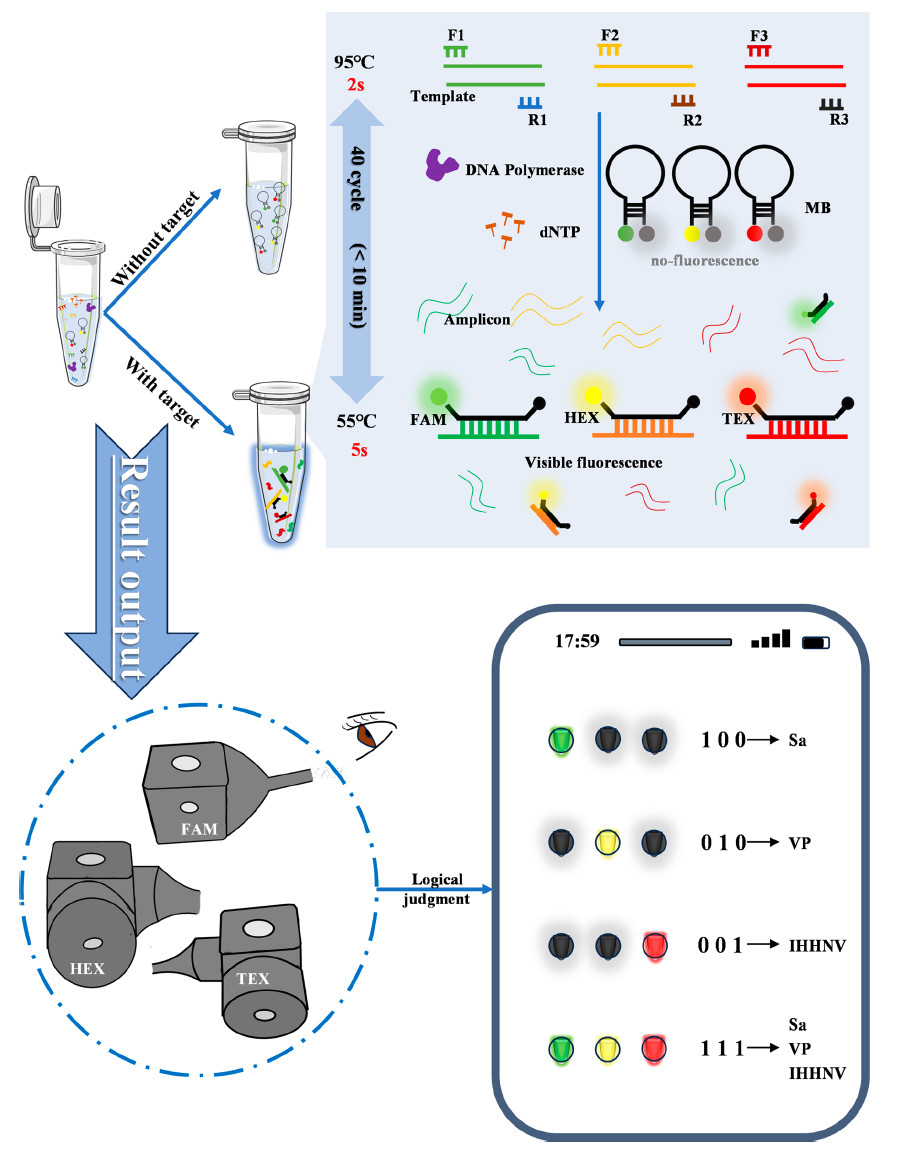
The schematic diagram of the multiplex visual detection strategy based on MVPCR
2
Cell Function Experiments and Bioinformatics Analysis Jointly Revealed the Antineoplastic Effect of Lumican on Hepatocellular Carcinoma

扫描二维码 | 下载PDF原文
论文DOI链接:
https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-024-00182-w
论文引用格式:
Zhou, X., Xing, Z., Dong, R. et al. Cell Function Experiments and Bioinformatics Analysis Jointly Revealed the Antineoplastic Effect of Lumican on Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Phenomics 5, 252–269 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-024-00182-w
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common cancers worldwide, and immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI)-based therapies are now an integral part of systemic treatment. In this study, we identify potential biomarker for HCC and further investigate its functional significance using both bioinformatic and experimental methods. Differential analysis and weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) were conducted, identifying lumican (LUM) as the target gene. Our results showed a significant downregulation of LUM in HCC. LUM expression was also associated with the progression-free interval and the infiltration of B cells, neutrophils, and myeloid dendritic cells. Enrichment analysis highlighted the involvement of LUM in focal adhesion and the extracellular matrix. In addition, overexpression of LUM suppressed proliferation, migration and invasion in hepatoma cell lines while promoting cell apoptosis. Our results demonstrate the importance of LUM in HCC development and may help to elucidate the underlying mechanisms and biological processes influenced by LUM.
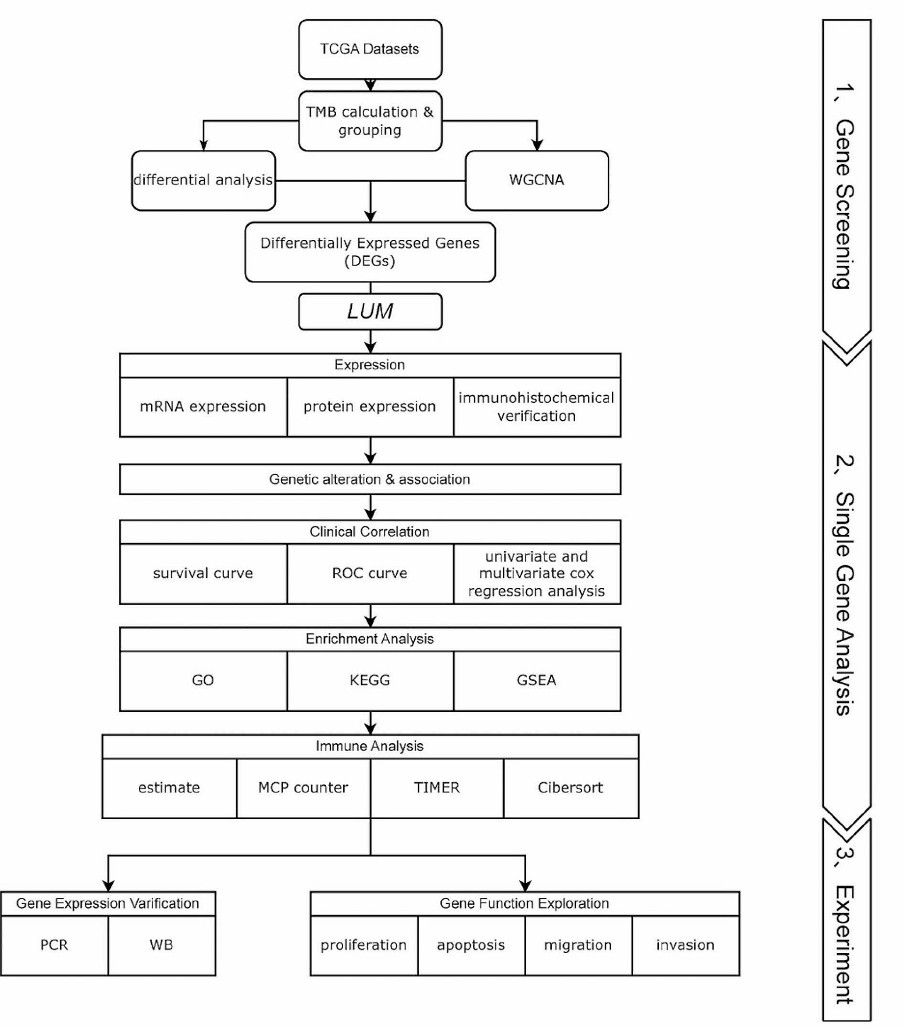
Flowchart for this work, divided into three parts: (1) gene screening, (2) single gene analysis, (3) experiment
3
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Risk of Common Cancer: Mendelian Randomization Interrogation of Causality and Mediation

扫描二维码 | 下载PDF原文
论文DOI链接:
https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-024-00159-9
论文引用格式:
Tan, X., Liu, G., Li, X. et al. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Risk of Common Cancer: Mendelian Randomization Interrogation of Causality and Mediation. Phenomics 5, 270–283 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-024-00159-9
Abstract
Compared with the well-documented inverse comorbidity of common neurodegenerative diseases with some types of cancer, the association of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) with cancer was obscure. This Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis was aimed to appraise the causal relationship of ALS with cancer. Leveraging summary statistics of genome-wide association study (GWAS) for ALS, overall-cancer and nine types of site-specific common solid cancer including colorectal cancer (CRC) in populations of European (discovery and replication) and East Asian ancestry, we investigated the causal association of ALS with cancer using inverse-variance weighted (IVW) method and complementary sensitivity analyses. We performed MR-based mediation analysis to assess possible role of serum lipid traits such as hyperlipidemia, one shared risk factor of ALS and CRC, in their causal association. We found that genetically-predicted ALS was not associated with overall-cancer and other tested types of cancer, but was causally associated with reduced risk of CRC [odds ratio (OR) 0.84; 95% confidence interval (95% CI) 0.74–0.96; p = 0.011, OR 0.32; 95% CI 0.15–0.69; p = 0.004, in datasets of European (discovery) and East Asian ancestry respectively]. We observed absences of directional pleiotropy (MR Egger, intercept = −0.02 and −0.02, p = 0.49 and 0.60), instrumental outlier (MR-PRESSO, p = 0.95 and 0.84) or heterogeneity (Cochran Q, p = 0.95 and 0.82). Null reverse causality of CRC with ALS was found in either datasets. However, we found no evidence of the inverse association of ALS with CRC in either the replication (OR 0.99; 95% CI 0.93–1.06) or the combined European datasets (OR 0.92; 95% CI 0.79–1.09). Mediation analysis in European datasets suggested that hyperlipidemia may affect the risk of CRC via ALS in an indirect manner, with the measured mediation effect of hyperlipidemia on CRC being −0.02 (95% CI −0.04 to −0.002, p = 0.03). Our two-sample MR study in trans-ethnic populations uncovered that genetically proxied ALS may be causally associated with reduced risk of CRC, providing new insight into the inverse comorbidity and etiological causality of neurodegenerative disease and cancer.
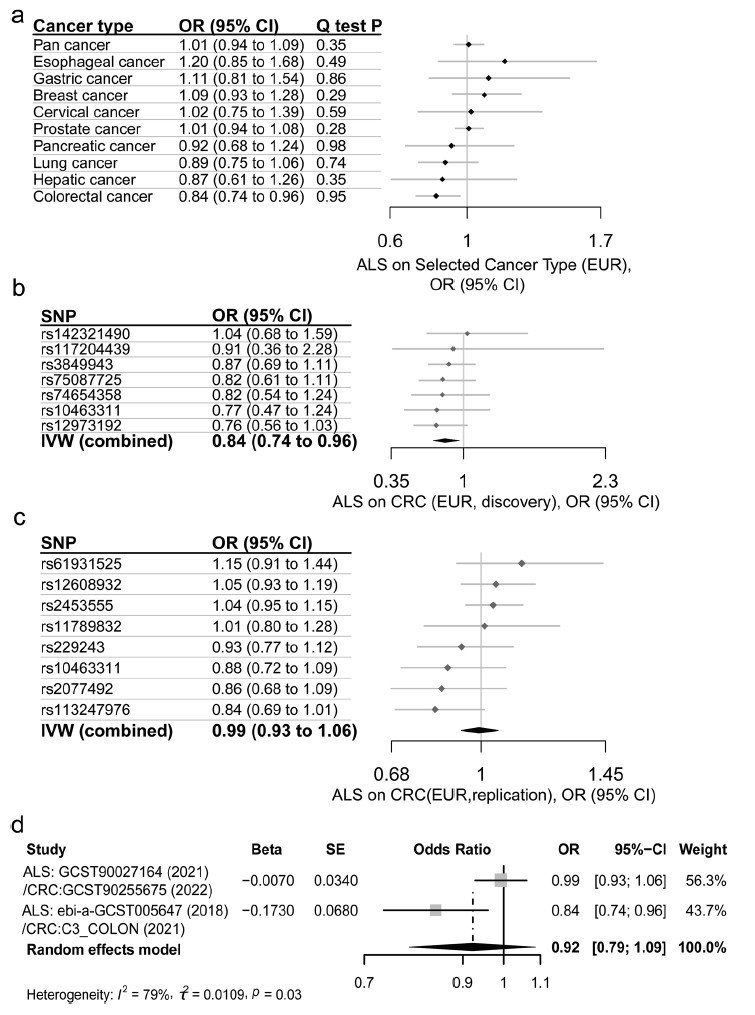
Graphical Abstract
4
Identification of a Novel Pyroptosis-Related lncRNAs Prognosis Model and Subtypes in Ovarian Cancer

扫描二维码 | 下载PDF原文
论文DOI链接:
https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-024-00173-x
论文引用格式:
Xie, Xf., Hu, Xq., Liu, Dx. et al. Identification of a Novel Pyroptosis-Related lncRNAs Prognosis Model and Subtypes in Ovarian Cancer. Phenomics 5, 284–300 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-024-00173-x
Abstract
Ovarian cancer (OC), a predominant gynecological malignancy, has consistently showcased grim prognostic outcomes. This investigation delves into the emerging field of pyroptosis and the intricacies of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), specifically the lesser-studied pyroptosis-related lncRNAs (PRlncRNAs), and their roles in OC prognosis. By harnessing transcriptome, and clinic data from the genotype-tissue expression (GTEx) and the cancer genome Atlas (TCGA), we formulated a unique PRlncRNAs risk model consisting of five prognostic lncRNAs by Cox regression and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression. Next, the Kaplan-Meier analysis, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, nomogram, and calibration were implemented to verify and evaluate the model. The model also showed general applicability in pan-cancer analysis. Remarkably, our model, upon rigorous validation, outperformed 16 pre-existing counterparts, offering a promising avenue for prognosis prediction. The risk score was used to classify patients into high and low-risk subgroups. The low-risk group showed improved overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS). The risk score was proved to be an independent prognosis factor. The low-risk group patients also exhibited a higher immune infiltration score and homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) score. Moreover, consensus clustering analysis was utilized to categorize OC patients into three distinct groups, predicated on the expression of the five prognostic lncRNAs. Patients within the third cluster exhibited noteworthy traits, encompassing elevated survival, heightened immune checkpoint expression, and the HRD score. Finally, the expressions of five PRlncRNAs were validated by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) in OC cell lines and tissues. In conclusion, the risk model based on the five PRlncRNAs might function as prognostic biomarkers to predict the immune and target drug treatment in OC.
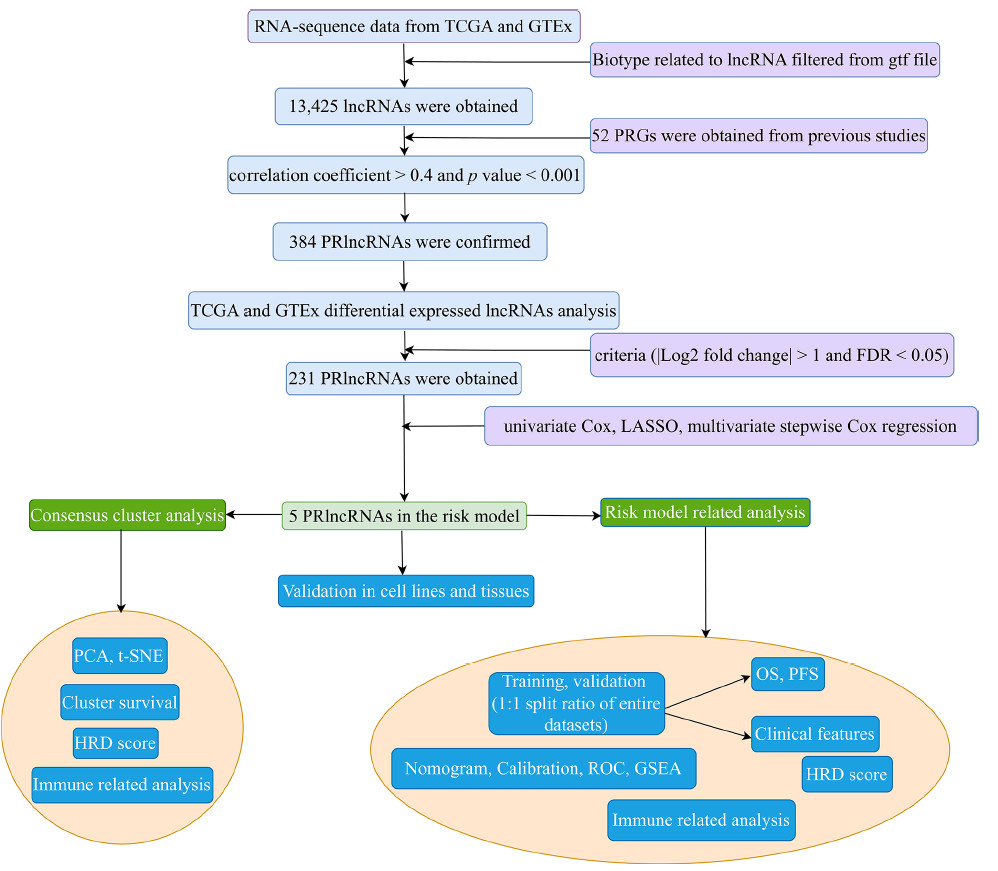
The flow diagram of the study
5
Cohort Profile: Precision Environmental Health Cohort of Healthy Undergraduates

扫描二维码 | 下载PDF原文
论文DOI链接:
https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-024-00215-4
论文引用格式:
Li, Y., Mei, Y., Zhao, J. et al. Cohort Profile: Precision Environmental Health Cohort of Healthy Undergraduates. Phenomics 5, 301–310 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-024-00215-4
Summary
Compared to similar studies, our project involved continuous monitoring over a longer period, with a relatively large sample size and total number of urine samples. Third, biological samples except first morning urine, such as 24-h urine, blood and hair, were not available because these samples are complicated to perform in a consecutive repeated-measures study design and might reduce compliance. Thus, it limited our ability to compare environmental chemicals levels across different matrixes. Moreover, this study is the lack of consideration for epigenetic factors, such as DNA methylation or histone modifications, as well as genotype that could influence the results. Future research should consider incorporating epigenetic analyses to better understand the role of prior environmental and dietary exposures in shaping participant responses. Another limitation of this study is the potential impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on participants' behavior and mental health due to strict lockdown policies, which may have influenced environmental exposures and lifestyle factors such as diet and physical activity. However, we have not provided an in-depth analysis of these effects in our study. Instead, we have primarily focused on describing the methods used to collect data on physical activity, diet, and mental health scales. These effects can be analyzed in detail for comparison in future studies.
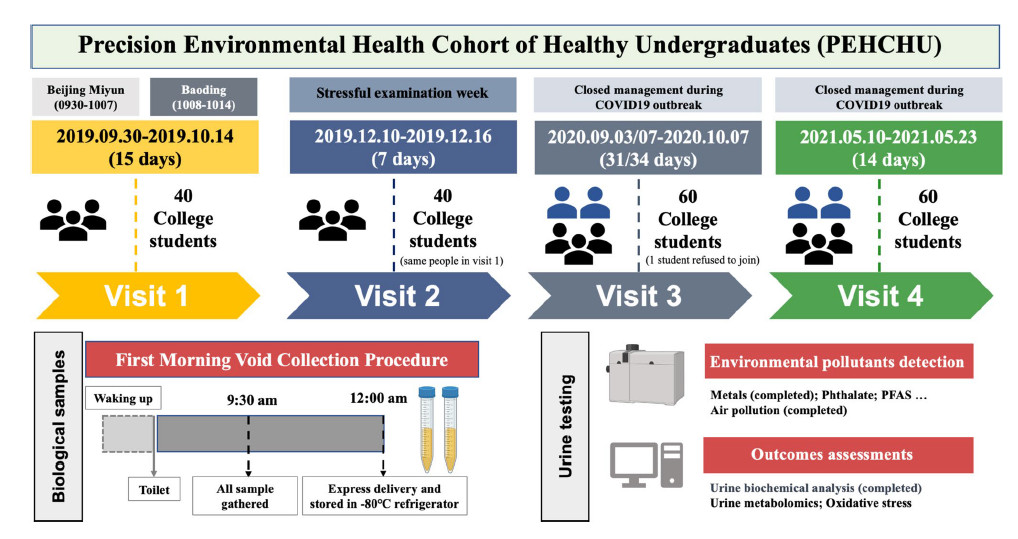
Study design of PEHCHU project
6
Multi-omics Quality Assessment in Personalized Medicine Through European Infrastructure for Translational Medicine (EATRIS): An Overview

扫描二维码 | 下载PDF原文
论文DOI链接:
https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-024-00170-0
论文引用格式:
EATRIS-Plus Multi-omics working group and Stakeholders. Multi-omics Quality Assessment in Personalized Medicine Through European Infrastructure for Translational Medicine (EATRIS): An Overview. Phenomics 5, 311–325 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-024-00170-0
Abstract
Molecular characterization of a biological sample, e.g., with omics approaches, is fundamental for the development and implementation of personalized and precision medicine approaches. In this context, quality assessment is one of the most critical aspects. Accurate performance and interpretation of omics techniques is based on consensus, harmonization, and standardization of protocols, procedures, data analysis and reference values and materials. EATRIS, the European Infrastructure for Translational Medicine (www.EATRIS.eu), brings together resources and services to support researchers in developing their biomedical discoveries into novel translational tools and interventions for better health outcomes. Here we describe the efforts within the Horizon 2020 EATRIS-Plus project and activities of member facilities of EATRIS towards quality assessment of pre-clinical sample processing, clinical omics data generation, multi-omics data integration, and dissemination of the resources in a Multi-Omics Toolbox, which is the principal deliverable of the EATRIS-Plus project for the consolidation of EATRIS towards translational medicine.
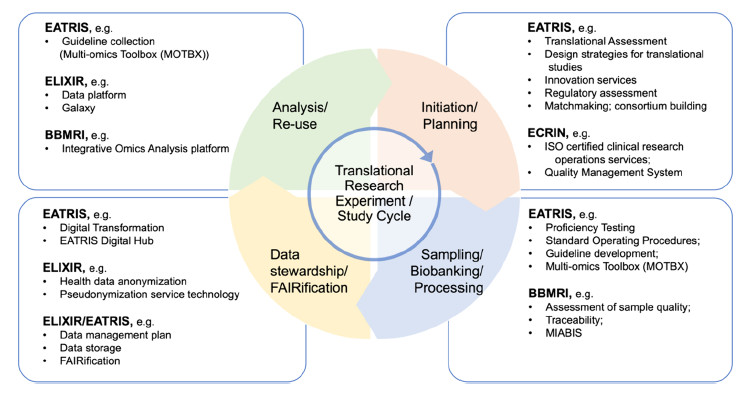
The translational biomedical process and involvement of selected biomedical Research Infrastructures (RIs) as stakeholders in quality assessment
7
The Impact of Lipase H Deficiency on Gut Aging and Lifespan in Drosophila

扫描二维码 | 下载PDF原文
论文DOI链接:
https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-025-00226-9
论文引用格式:
Nisar, A., Khan, S. & He, Y. The Impact of Lipase H Deficiency on Gut Aging and Lifespan in Drosophila. Phenomics 5, 326–329 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-025-00226-9
Summary
In conclusion, the study by Sun et al. (2024) advances our understanding of gut aging by identifying CG6295/Liph as a novel regulator of gut health and lifespan. As our population continues to age, such insights will be invaluable in developing strategies to enhance the quality of life for the elderly. The research highlights the crucial role of lipid metabolism and inflammation in gut aging, providing potential targets for therapeutic interventions. While the findings are promising, further research is needed to validate these results in mammalian models and explore additional therapeutic strategies. Overall, this study contributes to the growing body of knowledge on gut aging and offers new directions for future research aimed at improving gut health and longevity.
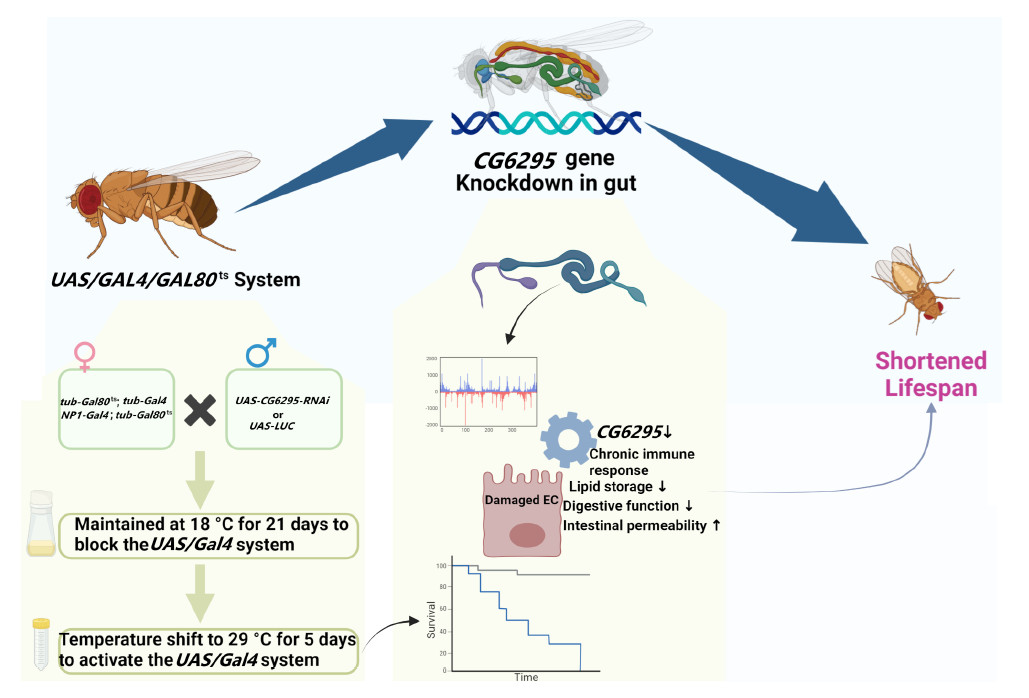
Schematic of the study. RNAi model was developed to knockdown the CG6295 gene, followed by survival curve estimation and RNA-Seq analysis
8
Links Between Psychiatric Disorders and Cardiovascular Diseases

扫描二维码 | 下载PDF原文
论文DOI链接:
https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-024-00217-2
论文引用格式:
Dai, M., Wang, Q. Links Between Psychiatric Disorders and Cardiovascular Diseases. Phenomics 5, 330–332 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-024-00217-2
Summary
Psychiatric disorders are associated with a substantially increased risk of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), with both behavioral and biological mechanisms contributing to this link. Using UK Biobank data, Han et al. (2024) examined over 44,000 patients with anxiety, depression, or stress-related disorders and matched controls, incorporating family history and polygenic risk scores (PRS) for CVD. During a mean follow-up of 12 years, patients with psychiatric disorders had a higher risk of CVD (HR 1.19), particularly in the first six months (HR 1.72), independent of genetic susceptibility or familial factors. Trajectory analysis identified primary hypertension, acute myocardial infarction, and stroke as key initial CVDs directly linked to psychiatric disorders. These findings emphasize that psychiatric disorders confer an independent risk for CVDs, highlighting the importance of early surveillance and intervention. Future studies should extend to severe mental and neurodevelopmental disorders to validate and expand these results.
9
A Simpler, More Convenient and More Comfortable Approach for Treating Multiple Keratinocytic Carcinoma

扫描二维码 | 下载PDF原文
论文DOI链接:
https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-025-00220-1
论文引用格式:
Jiang, Z., Liu, X., Peng, L. et al. A Simpler, More Convenient and More Comfortable Approach for Treating Multiple Keratinocytic Carcinoma. Phenomics 5, 333–337 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-025-00220-1
Summary
Collectively, in situ surgery combined with photodynamic therapy may be considered a potential treatment for multiple keratinocytic carcinoma. Meanwhile, the elevation of MMP-2 expression as well as cell ferroptosis inhibition in the lesions may predict recurrence after in situ surgery combined with PDT for multiple KCs patients.
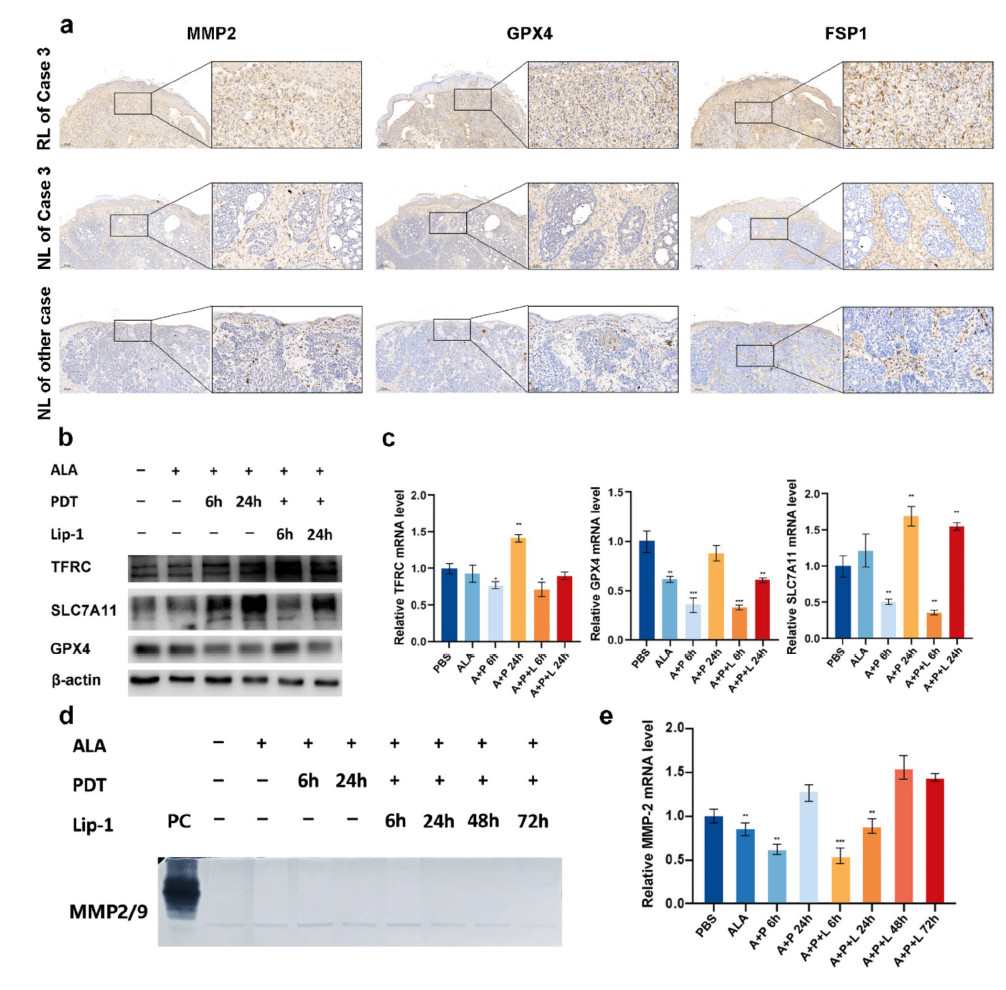
MMP-2 and ferroptosis-associated proteins as biomarker indicated the recurrence of multiple KCs patients after PDT treatment and PDT-induced ferroptosis and regulated the activity and expression of MMP2 in SCC A431 cells
10
Baseline Plasma GPX3 Level Predicts Efficacy of Insulin-Sensitization Drug Chiglitazar in Type 2 Diabetes

扫描二维码 | 下载PDF原文
论文DOI链接:
https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-025-00266-1
论文引用格式:
Cao, Z., Chen, H., Chen, Q. et al. Baseline Plasma GPX3 Level Predicts Efficacy of Insulin-Sensitization Drug Chiglitazar in Type 2 Diabetes. Phenomics 5, 338–342 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-025-00266-1
Summary
Together, our findings highlight GPX3 as a promising biomarker for treatment stratification in T2D, and lay the groundwork for its future clinical validation and implementation in personalized therapy.
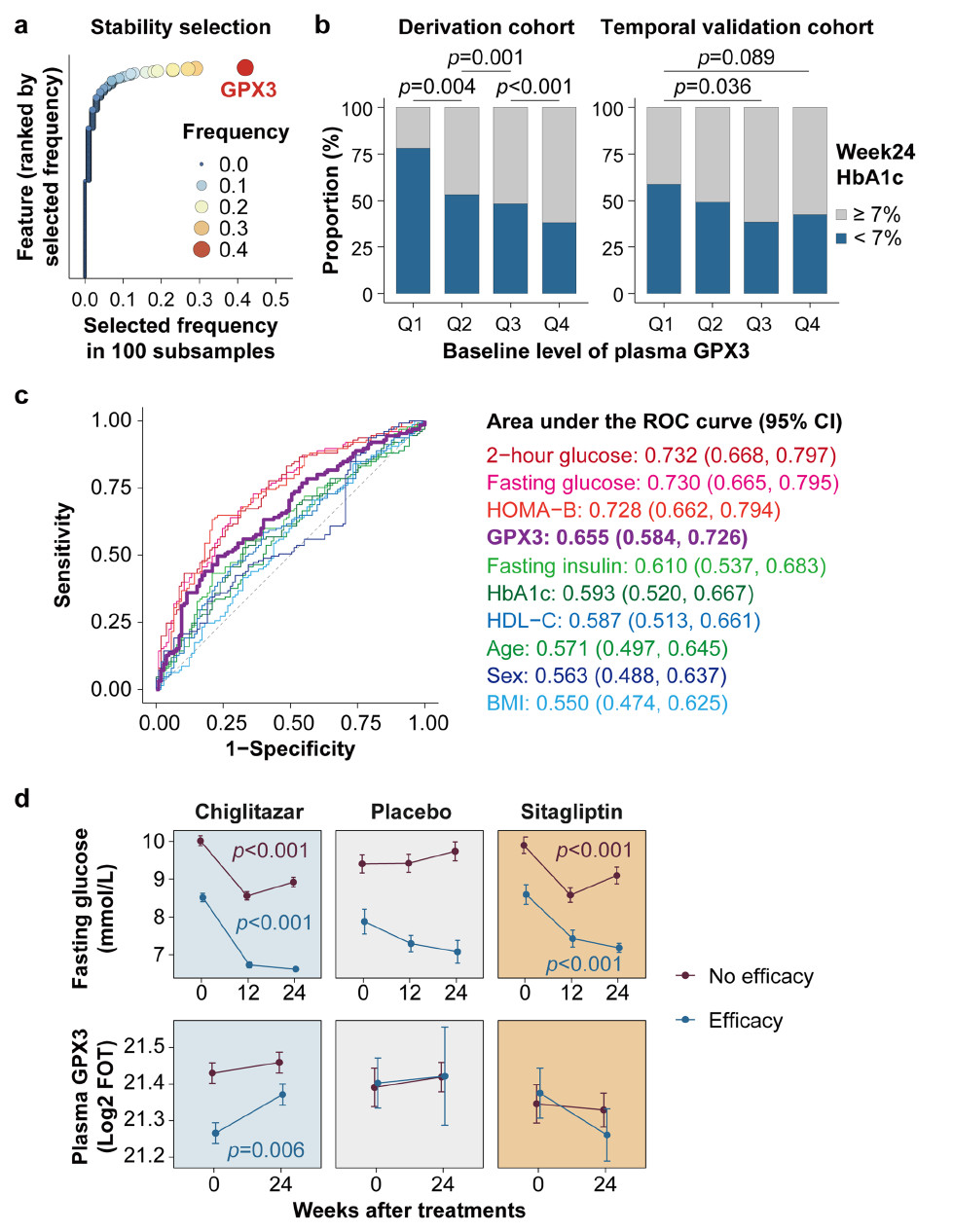
Baseline Plasma GPX3 Level Predicts Efficacy of Insulin-Sensitization Drug Chiglitazar in Type 2 Diabetes.
11
Metabolomics for the Identification of Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis

扫描二维码 | 下载PDF原文
论文DOI链接:
https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-025-00242-9
论文引用格式:
Pandey, S. Metabolomics for the Identification of Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Phenomics 5, 343–345 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-025-00242-9
Summary
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease lacking specific and reliable diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers. Conventional markers such as ACPA and RF are limited in sensitivity and specificity, particularly in seronegative patients. Metabolomics, enabled by MS, LC, and NMR, offers comprehensive metabolic profiling to uncover alterations in amino acids, lipids, and primary metabolites associated with RA onset, progression, and drug response. Studies show that methotrexate partially restores lipid metabolism, while Janus kinase inhibitors elevate anti-inflammatory fatty acids, highlighting metabolomics as a tool for monitoring treatment efficacy. Integration of metabolomics with other omics approaches holds promise for biomarker discovery, improved disease understanding, and precision medicine in RA.
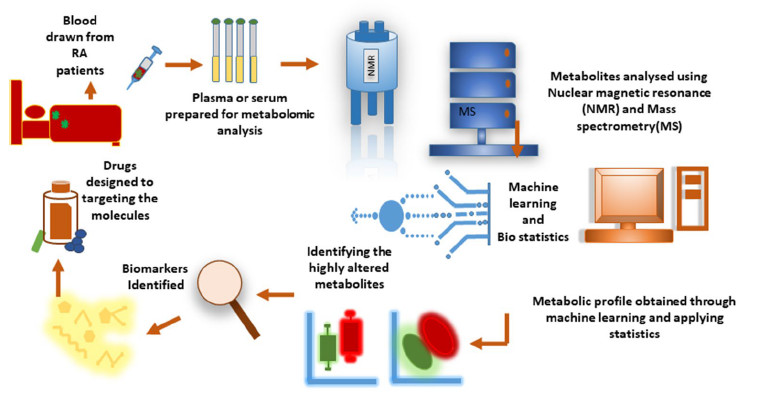
Overview of metabolomics workflow in rheumatoid arthritis
https://wap.sciencenet.cn/blog-3558836-1501547.html
上一篇:Phenomics | 中南大学湘雅医院吴丽莎教授团队揭示原位手术联合光动力治疗非黑色素瘤性皮肤肿瘤的潜力
下一篇:Phenomics | 首都医科大学附属北京友谊医院田丹教授团队构建小鼠肠道非经典T细胞高维流式检测体系
全部作者的其他最新博文
- • Phenomics | 中山大学肿瘤防治中心曾木圣院士团队发表综述:肿瘤诊疗新靶点,整合素α6靶向技术引领精准医疗新时代
- • Phenomics | 上海交通大学医学院张孝勇教授团队开发磁共振成像降噪新方法,有潜力改善脑小血管病的诊断效能
- • Phenomics | 复旦大学倪挺教授团队揭示基因内含子多聚腺苷酸化调控细胞衰老新机制
- • Phenomics | 加拿大阿尔伯塔大学和复旦大学联合开发基于文本、音频和视频的多模态抑郁症检测与评估方法
- • Phenomics | 翟振国/蒋太交/张鹏团队合作开发自适应多基因风险评估模型提升汉族人群静脉血栓栓塞症的风险预测能力
- • 祝贺 | 《表型组学(英文)》成功入选2025年“中国科技核心期刊”