博文
Phenomics | 首都医科大学附属北京友谊医院田丹教授团队构建小鼠肠道非经典T细胞高维流式检测体系
|
近日,《表型组学(英文)》(Phenomics)在线发表了首都医科大学附属北京友谊医院田丹教授团队题为“Immunophenotyping of Mouse Colonic Unconventional T cells by Mapping Cell Phenomics with 22-Color Flow Cytometry Assays”的研究文章。
该团队通过开发22色高维流式方案,系统描绘了小鼠肠道γδT、NKT和DNT等非典型T细胞亚群的免疫表型、增殖、细胞毒性及免疫检查点表达,揭示了上皮内与固有层细胞功能异质性,为肠道炎症机制与靶向治疗提供有价值的见解。
文末点击“阅读原文”可在线阅读文章。

扫描二维码 | 下载PDF原文
论文DOI链接:
https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-025-00237-6
论文引用格式:
Pan, L., Shen, C., Huang, S. et al. Immunophenotyping of Mouse Colonic Unconventional T Cells by Mapping Cell Phenomics With 22-Color Flow Cytometry Assays. Phenomics (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-025-00237-6
研究背景
肠道黏膜免疫系统在维持机体健康中扮演着守卫者的角色,既要耐受共生微生物,又要有效抵御病原体入侵。这一平衡一旦被打破,便可能引发炎症性肠病(Inflammatory bowel disease, IBD)等多种胃肠道疾病。非典型T细胞,如γδT细胞、NKT细胞、MAIT细胞和DNT细胞,是肠道黏膜免疫的关键成员,它们分布在上皮层和固有层,通过分泌细胞因子和直接细胞作用参与免疫调节与屏障维护。然而,受限于技术手段,这些细胞在肠道中的具体组成和功能状态仍不明确。
研究结果
1,22色流式细胞术方案建立
本研究首次开发并优化了一套适用于小鼠结肠组织的22色流式细胞术检测方案,涵盖T细胞分型、活化状态、增殖、细胞因子和免疫检查点分子等多个维度,显著提升了对非典型T细胞的解析能力。通过梯度浓度滴定,确定每个通道所用抗体最佳使用浓度。
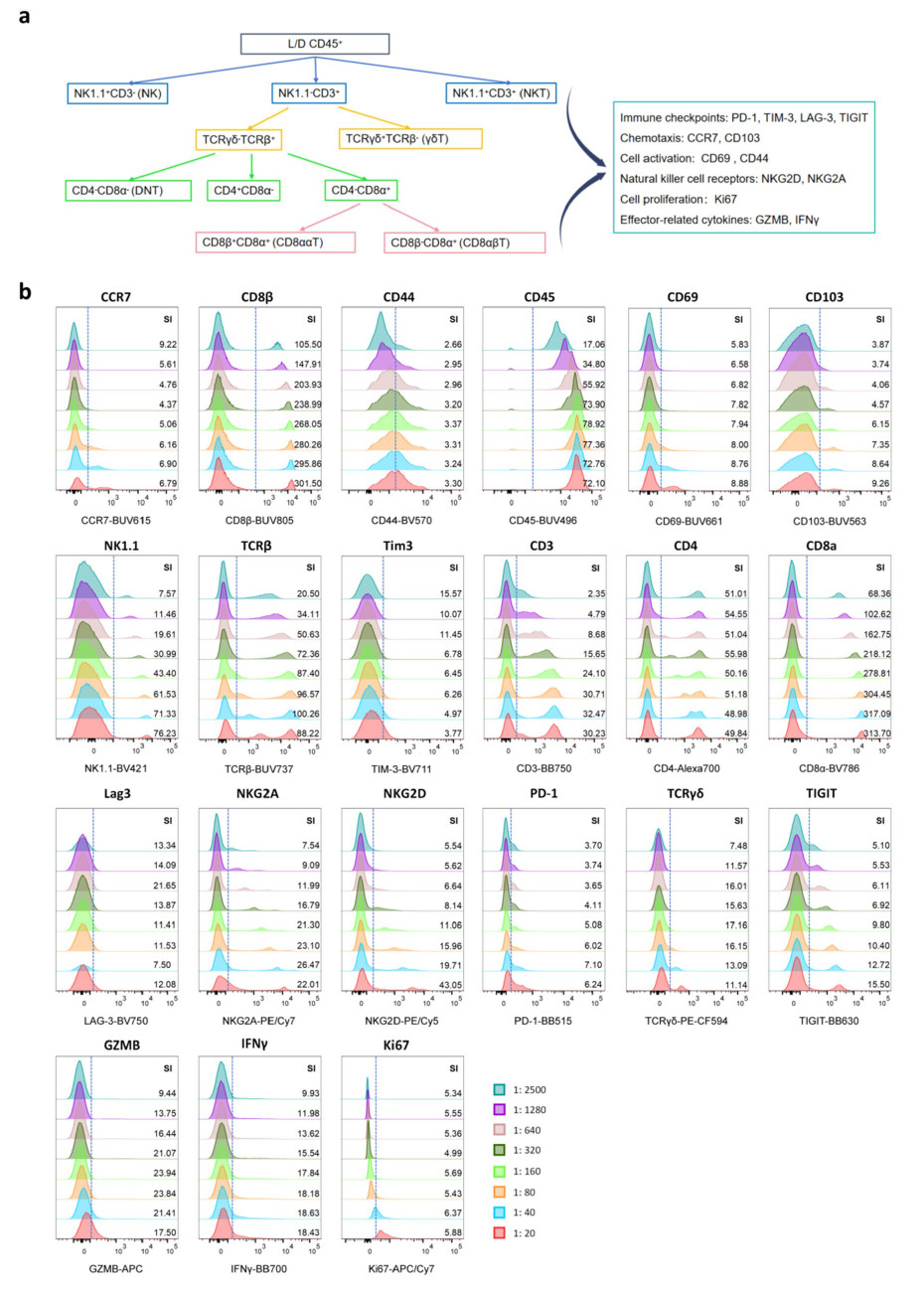
图1 高维流式细胞术染色方案
2,圈门策略
使用CD3、TCRβ、TCRγδ、NK1.1等鉴定多种T细胞亚群(CD4+、CD8αα+、CD8αβ+、γδT、NKT、DNT)。通过上皮内淋巴细胞(IELs)和固有层淋巴细胞(LPLs)之间的比较分析揭示了细胞组成和比例的差异。
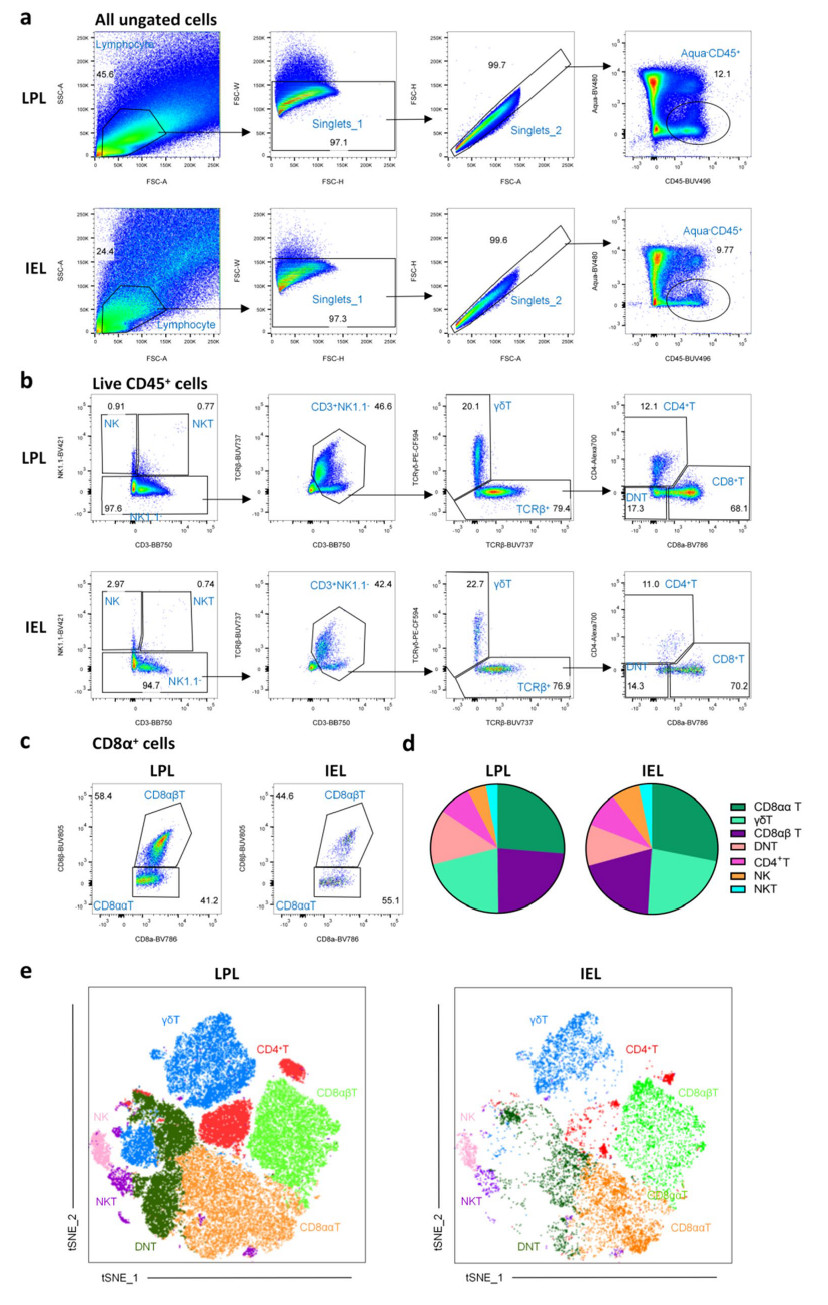
图2 小鼠肠道淋巴细胞的门控策略
3,上皮层与固有层淋巴细胞表型差异显著
研究发现,上皮内淋巴细胞(IELs)与固有层淋巴细胞(LPLs)在多个功能标志物表达上存在明显差异。IELs中非经典T细胞普遍高表达PD-1、TIM-3、LAG-3和TIGIT等免疫检查点分子,提示该区域免疫调节更为活跃,可能有助于控制局部炎症反应。
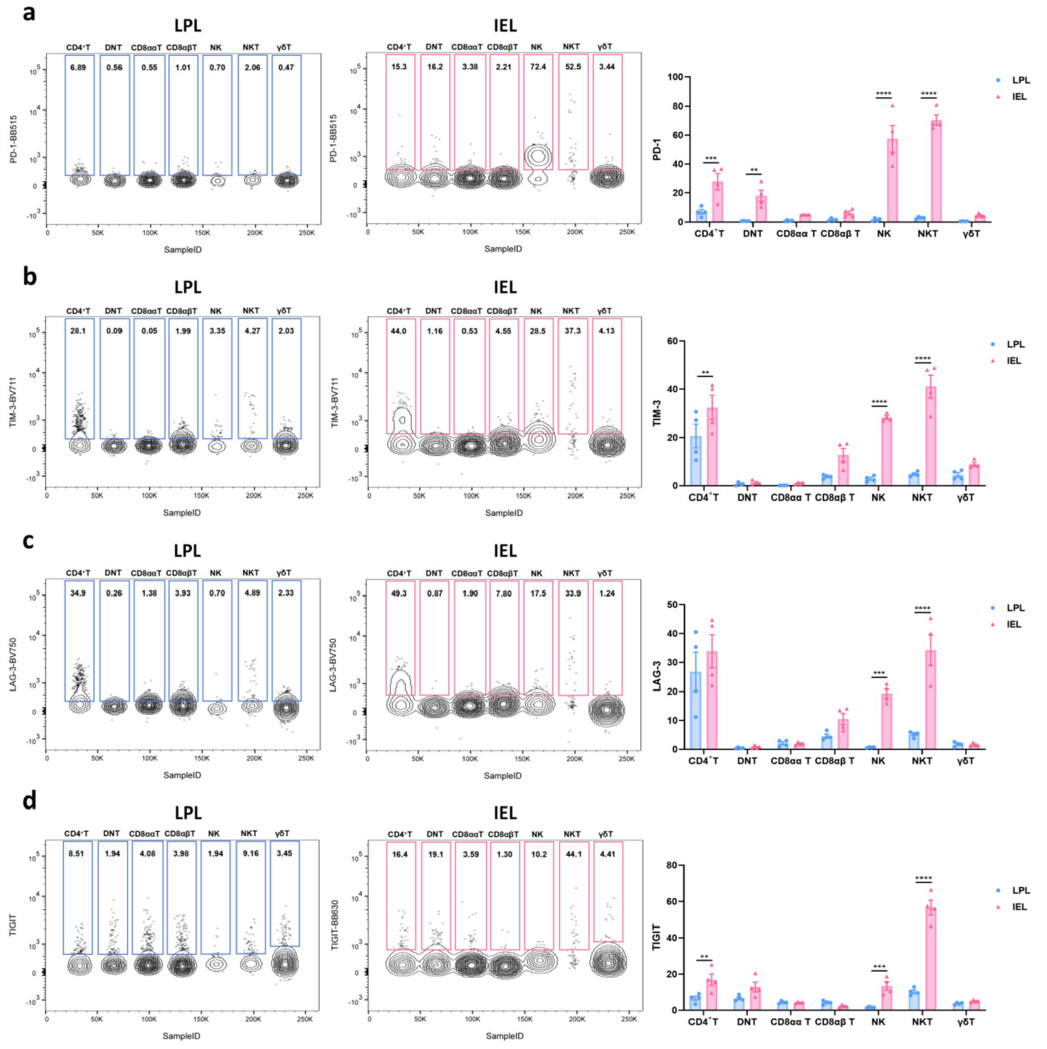
图3 小鼠肠道淋巴细胞表面免疫检查点分子的表达水平
4,细胞增殖与效应功能具区域特异性
IELs中多个细胞群体(如DNT、NKT、NK细胞等)增殖标志物Ki-67表达升高,显示其处于高度活化状态。此外,细胞毒性分子Granzyme B主要由CD8αβ⁺ T和γδ T细胞产生,而IFN-γ则主要在NK和NKT细胞中高表达,说明不同细胞类型在肠道免疫中职能分工明确。
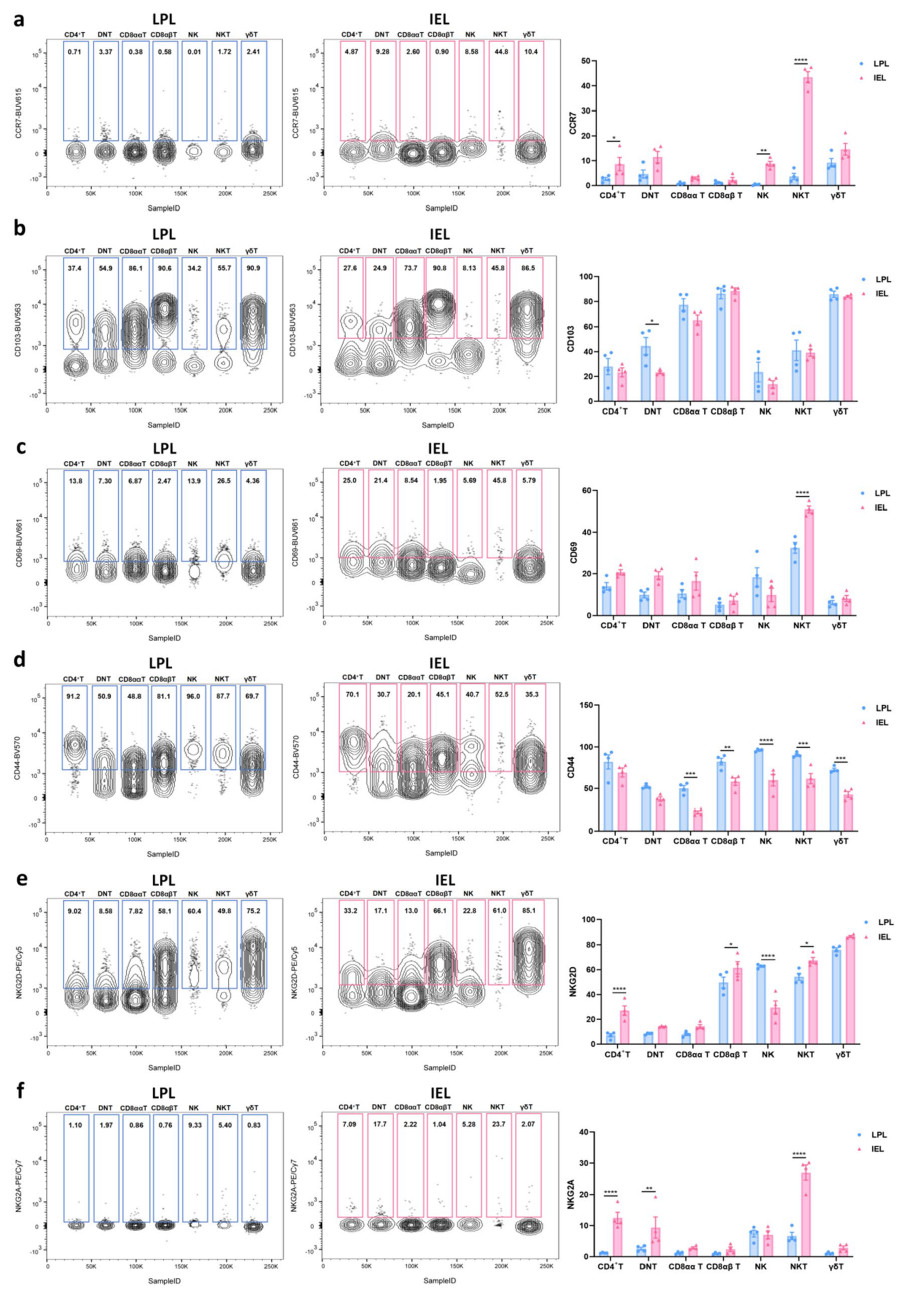
图4 结肠淋巴细胞中其他表面标志物的表达水平
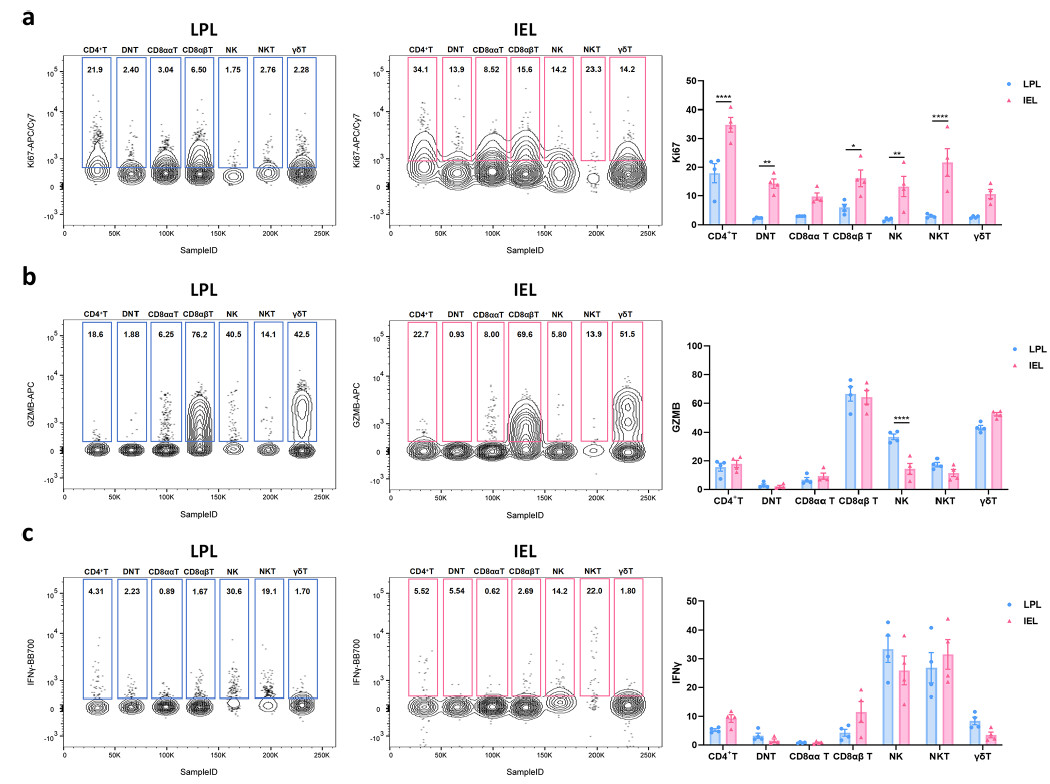
图5 评估小鼠肠淋巴细胞的细胞内因子表达水平
研究结论
本研究通过高维流式细胞术深入揭示了小鼠结肠非典型T细胞的异质性与功能特点,首次系统比较了IELs与LPLs在不同免疫标志物表达上的差异,为理解肠道免疫微环境提供了重要数据支持。研究成果不仅为炎症性肠病等相关疾病的机制研究提供新思路,也为未来靶向免疫检查点的治疗策略奠定基础。
Abstract
The intestinal epithelium is continually exposed to food-derived antigens and microbiota. This continual exposure requires a delicate immune homeostasis for food tolerance and protection against infection. Unconventional T lymphocytes, including γδT cells, Natural killer T (NKT) cells, Mucosal-Associated Invariant T (MAIT) cells, and Double-Negative T (DNT) cells, typically reside in the mucosal tissue, such as the colon. These cells play crucial roles in maintaining the integrity of the mucosal barrier and immune homeostasis through cytokine secretion and direct cell-mediated effects. Understanding the proportions and functional status of unconventional T lymphocytes in the colon is crucial for elucidating disease mechanisms. In this study, we developed a 22-color flow cytometry panel for comprehensive immunophenotyping of unconventional T lymphocytes in the murine colon. Our optimized protocol included antibody titration and customized gating strategies. We identified distinct populations of unconventional T lymphocytes, including γδT cells, NKT cells and DNT cells, and compared them with conventional T lymphocyte subsets (CD4+ T, CD8αα+ T, and CD8αβ+ T). We assessed their proliferation, cytotoxicity, cytokine production, and immune checkpoint molecule expression. Inhibitory receptor levels on intraepithelial and lamina propria unconventional T lymphocytes differed, suggesting distinct local environments and regulatory mechanisms. Our findings elucidate the status and function characteristics of unconventional T cells in colonic tissues, providing insights for mechanistic studies and the development of therapies for gastrointestinal diseases.
作者简介
通讯作者

田丹,副教授,博士生导师
首都医科大学附属北京友谊医院国家消化中心普外分中心实验室 副主任
消化健康全国重点实验室 PI
北京市“科技新星”获得者(2024年)
北京免疫学会青年学者奖(2022年)
获得世界免疫学大会“Travel Award”奖项(2019年)
主要研究方向:消化免疫和肿瘤免疫
以通讯或第一作者(含共同)在Gastroenterology、Nature Communications 、Journal of Autoimmunity 、Theranostics、Cell Reports等杂志发表SCI论文20余篇。
第一作者

潘乐涵,研究实习员
首都医科大学附属北京友谊医院 医学博士
首都医科大学附属北京友谊医院国家消化中心普外分中心实验室
消化健康全国重点实验室
主要研究方向:肠道免疫
https://wap.sciencenet.cn/blog-3558836-1502649.html
上一篇:Phenomics | 《表型组学(英文)》2025 年第三期文章合集
下一篇:祝贺 | Phenomics主编金力院士被授予“上海科技期刊杰出科技人物”
全部作者的其他最新博文
- • Phenomics | 中山大学肿瘤防治中心曾木圣院士团队发表综述:肿瘤诊疗新靶点,整合素α6靶向技术引领精准医疗新时代
- • Phenomics | 上海交通大学医学院张孝勇教授团队开发磁共振成像降噪新方法,有潜力改善脑小血管病的诊断效能
- • Phenomics | 复旦大学倪挺教授团队揭示基因内含子多聚腺苷酸化调控细胞衰老新机制
- • Phenomics | 加拿大阿尔伯塔大学和复旦大学联合开发基于文本、音频和视频的多模态抑郁症检测与评估方法
- • Phenomics | 翟振国/蒋太交/张鹏团队合作开发自适应多基因风险评估模型提升汉族人群静脉血栓栓塞症的风险预测能力
- • 祝贺 | 《表型组学(英文)》成功入选2025年“中国科技核心期刊”