By王从彦
植物凋落物失重率
植物凋落物的失重率以初始凋落物质量与经过时间t分解后的凋落物质量之差与初始凋落物质量之比进行计算(Voříšková and Baldrian, 2013 Voříšková, J., Baldrian, P., 2013. Fungal community on decomposing leaf litter undergoes rapid successional changes. The ISME Journal 7, 477-486.; Li et al., 2017 Li, H., Wei, Z., Huangfu, C., Chen, X., Yang, D., 2017. Litter mixture dominated by leaf litter of the invasive species, Flaveria bidentis, accelerates decomposition and favors nitrogen release. Journal of Plant Research 130, 167-180.; Hu et al., 2022 Hu, X., Arif, M., Ding, D.D., Li, J.J., He, X.R., Li, C.X., 2022. Invasive plants and species richness impact litter decomposition in Riparian Zones. Frontiers in Plant Science 13, 955656. ; Zhang et al., 2024 Zhang, S.M., Landuyt, D., Dhiedt, E., De Frenne, P., Verheyen, K., 2024. Tree Species Diversity Affects Litter Decomposition via Modification of the Microenvironment. Ecosystems 27, 508-522.)。
植物凋落物分解速率
植物凋落物分解速率(Litter decomposition coefficient, k)拟根据分解指数方程(Olson 1963 Olson JS. 1963. Energy storage and the balance of producers and decomposers in ecological systems. Ecology 44: 322‒31.; Wieder and Lang 1982 Wieder, R.K., Lang, G.E., 1982. A critique of the analytical methods used in examining decomposition data obtained from litter bags. Ecology 63, 1636‒1642.)进行计算:
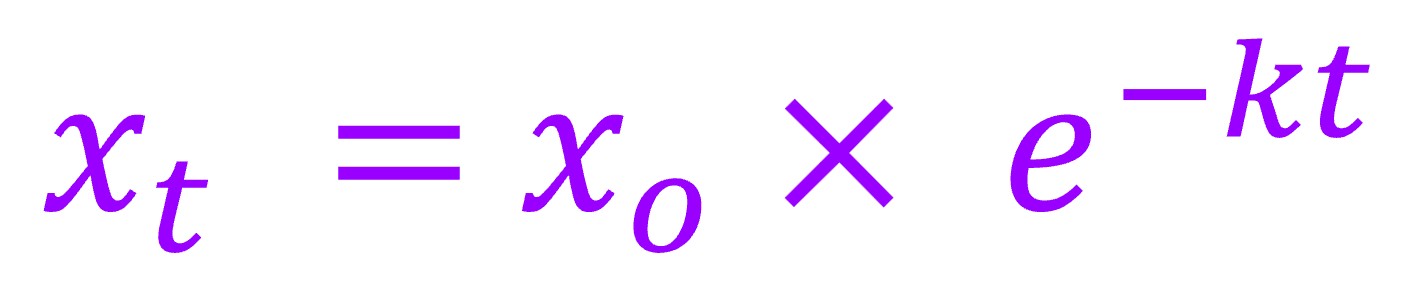
式中xo为初始凋落物质量,xt为经过时间t分解后的凋落物质量,k为凋落物分解速率指数(year‒1)。
The index of real-time decomposition rate (Ki)
The index of real-time decomposition rate (Ki) we proposed was fitted to the negative exponential decomposition model (Yang RR, Dong JY, Li CC, Wang LF, Quan Q, Liu J (2021) The decomposition process and nutrient release of invasive plant litter regulated by nutrient enrichment and water level change. PLoS One 16: e0250880):
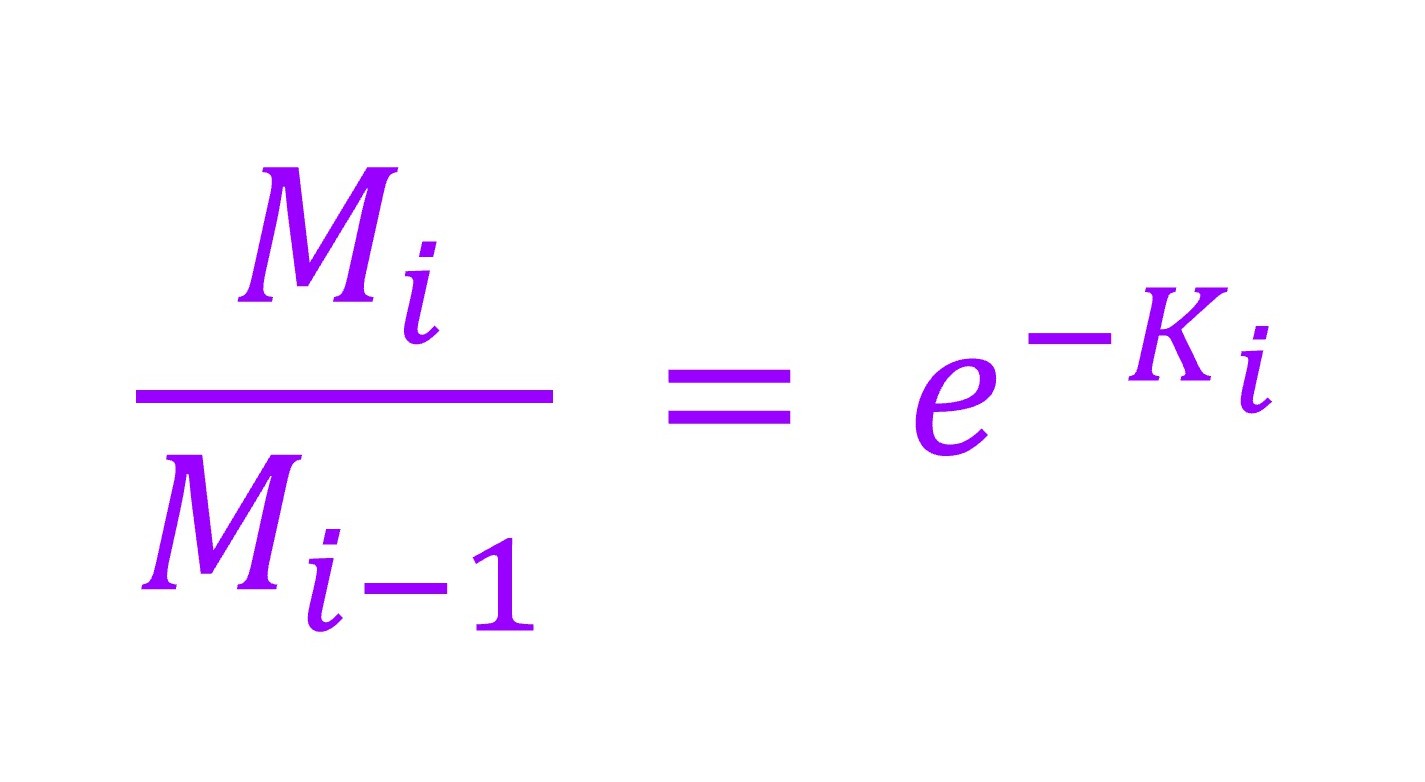
where Ki represents the dry weight of litter remaining after i time of decomposition, Ki-1 represents the dry weight of litter remaining after i-1 time of decomposition, i and i-1 are the time points (day), Ki is regarded as the decomposition rate at time i.
植物凋落物分解时间
凋落物分解50%所需时间(T50%)计算公式为(Olson 1963 Olson JS. 1963. Energy storage and the balance of producers and decomposers in ecological systems. Ecology 44: 322‒331.):
T50% = ‒ln(1 ‒ 0.50) / k = 0.693147181 / k
植物凋落物分解时间
凋落物分解95%所需时间(T95%)计算公式为(Olson 1963 Olson JS. 1963. Energy storage and the balance of producers and decomposers in ecological systems. Ecology 44: 322‒331.):
T95% = ‒ln(1 ‒ 0.95) / k = 2.995732274 / k
多种植物凋落物复合分解效应
The expected decomposition coefficient for the litter mixtures with 50% of one plant and 50% of another plant was assessed as follows (Hoorens et al. 2003 Hoorens, B., Aerts, R., Stroetenga, M., 2003. Does initial litter chemistry explain litter mixture effects on decomposition? Oecologia 137, 578–586.; Lecerf et al. 2011 Lecerf, A., Marie, G., Kominoski, J.S., Leroy, C.J., Bernadet, C., Swan, C.M., 2011. Incubation time, functional litter diversity, and habitat characteristics predict litter mixing effects on decomposition. Ecology 92, 160–169.; Jiang et al. 2019 Jiang, L., Kou, L., & Li, S.G. (2019). Decomposition of leaf mixtures and absorptive-root mixtures synchronously changes with deposition of nitrogen and phosphorus. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 138, 107602.; Jones et al. 2019 Jones, G. L., Scullion, J., Worgan, H., Gwynn-Jones, D. (2019). Litter of the invasive shrub Rhododendron ponticum (Ericaceae) modifies the decomposition rate of native UK woodland litter. Ecological Indicators, 107, 105597.; Hu et al., 2022 Hu, X., Arif, M., Ding, D.D., Li, J.J., He, X.R., Li, C.X., 2022. Invasive plants and species richness impact litter decomposition in Riparian Zones. Frontiers in Plant Science 13, 955656.). Expected values for the litter mixtures with 50% of one plant and 50% of another plant were calculated as:
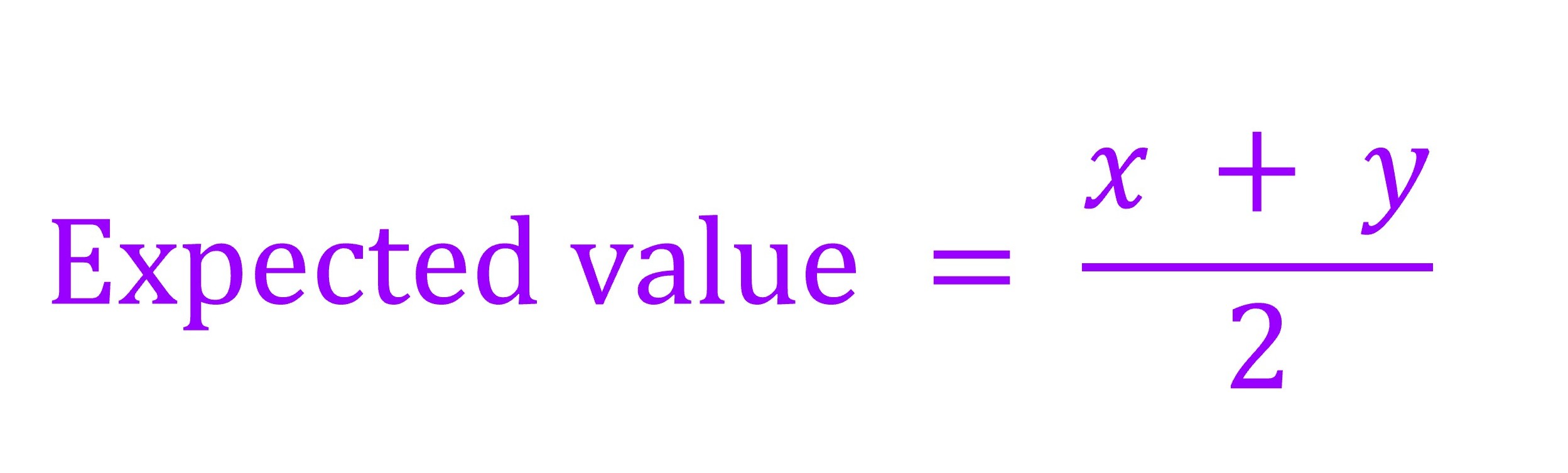
或
Expected value = (x + y) / 2
where x represents the observed litter decomposition coefficient for one plant and y represents the observed litter decomposition coefficient for another plant.
The previous formula was adapted for litter mixtures with 75% of one plant and 25% of another plant:
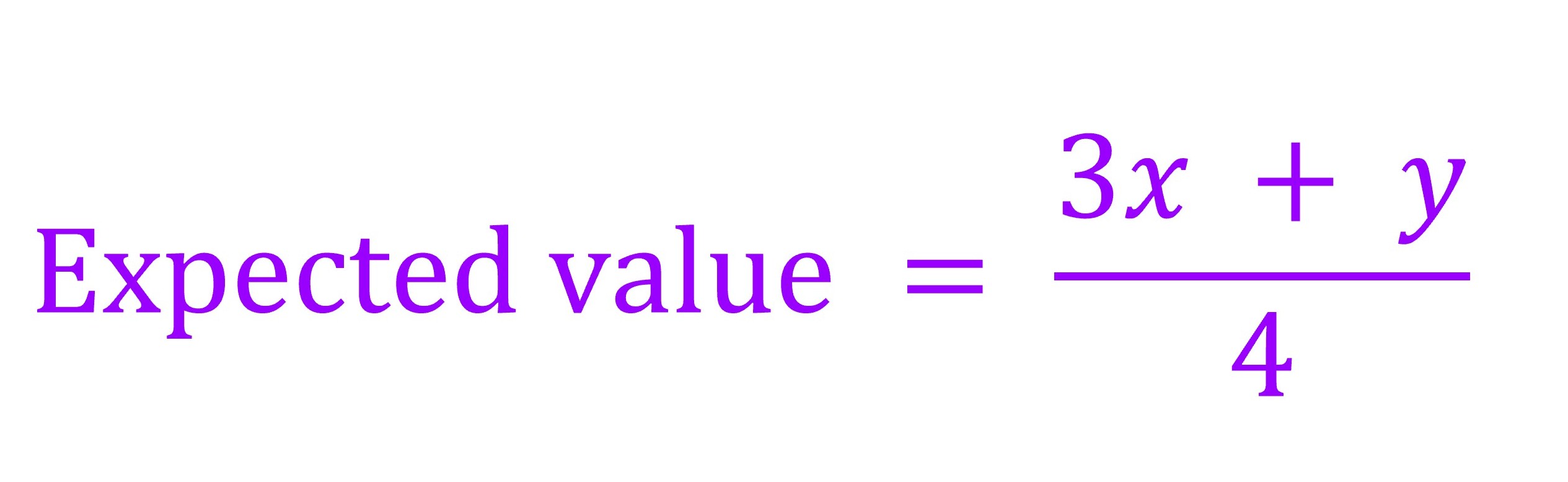
或
Expected value = (3x + y) / 4
where x represents the observed litter decomposition coefficient for one plant and y represents the observed litter decomposition coefficient for another plant.
The expected decomposition coefficient for the equally mixed leaves from multiple plants was assessed as follows (Hoorens et al. 2003 Hoorens, B., Aerts, R., Stroetenga, M., 2003. Does initial litter chemistry explain litter mixture effects on decomposition? Oecologia 137, 578–586.; Lecerf et al. 2011 Lecerf, A., Marie, G., Kominoski, J.S., Leroy, C.J., Bernadet, C., Swan, C.M., 2011. Incubation time, functional litter diversity, and habitat characteristics predict litter mixing effects on decomposition. Ecology 92, 160–169.; Jiang et al. 2019 Jiang, L., Kou, L., & Li, S.G. (2019). Decomposition of leaf mixtures and absorptive-root mixtures synchronously changes with deposition of nitrogen and phosphorus. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 138, 107602.; Jones et al. 2019 Jones, G. L., Scullion, J., Worgan, H., Gwynn-Jones, D. (2019). Litter of the invasive shrub Rhododendron ponticum (Ericaceae) modifies the decomposition rate of native UK woodland litter. Ecological Indicators, 107, 105597.; Hu et al., 2022 Hu, X., Arif, M., Ding, D.D., Li, J.J., He, X.R., Li, C.X., 2022. Invasive plants and species richness impact litter decomposition in Riparian Zones. Frontiers in Plant Science 13, 955656.):
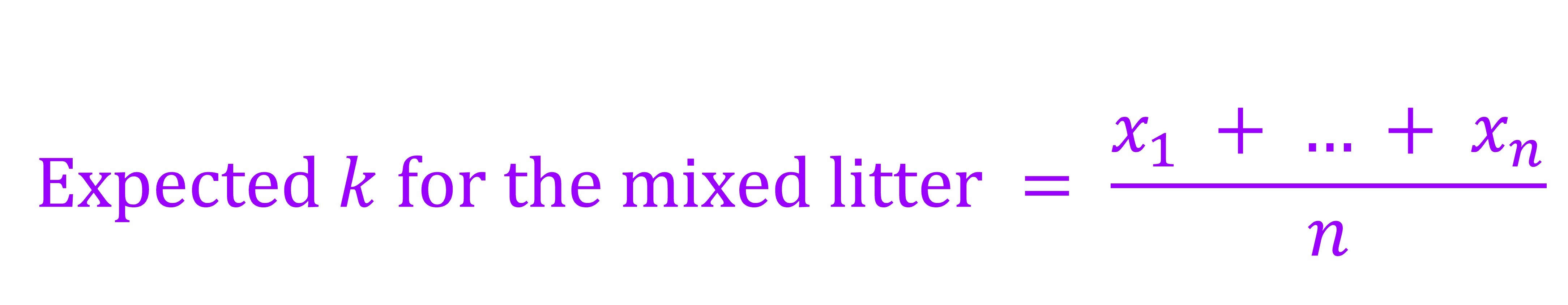
where x1 to xn is the observed k of plant 1 to n, respectively, and n is the species number of plants, respectively.
两种植物凋落物共同分解的复合作用The mixed-effect intensity of co-decomposition
两种植物凋落物共同分解的复合作用The mixed-effect intensity of co-decomposition计算公式为(Hoorens et al. 2003 Hoorens, B., Aerts, R., Stroetenga, M., 2003. Does initial litter chemistry explain litter mixture effects on decomposition? Oecologia 137, 578–586.; Jiang et al. 2019 Jiang, L., Kou, L., & Li, S.G. (2019). Decomposition of leaf mixtures and absorptive-root mixtures synchronously changes with deposition of nitrogen and phosphorus. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 138, 107602.; Jones et al. 2019 Jones, G. L., Scullion, J., Worgan, H., Gwynn-Jones, D. (2019). Litter of the invasive shrub Rhododendron ponticum (Ericaceae) modifies the decomposition rate of native UK woodland litter. Ecological Indicators, 107, 105597.; Hu et al., 2022 Hu, X., Arif, M., Ding, D.D., Li, J.J., He, X.R., Li, C.X., 2022. Invasive plants and species richness impact litter decomposition in Riparian Zones. Frontiers in Plant Science 13, 955656.):
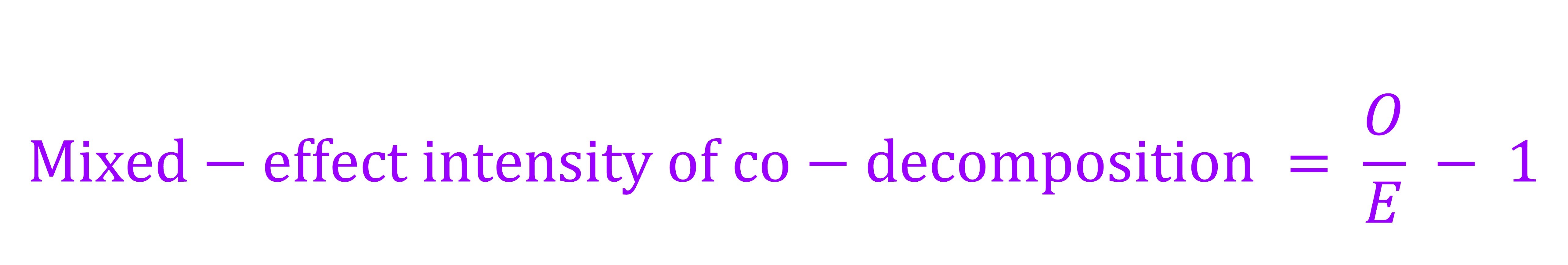
或The mixed-effect intensity of co-decomposition = (O / E) ‒ 1
式中O为实验实际测定得到的两种植物凋落物共同分解的分解速率指数(year‒1),E为理论计算得到的两种植物凋落物共同分解的分解速率指数(year‒1)。
E计算公式为(Hoorens et al. 2003 Hoorens, B., Aerts, R., Stroetenga, M., 2003. Does initial litter chemistry explain litter mixture effects on decomposition? Oecologia 137, 578–586.; Lecerf et al. 2011 Lecerf, A., Marie, G., Kominoski, J.S., Leroy, C.J., Bernadet, C., Swan, C.M., 2011. Incubation time, functional litter diversity, and habitat characteristics predict litter mixing effects on decomposition. Ecology 92, 160–169.; Jiang et al. 2019 Jiang, L., Kou, L., & Li, S.G. (2019). Decomposition of leaf mixtures and absorptive-root mixtures synchronously changes with deposition of nitrogen and phosphorus. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 138, 107602.; Jones et al. 2019 Jones, G. L., Scullion, J., Worgan, H., Gwynn-Jones, D. (2019). Litter of the invasive shrub Rhododendron ponticum (Ericaceae) modifies the decomposition rate of native UK woodland litter. Ecological Indicators, 107, 105597.; Hu et al., 2022 Hu, X., Arif, M., Ding, D.D., Li, J.J., He, X.R., Li, C.X., 2022. Invasive plants and species richness impact litter decomposition in Riparian Zones. Frontiers in Plant Science 13, 955656.):
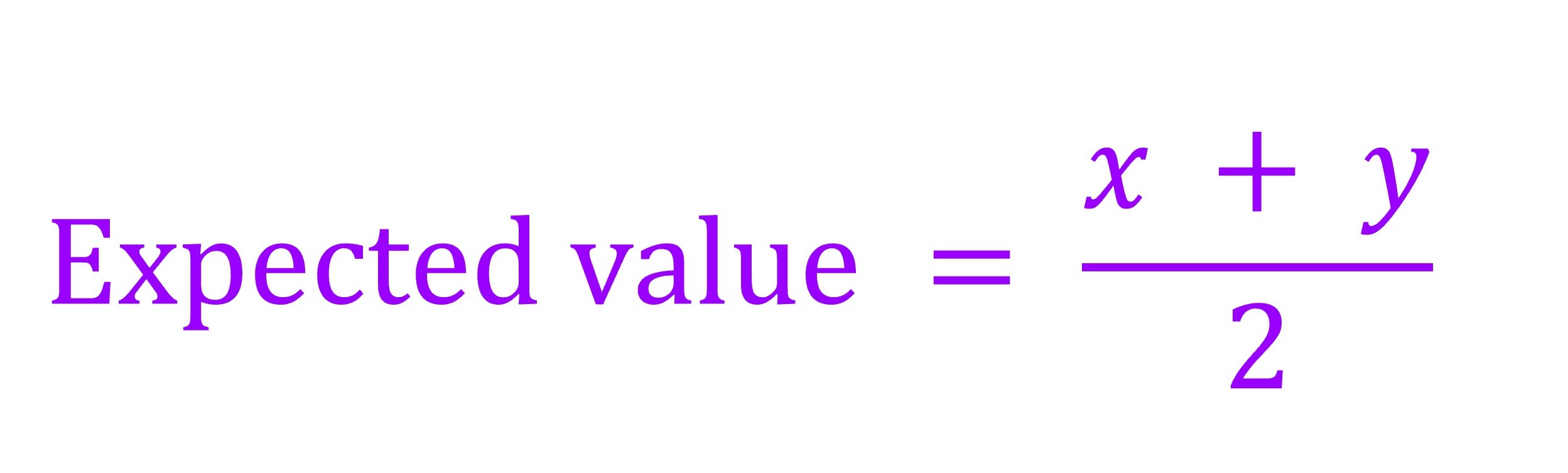
或
Expected value = (x + y) / 2
式中x为实验实际测定得到的第一种植物凋落物单独分解的分解速率指数(year‒1),y为实验实际测定得到的第二种植物凋落物单独分解的分解速率指数(year‒1)。若复合作用强度值大于零,两种植物凋落物共同分解存在协同作用;若复合作用强度值小于零,两种植物凋落物共同分解存在拮抗作用;若复合作用强度值等于零,两种植物凋落物共同分解未发生复合作用。复合作用强度值偏离零的程度越大,则意味着复合作用强度越大。
注:囿于个人水平有限,错误在所难免。敬请批评指正!
转载本文请联系原作者获取授权,同时请注明本文来自王从彦科学网博客。
链接地址:https://wap.sciencenet.cn/blog-565899-1479171.html?mobile=1
收藏

