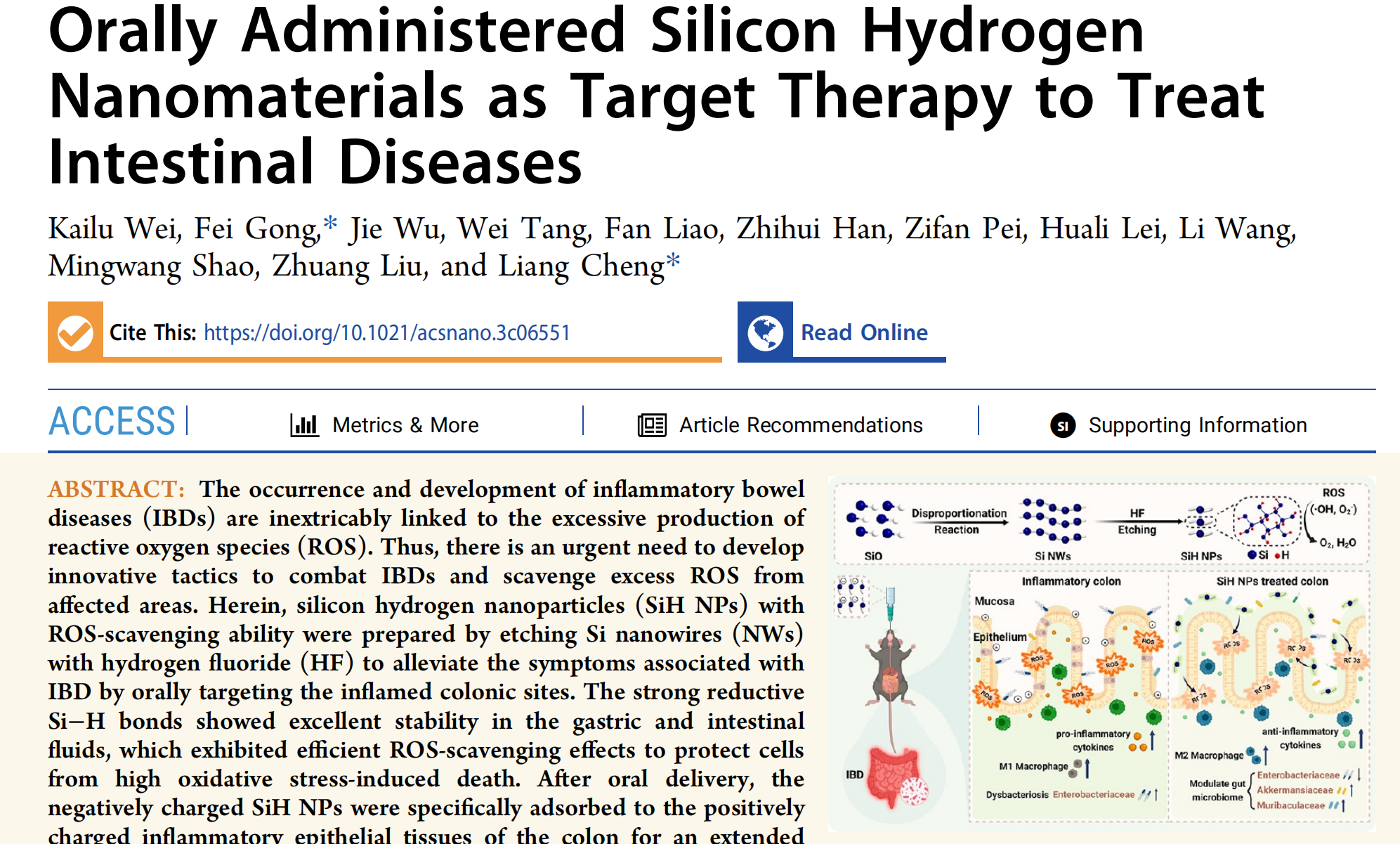
炎症性肠病(IBD)的发生和发展与活性氧(ROS)的过量产生密不可分。因此,迫切需要制定创新策略来对抗IBD并从受影响地区清除多余的ROS。本文通过氟化氢(HF)蚀刻Si纳米线(NWs)制备具有ROS清除能力的硅氢纳米颗粒(SiH NPs),通过口服发炎的结肠部位来缓解IBD的相关症状。强还原性Si-H键在胃液和肠液中表现出优异的稳定性,表现出有效的ROS清除作用,保护细胞免受高氧化应激诱导的死亡。口服给药后,带负电荷的SiH NPs通过静电相互作用特异性吸附到结肠带正电荷的炎性上皮组织中,延长结肠停留时间。SiH NPs通过抑制结肠缩短、减少促炎细胞因子分泌、调节巨噬细胞极化和保护结肠屏障,在葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的预防和治疗小鼠模型中表现出显著的预防和治疗效果。经16S rDNA高通量测序测定,口服SiH NPs处理导致肠道微生物组丰度发生变化,改善了结肠发炎后细菌多样性,恢复了有益菌的相对丰度。总体而言,我们的研究结果强调了基于SiH的抗炎药在治疗IBD和其他炎症性疾病中的广泛应用。
硅和氢化硅都可以和水反应大量产生氢气,本研究使用氢化硅材料,通过口服发现能显著改善结肠炎动物肠道炎症,理论上推测氢气经过肠道吸收可以进入全身,对全身炎症相关疾病都可能产生作用。据我初步判断,这应该是第一篇使用氢化硅材料进行的生物医学效应研究。
本研究作者来自苏州大学功能纳米与软材料研究所和澳门科技大学澳门材料科学与工程学院,论文近日发表在ACS Nano.
氢点评:氢气生物学作用的特点是安全性,但产生氢气的材料就不一定。如氢化硅等材料,由于还原性非常强,其潜在毒性需要认真对待。使用产氢气材料进行生物效应研究和应用,必需首先对这类材料的安全性进行评估。从事产品开发的同行有时候觉得氢气非常安全,就简单推测产氢气材料同样安全,这是完全不同性质的问题,重点提醒同行们重视。
Wei K, Gong F, Wu J, Tang W, Liao F, Han Z, Pei Z, Lei H, Wang L, Shao M, Liu Z, Cheng L. Orally Administered Silicon Hydrogen Nanomaterials as Target Therapy to Treat Intestinal Diseases. ACS Nano. 2023 Oct 16.
The occurrence and development of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs) are inextricably linked to the excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Thus, there is an urgent need to develop innovative tactics to combat IBDs and scavenge excess ROS from affected areas. Herein, silicon hydrogen nanoparticles (SiH NPs) with ROS-scavenging ability were prepared by etching Si nanowires (NWs) with hydrogen fluoride (HF) to alleviate the symptoms associated with IBD by orally targeting the inflamed colonic sites. The strong reductive Si–H bonds showed excellent stability in the gastric and intestinal fluids, which exhibited efficient ROS-scavenging effects to protect cells from high oxidative stress-induced death. After oral delivery, the negatively charged SiH NPs were specifically adsorbed to the positively charged inflammatory epithelial tissues of the colon for an extended period via electrostatic interactions to prolong the colonic residence time. SiH NPs exhibited significant preventive and therapeutic effects in dextran sodium sulfate-induced prophylactic and therapeutic mouse models by inhibiting colonic shortening, reducing the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, regulating macrophage polarization, and protecting the colonic barrier. As determined using 16S rDNA high-throughput sequencing, the oral administration of SiH NPs treatment led to changes in the abundance of the intestinal microbiome, which improved the bacterial diversity and restored the relative abundance of beneficial bacteria after the inflamed colon. Overall, our findings highlight the broad application of SiH-based anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of IBD and other inflammatory diseases.
转载本文请联系原作者获取授权,同时请注明本文来自孙学军科学网博客。
链接地址:https://wap.sciencenet.cn/blog-41174-1406188.html?mobile=1
收藏

