虚拟专辑简介
Cancer poses a significant risk to human health and quality of life, making it crucial to conduct more in-depth and accurate research into the mechanisms of cancer development and treatment. This compilation presents a collection of seven articles that delve into various aspects of cancer research, offering insights into the molecular mechanisms, clinical management, and therapeutic strategies. The articles cover a range of topics, from the role of DDR1 in solid tumors, the intratumor microbiome-host interactions in lung cancer, to the clinical management of neuroendocrine tumors and hepatocellular carcinoma. Each article provides a unique perspective, contributing to the broader understanding of cancer biology and treatment. Together, these studies underscore the complexity of cancer and highlight the importance of multidisciplinary approaches in advancing oncology research and improving patient outcomes.
好文速读
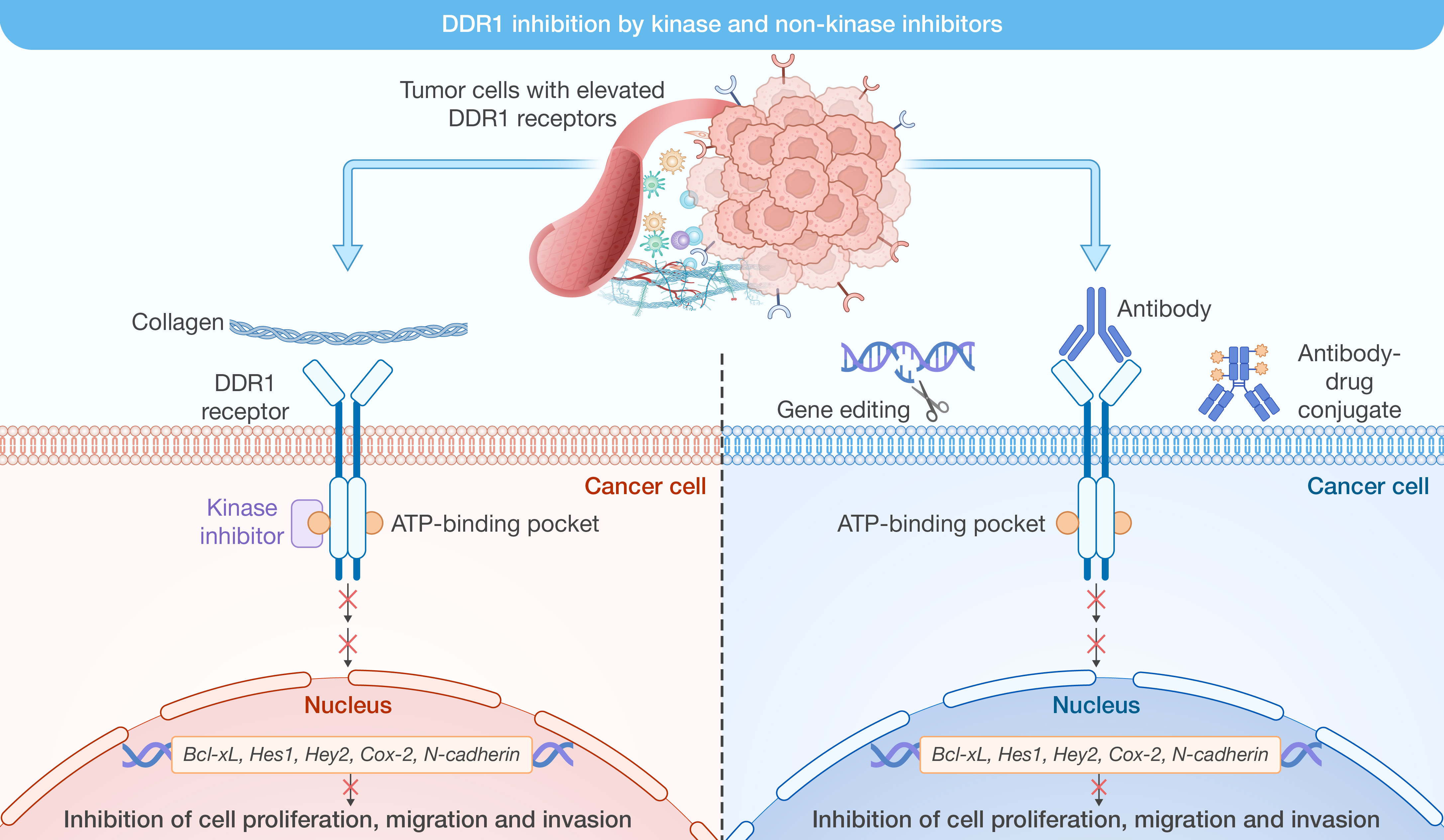
1. Discoidin domain receptor 1 as a potent therapeutic target in solid tumors
通讯作者:金腾川
本文讨论了人类跨膜蛋白盘状蛋白结构域受体1(DDR1)的结构、功能和病理特征,揭示了DDR1在实体瘤微环境中的作用,并提出了其作为潜在治疗靶点的可行性。
引用:
Bibi S, Zeng W, Zheng P, et al. Discoidin domain receptor 1 as a potent therapeutic target in solid tumors. hLife 2024; 2: 454–466.
2. Dissection of intratumor microbiome-host interactions at single-cell level in lung cancer
hLife | 上海交大刘宁宁等团队揭示肺癌瘤内微生物组与宿主在单细胞水平相互作用机制
通讯作者:刘宁宁,吴文娟
本研究整合了公开发表的6套共149个肺癌患者组织样本的单细胞RNA测序数据集(包含肺癌、癌旁和脑转移组织三种样本类型),利用SAHMI(宿主单细胞-微生物组互作技术)对单细胞转录组测序序列进行分析来识别与单细胞相关的微生物,通过排除潜在的污染和假阳性的微生物序列,同时去除多数据集整合的批次效应,最终确定了与单个宿主细胞相关的真实微生物序列。通过与对应组织的单细胞转录组联合分析,探究了单细胞分辨率下不同类型宿主细胞与肿瘤内特定细菌和真菌相互作用的潜在机制,为理解瘤内微生物组与肺癌发展的关系提供了新理论,有望发现新的癌症诊断和治疗靶点。
引用:
Ma YJ, Sun YC, Wang L, et al. Dissection of intratumor microbiome–host interactions at single-cell level in lung cancer. hLife 2024.
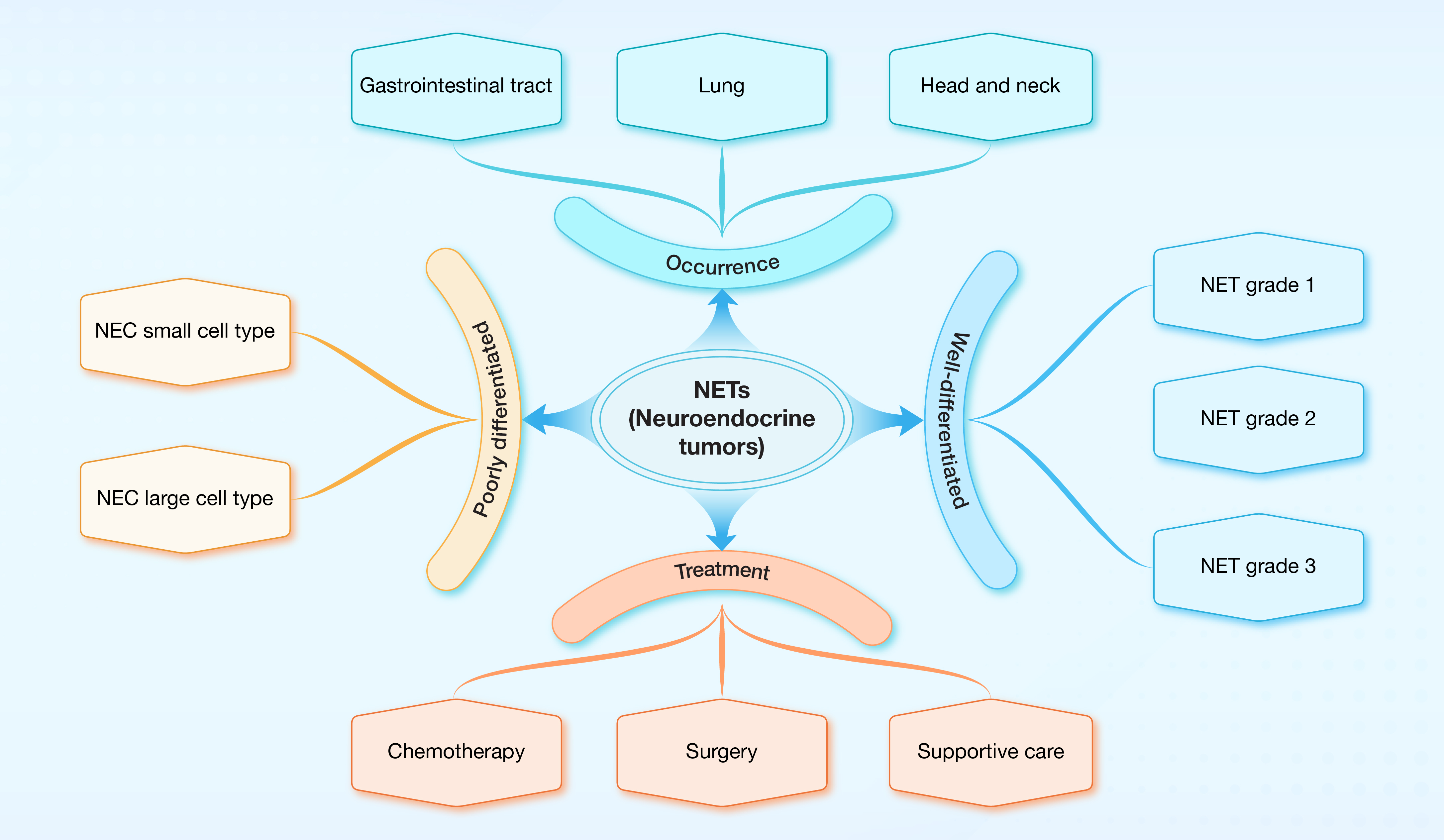
3. Current perspectives on neuroendocrine tumors
hLife | 神经内分泌肿瘤研究进展与展望
通讯作者:Devendra Singh
本研究总结了目前NETs领域的研究进展,包括其发病机制、分类、临床表现、诊断方法、治疗选择和预后指征等,并为未来NETs的发病机制研究和治疗手段开发提供了新的见解。
引用:
Verma SK, Khare R, Singh D. Current perspectives on neuroendocrine tumors. hLife 2024; 2: 563–575.
通讯作者:Bassey E. Ekeng
The clinical presentation of histoplasmosis is non-specific and has several mimics as documented in the literature. Regarding cancers, previous reviews emphasized mainly the clinical and radiological similarities between histoplasmosis and pulmonary malignancies. Besides lung cancers, histoplasmosis also masquerades as other malignancies. We identified one hundred and twenty-four cases of histoplasmosis clinically mistaken for malignancies. Of the 124,84 (67.7%) were included in the analyses of demographics, immune status, clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment outcomes. The remainder were excluded as the available data was mainly on diagnosis. Of the eighty-four, histoplasmosis was predominantly misdiagnosed as lung cancers (n = 16, 19.0%), gastrointestinal tumors (n = 15, 17.9%), and lymphomas/hematological malignancies (n = 15, 17.9%). Fifty-four (64.3%) were immunocompromised including 16 (29.6%) who were living with HIV, while the remainder were immunocompetent. We conclude that infective aetiologies like histoplasmosis should be considered or ruled out in patients clinically suspected of malignancy regardless of their immune status.
引用:
Benjamin OE., Bassey TE., Nwagboso CI., et al. Histoplasmosis misdiagnosed as malignancies in immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients: A global perspective on clinical presentation, radiological and pathological findings. hLife 2024.
通讯作者:刘鹏,章薇,胡亚伟
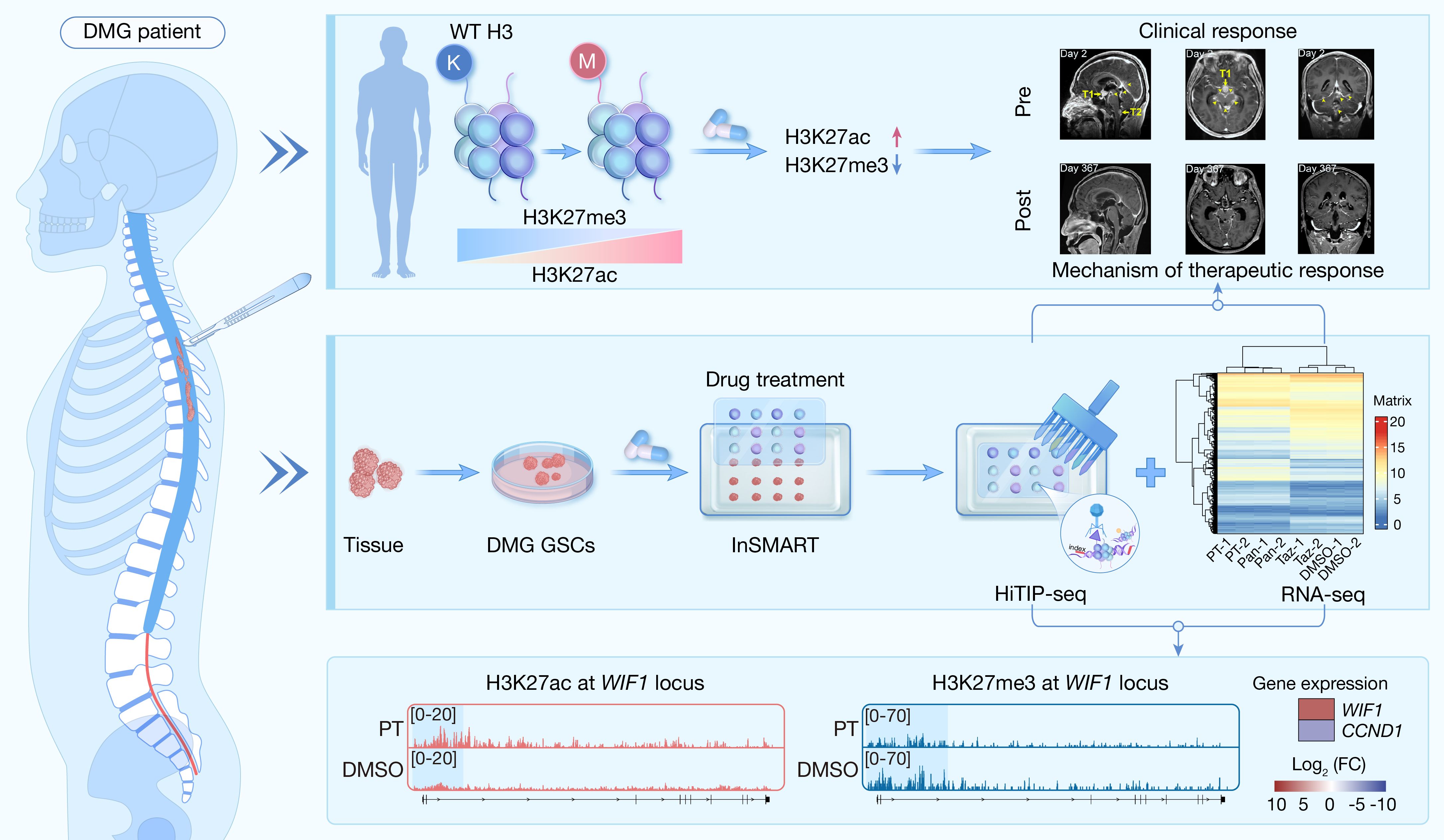
本研究基于微阵列芯片开发出一种高通量原位标记免疫沉淀测序技术(HiTIP-seq),不仅为DMG研究提供了新技术,更为其治疗新策略提供了科学依据。
引用:
Chen Z, Gao Q, Shang Y, et al. HiTIP-seq profiles epigenomic reprogramming of patient-derived diffuse midline glioma stem cells to epigenetic therapy. hLife 2024; 2: 471–487.
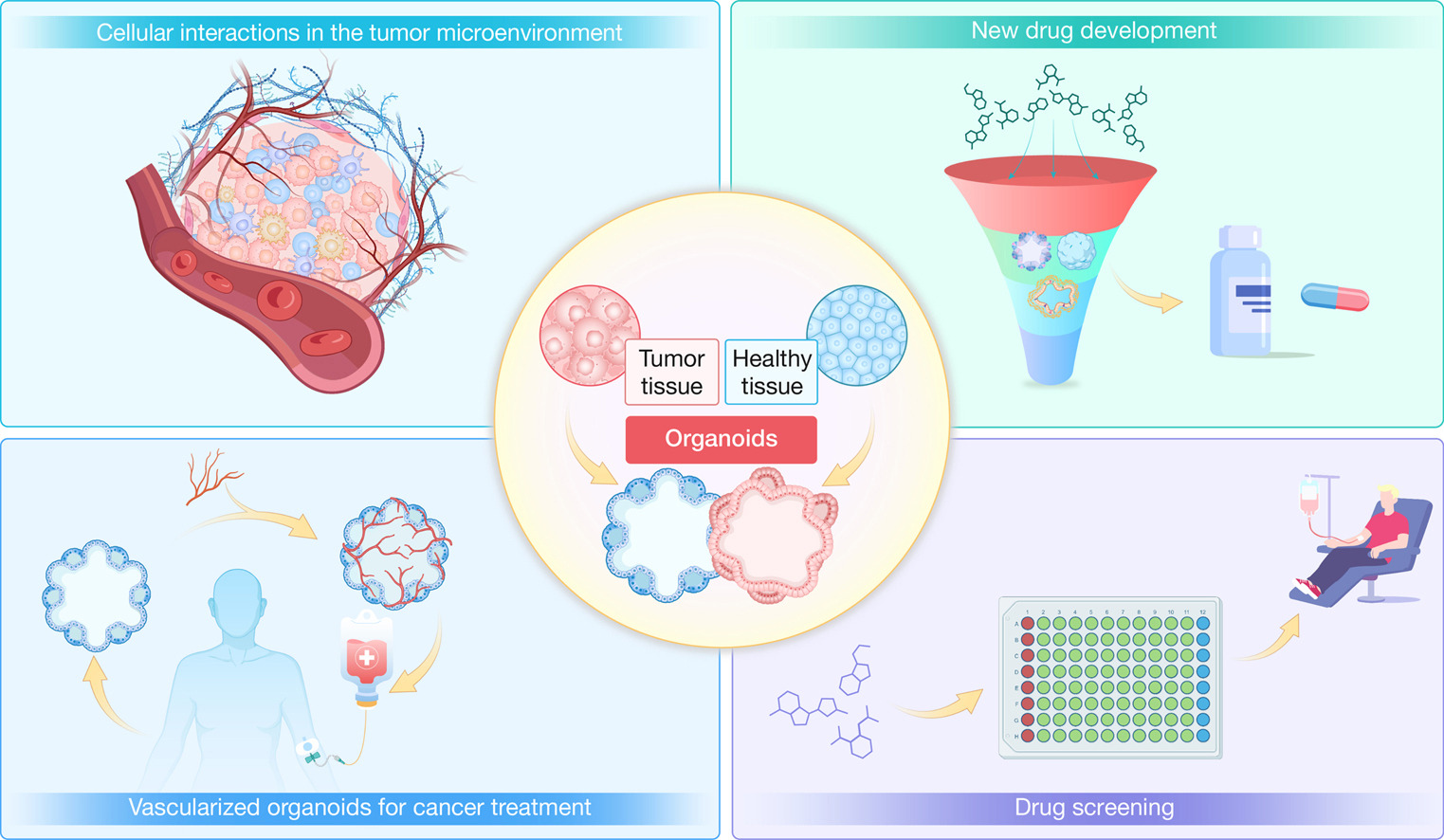
hLife Review | 癌症研究的革命: 揭示类器官的力量及其在癌症治疗中的潜力
通讯作者:周西坤,李敬
本文系统回顾了类器官的发展历史与研究现状,重点关注了类器官在癌症研究与治疗中的进展与应用,最后讨论了目前类器官需要克服的挑战并展望了类器官领域未来的研究与发展方向。
引用:
Zhang Y, Liu M, Xie N, et al. Cancer research revolutionized: Unveiling the power of organoids and their therapeutic potential in oncology. hLife 2024.
7. Candida albicans overgrowth impairs anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in oral tumor-bearing mice
通讯作者:闫志敏
Fungi, an essential component of the human microbiota, is gradually gaining attention in the field of cancer research. Intratumoral Cladosporium spp., as well as gut Schizosaccharomyces octosporus and Saccharomyces paradoxus were reported to be associated with immunotherapy response in cancer patients. In our study, C. albicans emerged as a potential factor affecting the efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy in oral cancer, which was dependent on its abundance. Moreover, the disrupted gut microbiome and the immunosuppressive microenvironment may be the mechanisms for C. albicans overgrowth impairing immunotherapy.
引用:
Wang X, Zhang X, Wu S, et al. Candida albicans overgrowth impairs anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in oral tumor-bearing mice. hLife 2025.
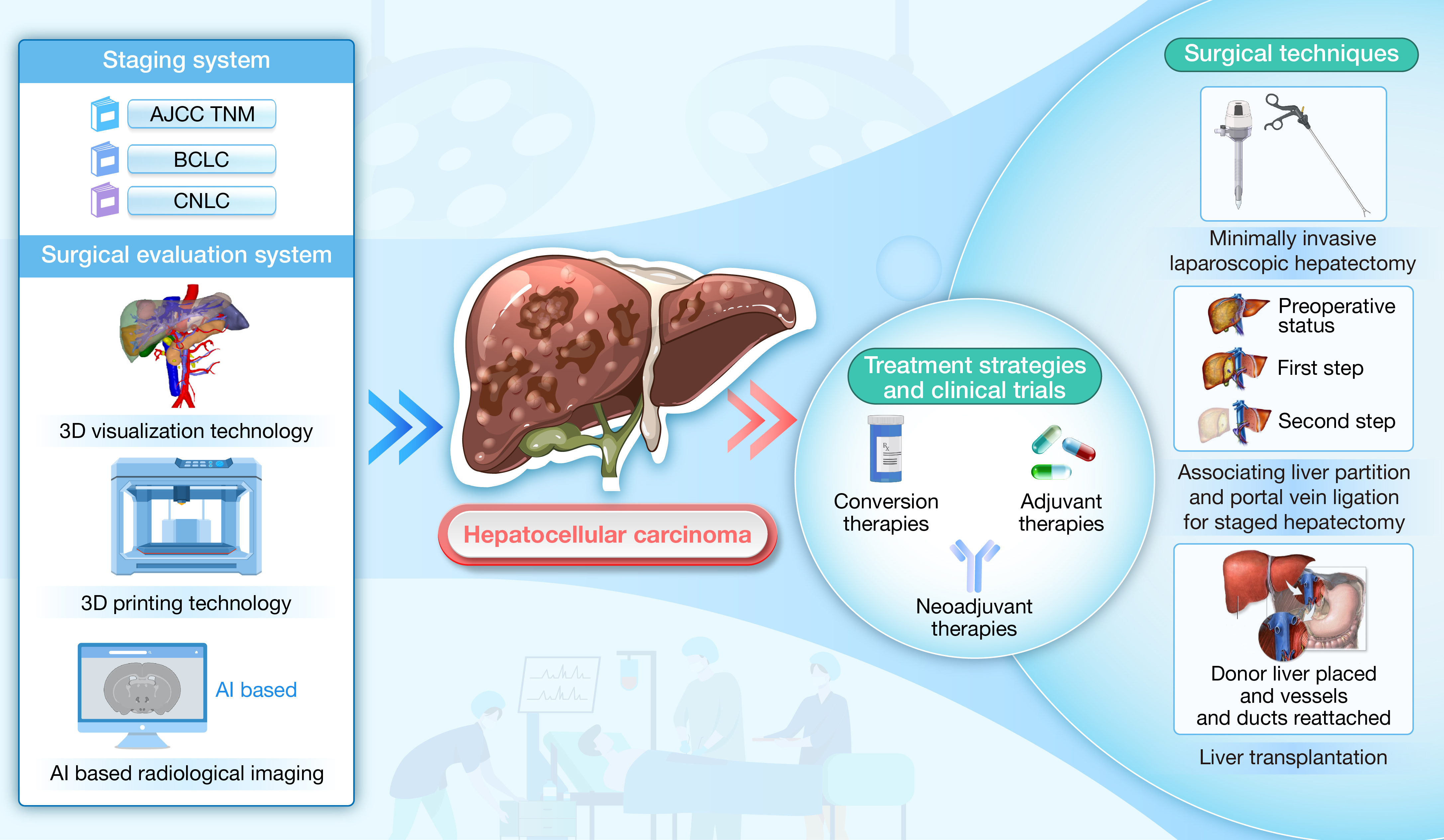
8. Recent advances in surgical management strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma
通讯作者:周俭
本文对术前评估、治疗技术、围手术期策略及创新临床试验在肝癌外科领域的最新进展进行阐释,并综述了HCC临床实践中的挑战,强调了外科治疗创新和系统治疗的贡献。
引用:
Ding ZB, Shi YH, Chen JF, et al. Recent advances in surgical management strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma. hLife 2024; 2: 439–453.
期刊简介
hLife由高福院士、董晨院士和Jules A. Hoffmann教授(2011诺奖获得者)领衔,是中国科学院微生物研究所主办,中国生物工程学会,浙江大学陈廷骅大健康学院,西湖大学医学院,上海市免疫治疗创新研究院和广州霍夫曼免疫研究所联合支持,与国际出版商爱思唯尔合作的健康科学领域综合性英文期刊。
hLife聚焦健康科学领域的前沿进展,旨在促进基础研究与临床应用的融合发展。期刊发表与医学相关各研究领域最新成果,学科领域包括(但不限于)病原生物学、流行病学、生理学、免疫学、结构生物学、疾病监测、肿瘤、药物、疫苗和健康政策等。
hLife是一本金色开放获取期刊,月刊出版;2022年成功入选“中国科技期刊卓越行动计划高起点新刊”;2023年11月正式创刊; 2024年5月被DOAJ收录;2024年8月被Scopus收录。
2026年前hLife接收的稿件免收文章处理费(APC)。
期刊网址:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/journ
转载本文请联系原作者获取授权,同时请注明本文来自闫群科学网博客。
链接地址:https://wap.sciencenet.cn/blog-3552961-1481130.html?mobile=1
收藏