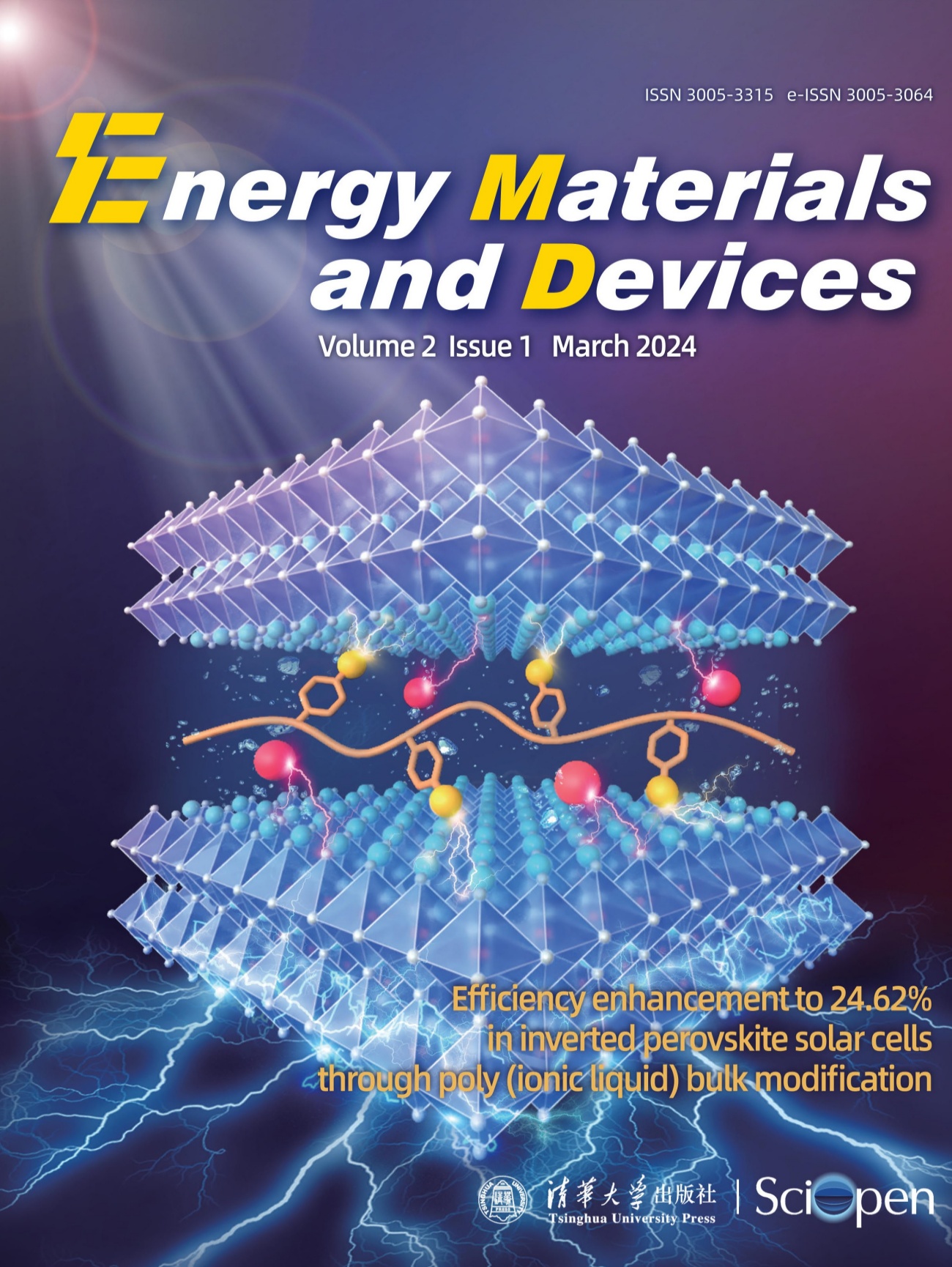
Cover Story
Small-molecule ionic liquids (ILs) are often used as efficient bulk phase modifiers for perovskite materials. However, their inherent characteristics pose challenges in addressing the stability issues associated with perovskite solar cells (PSCs). In this study, a poly(IL) is designed with multiple active sites, named poly[4-styrenesulfonyl(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide] pyridine (P[STFSI][PPyri]), as an efficient additive of perovskite materials. P[STFSI][PPyri] demonstrates the ability to passivate defects and suppress nonradiative recombination in PSCs. Additionally, it facilitates the fixation of organic and halide ions, thereby enhancing the device’s stability and photoelectric performance. Consequently, the introduction of P[STFSI][PPyri] as a dopant in the devices resulted in an excellent efficiency and outstanding long-term operational stability. (See the article by Chen X. Y. et al. https://doi.org/10.26599/EMD.2024.9370029)
(请看这里👉李炫华/曹琦/尹剑波/蒋龙等研究论文:聚离子液体体相修饰使反式钙钛矿太阳能电池效率提高到24.62% )

Cover Story
Sb2Se3 semiconducting material has been widely applied in single-junction solar cells. It has a band gap of 1.05−1.2 eV, and is used as the bottom cell absorber material in tandem solar cells. Sb2Se3 solar cells exhibit excellent stability with nontoxic compositional elements. The band gap of organic−inorganic hybrid perovskite is tunable over a wide range. In this work, a perovskite/antimony selenide fourterminal tandem solar cell with a specially designed and fabricated transparent electrode for an optimized spectral response is demonstrated for the first time. Through adjusting the thickness of the transparent electrode layer of the top cell, and optimizing antimony selenide bottom cell by introducing a double electron transport layer, the four-terminal tandem solar cell achieves an impressive efficiency exceeding 20%. This work provides a new tandem device structure and demonstrates that antimony selenide is a promising absorber material for bottom cell applications in tandem solar cells. (See the article by Cai Z. Y. et al. https://doi.org/10.26599/EMD.2024.9370027)
(请看这里👉中科大陈涛、合工大罗派峰等:以硒化锑为底电池的钙钛矿/硒化锑新型叠层太阳能电池)
Energy Materials and Devices (ISSN 3005-3315)由清华大学主办,清华大学出版社出版,清华大学出版社自主研发的出版传播平台SciOpen发行,聚焦能源材料与器件领域的基础研究、技术创新、成果转化和产业化全链条创新研究成果,通过开放获取(Open Access)方式面向全球发表原创性、引领性、前瞻性研究进展,推动能源科学和产业发展,助力“碳达峰、碳中和”。Energy Materials and Devices 创刊于2023年9月,由清华大学康飞宇教授担任主编,截止目前,共出版3期,总浏览量5.3万余次,下载量1.2万余次。
大事记
2023年5月26日
ScholarOne投审稿系统上线
(请看这里👉新刊上线 | Energy Materials and Devices 诚邀投稿!)
2023年6月13日
第一届编委会成立
(请看这里👉新刊介绍 || Energy Materials and Devices 第一届编委会成立)
2023年10月30日
第1卷第1期正式出版
(请看这里👉创精品期刊, 立学术标杆| Energy Materials and Devices Vol. 1 No. 1 正式出版)
2023年12月14日
首届青年编委会成立
(请看这里👉Energy Materials and Devices 首届青年编委名单公布)
2024年1月31日
第1卷第2期正式出版
(请看这里👉Energy Materials and Devices 2023年第2期正式出版)
本期内容概览
转载本文请联系原作者获取授权,同时请注明本文来自清华大学出版社学术期刊科学网博客。
链接地址:https://wap.sciencenet.cn/blog-3534092-1430164.html?mobile=1
收藏


