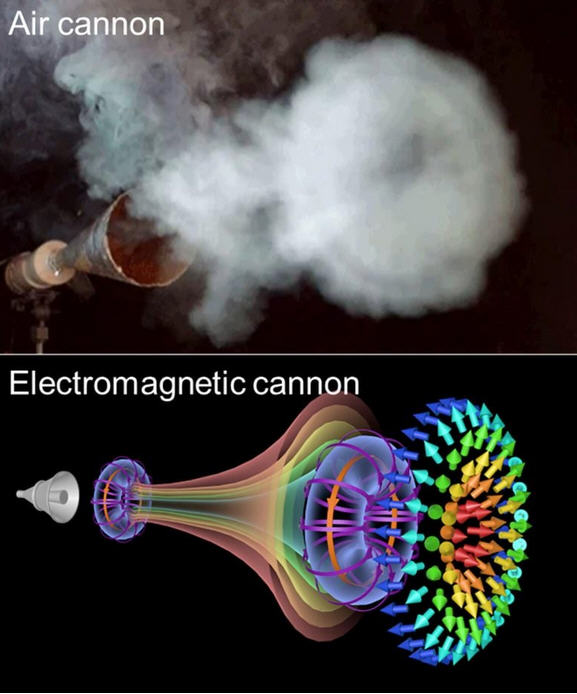
中国科学家研制出一种电磁旋涡炮
诸平
据《科技日报》(SciTechDaily)网站2024年9月10日刊发的来自中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所{Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics (CIOMP), Chinese Academy of Sciences}提供的消息,中国科学家研制出一种电磁旋涡炮(Chinese Scientists Have Developed an Electromagnetic Vortex Cannon)。
涡旋环(Vortex rings),无论是在空气中还是在电磁波中,都是令人着迷的结构。最近的研究已经开发出发射电磁涡流环的方法,在通信、传感和数据处理方面提供了潜在的应用。这项技术可能会彻底改变无线网络,并为数据存储和计量技术的创新铺平道路。
涡旋环是一种神秘而迷人的自然现象,在空气和电磁波中都表现出令人惊叹的结构和行为。想象一下,一门空气炮可以发射漩涡环,创造一个完美的空气漩涡,在空气中优雅地移动,就像一只看不见的手在天空中勾勒出优雅的曲线。这种涡旋现象不仅是物理学的奇观,也是大自然的杰作。
空气漩涡的创造是科学与美学的迷人结合。当空气炮开火时,瞬时的压力差使空气形成一个旋转的环形结构,在空气中稳定地传播,展示了涡旋的独特形状和动力学。
电磁旋涡环(Electromagnetic Vortex Rings)
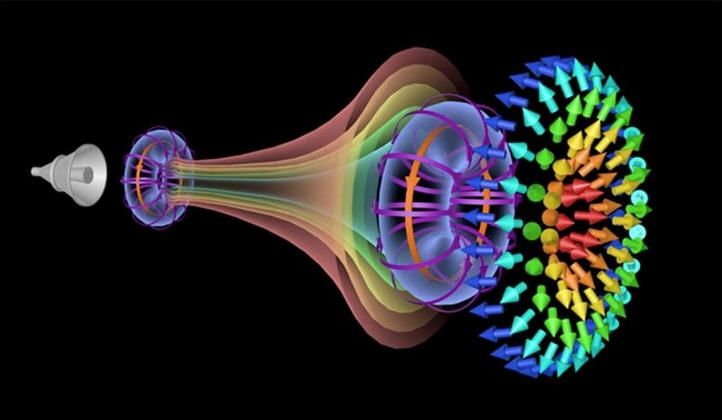
将同样的原理应用于电磁波,我们可以设想一种直接发射电磁旋涡环的电磁旋涡炮。由于研究人员的不懈努力,这一概念正逐渐成为现实。最近,中国电子科技大学(University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, , Chengdu, China)的王任(Ren Wang)副教授、新加坡南洋理工大学(Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, Singapore)的沈义杰(Yijie Shen音译)助理教授以及英国南安普顿大学(University of Southampton, Southampton SO17 1BJ, UK)的合作者提出了一种利用同轴喇叭天线(coaxial horn antennas)直接发射电磁涡流(electromagnetic vortices)的方法。
他们观察了这些涡旋的弹性传播特性(resilient propagation characteristics)和斯格明子拓扑结构(skyrmion topological structures)。他们的研究成果2024年8月2日已经在《应用物理评论》的专题文章(Featured Article in Applied Physics Reviews)中发表——Ren Wang; Pan-Yi Bao; Zhi-Qiang Hu; Shuai Shi; Bing-Zhong Wang; Nikolay I. Zheludev; Yijie Shen. Observation of resilient propagation and free-space skyrmions in toroidal electromagnetic pulses. Applied Physics Reviews, 2024, 11: 031411. DOI: 10.1063/5.0218207. ePub. August 02 2024. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0218207
电磁涡流炮的工作原理(Operating Principles of the Electromagnetic Vortex Cannon)
这些科学家总结了他们的电磁炮的工作原理:“该原理涉及利用超宽带(ultra-wideband),径向极化(radially polarized),锥形同轴喇叭天线(conical coaxial horn antennas)来创建旋转电磁波结构。当天线发射时,它会产生瞬时的压力差,形成这些涡流环,在很长的距离内保持它们的形状和能量。这种方法的独特之处在于它能够产生具有复杂拓扑特征的电磁脉冲,如斯格明子(Skyrmions),在传播过程中显示出卓越的弹性和自愈特性(self-healing property)。”
在通信和传感中的应用(Applications in Communication and Sensing)
研究者预测:“这项技术的潜在应用是巨大而令人兴奋的。在高容量的通信系统中,这些涡旋脉冲可以通过提供高效和强大的数据编码方法来彻底改变我们传输信息的方式。与传统波相比,涡旋环独特的光谱和极化特性使它们能够携带更多的信息,使它们成为下一代通信网络的理想候选者。此外,即使在存在环境干扰的情况下,它们也能保持结构完整性,这使它们成为遥感和目标探测的宝贵工具。科学家们预测,通过分析这些漩涡脉冲的独特模式,我们可以开发出更精确、更可靠的方法来探测和定位物体,无论是在国防系统还是在太空探索中。
当我们反思我们的发现的意义时,我们对这项研究将如何在计量和信息处理方面取得突破性进展感到特别兴奋。涡旋脉冲的时空不可分离性为开发复杂数据编码和高精度测量新技术提供了基础。此外,嵌入在漩涡环中的斯格明子(Skyrmion)纹理为拓扑数据存储和处理提供了有趣的可能性,可能导致更有效的管理和分析大型数据集的方法。”
科学家们补充说,“这项工作不仅展示了电磁涡流环令人难以置信的多功能性,而且为未来无线技术的创新奠定了基础,创造了重新定义我们对电磁现象理解的机会。”
本研究得到了中国国家自然科学基金{National Natural Science Foundation of China (62171081, 61901086)}、中国四川省自然科学基金{ the Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province (2022NSFSC0039)}、欧洲研究理事会{European Research Council (FLEET-786851)}、新加坡教育部AcRF一级基金{Singapore Ministry of Education (MOE) AcRF Tier 1 grant (RG157/23, RT11/23)}以及新加坡南洋理工大学创业基金(Nanyang Technological University Start Up Grant)资助或支持。
上述介绍,仅供参考。欲了解更多信息,敬请注意浏览原文或者相关报道。
Toroidal electromagnetic pulses have been recently reported as nontransverse, space-time nonseparable topological excitations of free space. However, their propagation dynamics and topological configurations have not been comprehensively experimentally characterized. In addition, the existing generators were limited in optical and terahertz domains; however, the feasibility and significance of generating such pulses at microwave frequencies have been overlooked. Here, we report that microwave toroidal pulses can be launched by a transient finite-aperture broadband horn antenna emitter, as an electromagnetic counterpart of “air vortex cannon.” Applying this effective generator, we experimentally map the toroidal pulses' topological skyrmionic textures in free space and demonstrate their resilient propagation dynamics, i.e., how that, during propagation, the pulses evolve toward stronger space-time nonseparability and closer proximity to the canonical Hellwarth–Nouchi toroidal pulses. Our work offers a practical opportunity for using topologically robust toroidal pulses as information carriers in high-capacity telecom, cell phone technology, remote sensing, and global positioning, especially where microwave frequencies are predominant.
转载本文请联系原作者获取授权,同时请注明本文来自诸平科学网博客。
链接地址:https://wap.sciencenet.cn/blog-212210-1450726.html?mobile=1
收藏