博文
光纤传感半月谈(11)
 精选
精选
|||
继续谈今年第一季度发表的文献。
1、光纤传感器在工程领域的应用
葡萄牙的B. J. A. Costa等报道了光纤传感器和传统的电学传感器在Trezói大桥上进行监测的对比试验(B. J. A. Costa andJ. A. Figueiras, "Evaluation of a strain monitoring system for existingsteel railway bridges," Journal ofConstructional Steel Research, vol. 72, pp. 179-191, May 2012.)

图1 Trezói大桥
中国台湾的C. Y. Wang等人报道了采用FBG传感器监测钢轨轴力的结果(C. Y. Wang, et al.,"Railway Track Performance Monitoring and Safety Warning System," Journal of Performance of ConstructedFacilities, vol. 25, pp. 577-586, Nov-Dec 2011.),图2。

图2 FBG传感器在钢轨的布设
马拉西亚的H. Mohamad等人报道了BOTDR传感器在土木工程中的应用(H. Mohamad, et al.,"Performance Monitoring of a Secant-Piled Wall Using Distributed FiberOptic Strain Sensing," Journal ofGeotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, vol. 137, pp. 1236-1243, Dec2011.)。
韩国的K.-S. Choi等人报道了采用FBG传感器对风力发电机叶片监测的结果(K.-S. Choi, et al., "A tip deflection calculation method for a windturbine blade using temperature compensated FBG sensors," SMART MATERIALS AND STRUCTURES, vol. 21,p. 025008, 2012.),图3。
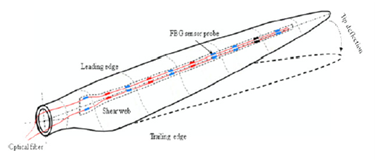
图3 利用FBG传感器对叶片监测
波兰的P. Lesiak等人报道了层压过程对埋入复合材料的光纤传感器的影响(P. Lesiak, et al., "Influence of lamination process on optical fibersensors embedded in composite material," Measurement.),证明了光纤的方向和涂覆材料对应力监测都有显著影响。
2、光纤传感器在医学领域的应用
日本的K. Ishihata等人报道了光纤传感器在牙周探深检查中的应用(K. Ishihata, et al., "Reproducibility of Probing Depth Measurement byan Experimental Periodontal Probe Incorporating Optical Fiber Sensor," Journal of Periodontology, vol. 83, pp.222-227, Feb 2012.),如图4。正巧笔者这些天正在口腔医院修牙,对牙周检查的痛苦深有体会,但是传感原理没有太看懂。
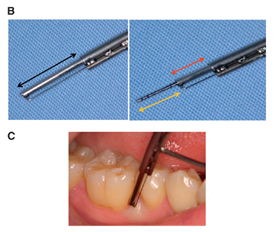
图4 光纤牙周探针
美国休斯敦大学的S. C. M. Ho等人报道了FBG传感器在心房穿孔监测中的应用(S. C. M. Ho, etal., "FBG Sensor for Contact Level Monitoring and Prediction ofPerforation in Cardiac Ablation," Sensors,vol. 12, pp. 1002-1013, Jan 2012.)图5。
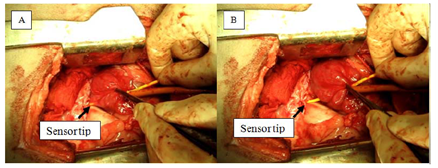
图5 FBG传感器在穿孔监测中应用
英国Aston 大学的D. Harvey等报道了光纤传感器在眼泪电解质分析中的应用(D. Harvey, et al., "Fibre optics sensors in tear electrolyteanalysis: Towards a novel point of care potassium sensor," Contact Lens and Anterior Eye.)。
其它生物医学领域应用的文献可见:
Optical Fibers and Sensors for Medical Diagnostics and TreatmentApplications XII, Proc. of SPIE Vol. 8218.
3、分布式光纤传感器
美国匹兹堡大学的T. Chen等人报道了利用PM光纤双折射进行分布式压力传感的方法(T. Chen, et al., "Distributed high-temperature pressure sensing usingair-hole microstructural fibers," Opt.Lett., vol. 37, pp. 1064-1066, 2012.)。
加拿大渥太华大学的X. Liu等报道了采用LEAF光纤的BOTDA传感用于温度和应变同时测量(X. Liu and X. Y.Bao, "Brillouin Spectrum in LEAF and Simultaneous Temperature and StrainMeasurement," JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVETECHNOLOGY, vol. 30, pp. 1053-1059, Apr 2012.)。
该课题组还报道了在BOTDA系统中采用差分脉冲对的方法在2 km的长度上实现了2 cm的空间分辨率(Y. K. Dong, et al.,"2 cm spatial-resolution and 2 km range Brillouin optical fiber sensorusing a transient differential pulse pair," APPLIED OPTICS, vol. 51, pp. 1229-1235, Mar 2012.)。
意大利的M. A. Soto等人报道了对上述方法的优化(M. A. Soto, et al.,"Optimization of a DPP-BOTDA sensor with 25 cm spatial resolution over 60km standard single-mode fiber using Simplex codes and opticalpre-amplification," OPTICS EXPRESS,vol. 20, pp. 6860-6869, Mar 2012.)。
加拿大渥太华大学的S. R. Xie等人报道了由于单模光纤的不均匀导致的偏振相关性对布里渊线宽和峰值频率的影响(S. R. Xie, et al., "Polarization dependence of Brillouin linewidthand peak frequency due to fiber inhomogeneity in single mode fiber and itsimpact on distributed fiber Brillouin sensing," OPTICS EXPRESS, vol. 20, pp. 6385-6399, Mar 2012.)。
美国Luna公司的D. K. Gifford等人报道了采用Rayleigh散射的光纤应变花(D. K. Gifford, etal., "Multiple Fiber Loop Strain Rosettes in a Single Fiber Using HighResolution Distributed Sensing," SensorsJournal, IEEE, vol. 12, pp. 55-63, 2012.),该课题组一直从事相关方面的研究,可参见文中的参考文献[8]、[11]~[16]。
4、其它报道
西班牙的M. Bravo等人报道了采用suspended-core光纤的Sagnac干涉仪用于位移传感的方法(M. Bravo, et al.,"High precision micro-displacement fiber sensor through a suspended-coreSagnac interferometer," Opt. Lett.,vol. 37, pp. 202-204, 2012.),图6。文中报道的精度高达0.45 μm,并认为如此高的灵敏度是由于Suspended-core光纤的双折射引起。
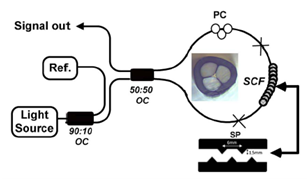
图6 采用suspended-core光纤的Sagnac干涉仪
新加坡南洋理工大学P. Zu等报道了采用Sagnac干涉仪的光纤磁场传感器(P. Zu, et al.,"Magneto-optical fiber sensor based on magnetic fluid," Opt. Lett., vol. 37, pp. 398-400, 2012.)。
台湾的T.-C. Liang等人报道了采用FBG的地震动传感器(T.-C. Liang andY.-L. Lin, "Ground vibrations detection with fiber optic sensor," Optics Communications.),该传感器采用质量块-力顺体结构,如图7。外场试验结果表明在10-250 Hz频带内与传统电学传感器有相似性能。
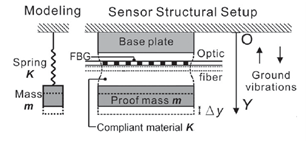
图7 FBG地震传感器
哈尔滨工程大学的F. Peng等人报道了基于Michelson干涉仪的振动传感器(F. Peng, et al.,"Compact fiber optic accelerometer," Chinese optics letters, vol. 10, Jan 2012.),图8。干涉仪的两臂分别放在两个金属管中,当受到振动时,金属管弯曲,而两光纤分别在中性面的两侧,从而引起光程变化。

图8 基于Michelson干涉仪的光纤振动传感器
日本东京大学的Q. Liu等人报道了采用边带滤波器方法的纳应变分辨率传感器(Q. Liu, et al., "Sub-nano resolution fiber-optic static strain sensorusing a sideband interrogation technique," Opt. Lett., vol. 37, pp. 434-436, 2012.),可视为在去年报道的方案上的改进(Q. Liu, et al., "Realization of nano static strain sensing with fiberBragg gratings interrogated by narrow linewidth tunable lasers," Opt. Express, vol. 19, pp. 20214-20223,2011.)。
武汉理工大学的M. Yang等人报道了采用WO3/Pt在FBG上涂覆形成的氢传感器(M. Yang, et al.,"Fiber Optic Hydrogen Sensors with Sol-Gel WO3 coatings," Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical.)。
美国NASA的研究人员报道了采用多芯光缆的形状传感器(J. P. Moore and M. D. Rogge, "Shape sensing using multi-core fiberoptic cable and parametric curve solutions," Opt. Express, vol. 20, pp. 2967-2973, 2012.)。
英国的M. Karimi等人讨论了一种不对称PM光纤的传感特性(M. Karimi, et al.,"Theoretical Analysis of a Non-Symmetric Polarization-MaintainingSingle-Mode Fiber for Sensor Applications," JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, vol. 30, pp. 362-367, Feb 2012.),图9。该光纤的包层中有一孔,文中对该种光纤的理论分析对相关设计具有很好的借鉴意义。
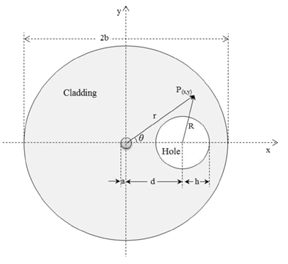
图9 非对称PM光纤
韩国的S. Kyung-Rak报道了基于FBG的流量传感器(S. Kyung-Rak,"Fiber Bragg Grating-Tuned Feedback Laser Flow Sensor System," Sensors and Actuators A: Physical.),图10。该FBG通过金属丝加热,当流量发生变化时,金属丝温度变化,从而引起FBG波长变化。

图10 FBG流量传感器
加拿大的S. J. Mihailov等人综述了苛刻环境下的FBG传感器应用(S. J. Mihailov,"Fiber Bragg Grating Sensors for Harsh Environments," Sensors, vol. 12, pp. 1898-1918, Feb2012.)。
韩国的B. H. Lee等对干涉式光纤传感器的进展进行了综述(B. H. Lee, et al., "Interferometric Fiber Optic Sensors," Sensors, vol. 12, pp. 2467-2486, Mar2012.)。
5、部分其它在这段时间内发表的光纤传感文献
1) M. W. Lee, et al., "Differential Phase-Shift-Keying Technique-BasedBrillouin Echo-Distributed Sensing," IEEE PHOTONICS TECHNOLOGY LETTERS,vol. 24, pp. 79-81, Jan 2012.
2) T. Wei, et al., "Optical fiber sensor based on a radio frequency Mach-Zehnderinterferometer," Opt. Lett., vol. 37, pp. 647-649, 2012.
3) B. Gu, et al., "Nonlinear fiber-optic strain sensor based onfour-wave mixing in microstructured optical fiber," Opt. Lett., vol. 37,pp. 794-796, 2012.
4) M. S. Ferreira, et al., "Spatial optical filter sensor based onhollow-core silica tube," Opt. Lett., vol. 37, pp. 890-892, 2012.
5) Z. Wang, et al., "New Optical Fiber Micro-Bend Pressure Sensors Basedon Fiber-Loop Ringdown," Procedia Engineering, vol. 29, pp. 4234-4238,2012.
6) M. Ding, et al., "A microfiber coupler tip thermometer," Opt.Express, vol. 20, pp. 5402-5408, 2012.
7) S. Dante, et al., "All-optical phase modulation for integratedinterferometric biosensors," Opt. Express, vol. 20, pp. 7195-7205, 2012.
8) Photonics and Optoelectronics Meetings (POEM) 2011, Proc. of SPIE Vol.8332
9) Optical Fibers and Sensors for Medical Diagnostics and TreatmentApplications XII, Proc. of SPIE Vol. 8218.
https://wap.sciencenet.cn/blog-585718-602338.html
上一篇:光纤传感半月谈(10)
下一篇:光纤传感技术的常用缩略语
全部作者的精选博文
- • 光纤传感半月谈(20)
- • 光纤传感半月谈(19)
- • 光纤传感半月谈(18)
- • 光纤传感半月谈(17)
- • 光纤传感半月谈(16)
- • 光纤传感半月谈(15)
全部作者的其他最新博文
- • 光纤传感半月谈(22)
- • 光纤传感半月谈(20)
- • 光纤传感半月谈(19)
- • 晒晒春节假期的工作
- • 光纤传感半月谈(18)