博文
near-infrared ratiometric fluorogenic probe for peroxynitrit
|
Zheng Wen a b 1,Mengyue Liu a b 1,Xueying Ji a,Wei Peng a b,Bishan Ye a b,Fabiao Yu a b,Heng Liu a b
a
Key Laboratory of Haikou Trauma, Key Laboratory of Hainan Trauma and Disaster Rescue, Key Laboratory of Emergency and Trauma of Ministry of Education, Department of Ophthalmology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, Hainan Medical University, Haikou 571199, China
b
Engineering Research Centre for Hainan Bio-Smart Materials and Bio-Medical Devices, Key Laboratory of Hainan Functional Materials and Molecular Imaging, College of Emergency and Trauma, Hainan Medical University, Haikou 571199, China
Received 15 April 2025, Revised 16 June 2025, Accepted 5 July 2025, Available online 6 July 2025, Version of Record 8 July 2025.
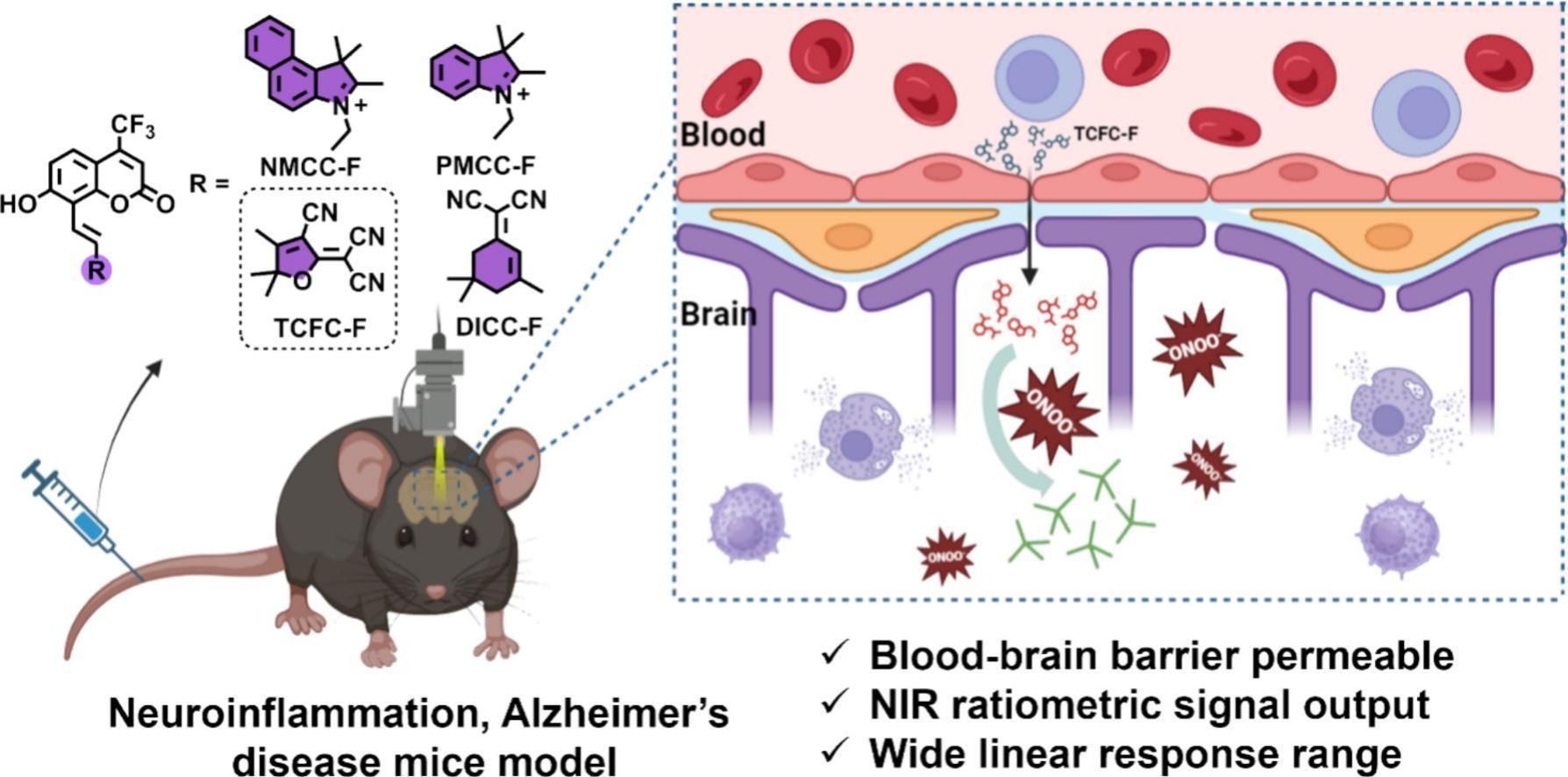
Highlights•The newly screened NIRF probe TCFC-F crossed the BBB and enabled precise detection of ONOO- in the brain.
•TCFC-F allowed dynamic tracking of ONOO- during neuroinflammation and Alzheimer's disease progression.
•TCFC-F visualized AGR’s neuroprotective in vivo, offering a valuable tool for therapeutic evaluation in neurodegenerative diseases.
Abstract
Excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) is a critical mechanism in the pathogenesis of neuroinflammation and Alzheimer's disease (AD). Peroxynitrite (ONOO−), in particular, is capable of oxidizing lipids, proteins, and DNA, leading to the destruction of cellular structure and function, and is considered a key marker of nerve injury. Therefore, the design of innovative fluorogenic probes for imaging ONOO− could contribute to a deeper understanding of neuroinflammation and AD pathogenesis, as well as aid in the development of early diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. In this work, we identified TCFC-F, a near-infrared fluorogenic (NIRF) probe based on trifluoromethyl coumarin dye with excellent blood-brain barrier (BBB) permeability, for the detection of ONOO−. Of the synthesized NIRF probes, only TCFC-F exhibited strong anti-interference capability, with the other three showing varying degrees of response to cysteine (Cys), glutathione (GSH), hydrogen sulfide (H2S), and sulfur dioxide (SO2). In PC12 cell models, TCFC-F demonstrated excellent ratiometric fluorescence response to exogenous and endogenous ONOO−. In a mouse model of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced neuroinflammation, TCFC-F distinguished between different levels of inflammation induced by varying doses of LPS and provided visual evidence of the neuroprotective effect of arctigenin (ARG). Finally, TCFC-F was successfully applied to dynamically monitor ONOO− levels in the brains of AD mice at different ages, revealing a positive correlation between ONOO− expression and disease progression. These findings demonstrate that TCFC-F is a highly sensitive and selective NIRF probe, suitable for the detection of ONOO− both in vitro and in vivo and is a promising tool for studying neurodegenerative diseases.
https://wap.sciencenet.cn/blog-2438823-1496798.html
上一篇:Near-Infrared Fluorogenic Probe for Hydrogen Polysulfide
下一篇:Visualizing peroxynitrite dynamics in an epilepsy model